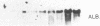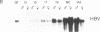Abstract
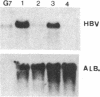
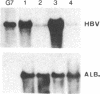
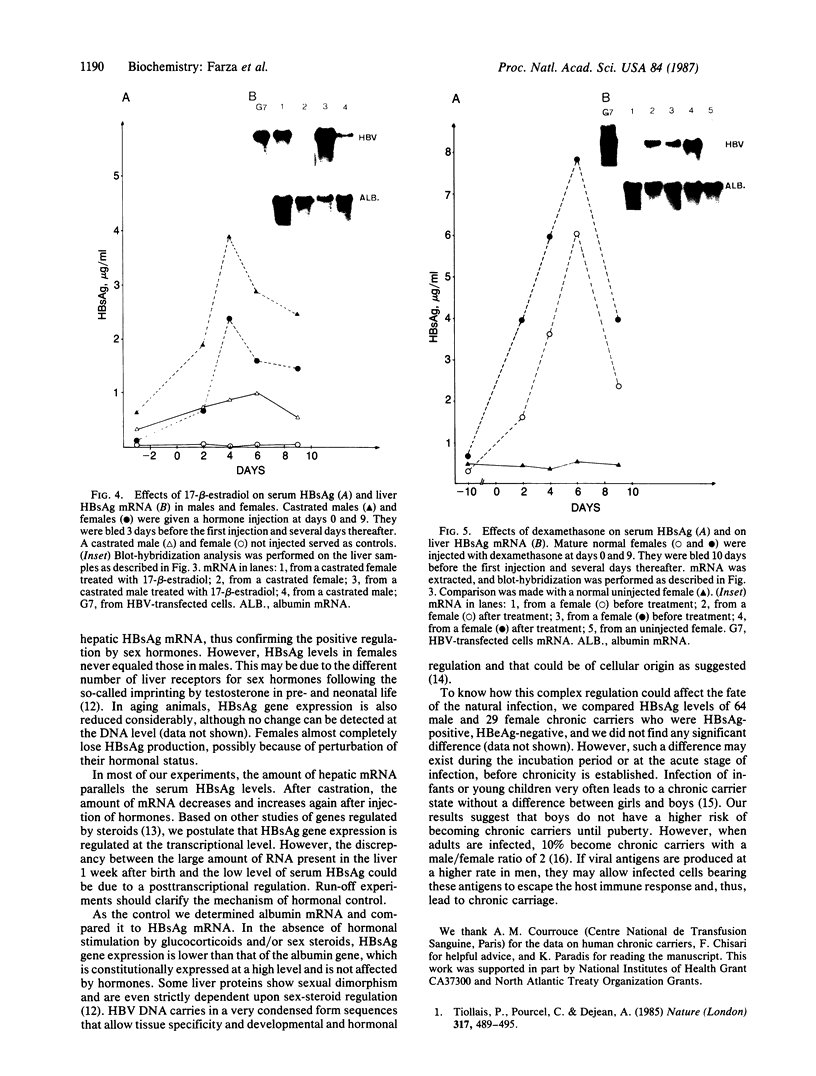
We have investigated the basis for liver-specific and sex-linked expression of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) gene in transgenic mice by monitoring the level of liver HBsAg mRNA and serum HBsAg at different stages of development and in response to sex-hormone regulation. Transcription of the HBsAg gene starts at day 15 of development, together with that of the albumin gene, and reaches a comparable level at birth. HBsAg mRNA level and HBsAg production are parallel in males and females during prenatal development and until the first month of life, but HBsAg gene expression increases 5-10 times in males at puberty. After castration, the level of expression decreases dramatically in both males and females and is subsequently increased by injection of testosterone or estradiol. Glucocorticoids also regulated positively expression of the HBsAg gene. Our results suggest that sex hormones play a role in hepatitis B virus gene expression during natural infection and could explain the difference in incidence of chronic carriers between men and women.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babinet C., Farza H., Morello D., Hadchouel M., Pourcel C. Specific expression of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in transgenic mice. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1160–1163. doi: 10.1126/science.3865370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Filippi P., McLachlan A., Milich D. R., Riggs M., Lee S., Palmiter R. D., Pinkert C. A., Brinster R. L. Expression of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide inhibits hepatitis B surface antigen secretion in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):880–887. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.880-887.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danesch U., Hashimoto S., Renkawitz R., Schütz G. Transcriptional regulation of the tryptophan oxygenase gene in rat liver by glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4750–4753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager L. J., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of mouse liver metallothionein-I gene by glucocorticoids. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):340–342. doi: 10.1038/291340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. E., Idzerda R. L., Brinster R. L., McKnight G. S. Estrogen regulation of the avian transferrin gene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1010–1014. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huh N., Utakoji T. Production of HBs-antigen by two new human hepatoma cell lines and its enhancement by dexamethasone. Gan. 1981 Feb;72(1):178–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Robinson W. S. Common evolutionary origin of hepatitis B virus and retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2531–2535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pourcel C., Louise A., Gervais M., Chenciner N., Dubois M. F., Tiollais P. Transcription of the hepatitis B surface antigen gene in mouse cells transformed with cloned viral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.100-105.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. R., Solter D. Glucocorticoid regulation of mouse mammary tumor virus sequences in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5880–5884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. K., Chatterjee B. Sexual dimorphism in the liver. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:37–50. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Rutter W. J., Laub O. A human hepatitis B viral enhancer element. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):427–430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Pourcel C., Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):489–495. doi: 10.1038/317489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tur-Kaspa R., Burk R. D., Shaul Y., Shafritz D. A. Hepatitis B virus DNA contains a glucocorticoid-responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1627–1631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]