Abstract
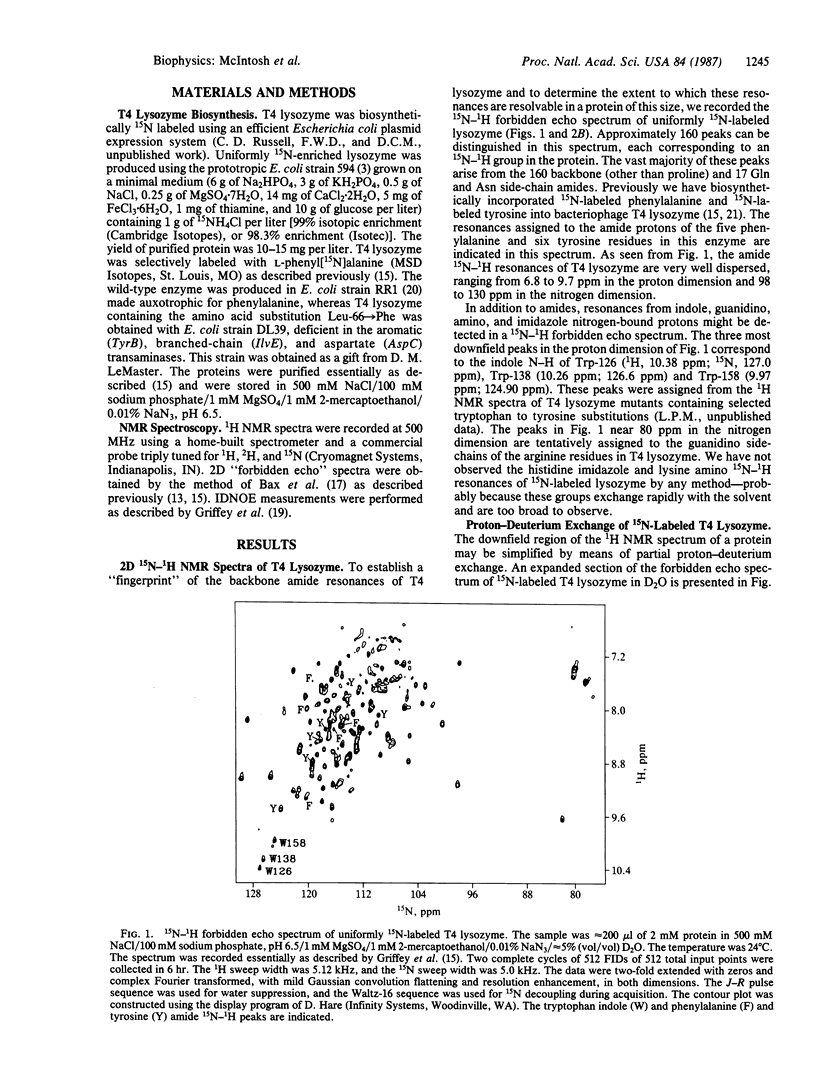
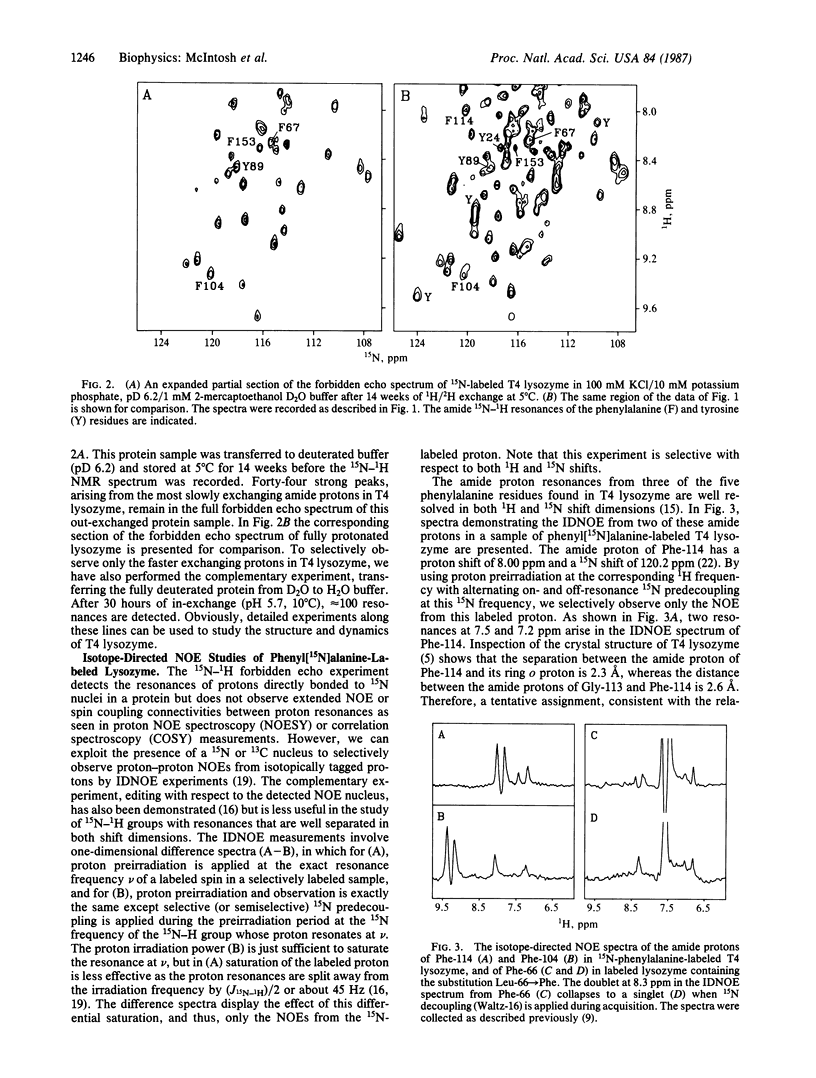
A strategy for resolution and assignment of single proton resonances in proteins of molecular mass up to at least 40 kDa is presented. This approach is based on 15N (or 13C) labeling of selected residues in a protein. The resonances from protons directly bonded to labeled atoms are detected in a two-dimensional 1H-15N (or 13C) spectrum. The nuclear Overhauser effects from isotopically tagged protons are selectively observed in one-dimensional isotope-directed measurements. Using this approach, we have observed approximately 160 resonances from 15N-bonded protons in the backbone and sidechains of uniformly 15N-labeled T4 lysozyme (molecular mass = 18.7 kDa). Partial proton-deuterium exchange can be used to simplify the 1H-15N spectrum of this protein. These resonances are identified by amino acid class using selective incorporation of 15N-labeled amino acids and are assigned to specific residues by mutational substitution, multiple 15N and 13C labeling, and isotope-directed nuclear Overhauser effect measurements. For example, using a phenyl[15N]alanine-labeled lysozyme variant containing two consecutive phenylalanine residues in an alpha-helical region, we observe an isotope-directed nuclear Overhauser effect from the amide proton of Phe-66 to that of Phe-67.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogusky M. J., Tsang P., Opella S. J. One- and two- dimensional 15N/1H NMR of filamentous phage coat proteins in solution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 15;127(2):540–545. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80193-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. The steric effect in lysogenization by bacteriophage lambda. I. Lysogenization of a partially diploid strain of Escherichia coli K-12. Virology. 1965 Nov;27(3):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90112-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell M. L., Schellman J. A. Stability of phage T4 lysozymes. I. Native properties and thermal stability of wild type and two mutant lysozymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 26;494(2):367–383. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90166-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffey R. H., Poulter C. D., Bax A., Hawkins B. L., Yamaizumi Z., Nishimura S. Multiple quantum two-dimensional 1H--15N nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: chemical shift correlation maps for exchangeable imino protons of Escherichia coli tRNAMetf in water. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5895–5897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffey R. H., Redfield A. G., Loomis R. E., Dahlquist F. W. Nuclear magnetic resonance observation and dynamics of specific amide protons in T4 lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 12;24(4):817–822. doi: 10.1021/bi00325a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grütter M. G., Hawkes R. B., Matthews B. W. Molecular basis of thermostability in the lysozyme from bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):667–669. doi: 10.1038/277667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Grutter M. G., Schellman J. Thermodynamic stability and point mutations of bacteriophage T4 lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 15;175(2):195–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90474-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainosho M., Tsuji T. Assignment of the three methionyl carbonyl carbon resonances in Streptomyces subtilisin inhibitor by a carbon-13 and nitrogen-15 double-labeling technique. A new strategy for structural studies of proteins in solution. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6273–6279. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima K., Kim P. S., Baldwin R. L. Strategy for trapping intermediates in the folding of ribonuclease and for using 1H-nmr to determine their structures. Biopolymers. 1983 Jan;22(1):59–67. doi: 10.1002/bip.360220111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMaster D. M., Richards F. M. 1H-15N heteronuclear NMR studies of Escherichia coli thioredoxin in samples isotopically labeled by residue type. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7263–7268. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington S. J., Anderson W. F., Owen J., Ten Eyck L. F., Grainger C. T., Matthews B. W. Structure of the lysozyme from bacteriophage T4: an electron density map at 2.4 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 5;118(1):81–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90245-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder H., Wüthrich K. Protein folding kinetics by combined use of rapid mixing techniques and NMR observation of individual amide protons. Proteins. 1986 Sep;1(1):34–42. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Papastavros M. Z., Sanchez V., Redfield A. G. Nitrogen-15-labeled yeast tRNAPhe: double and two-dimensional heteronuclear NMR of guanosine and uracil ring NH groups. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 11;23(19):4395–4400. doi: 10.1021/bi00314a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez V., Redfield A. G., Johnston P. D., Tropp J. Nuclear Overhauser effect in specifically deuterated macromolecules: NMR assay for unusual base pairing in transfer RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5659–5662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsugita A., Inouye M. Complete primary structure of phage lysozyme from Escherichia coli T4. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. A., Redfield A. G., Griffey R. H. Isotope-detected 1H NMR studies of proteins: a general strategy for editing interproton nuclear Overhauser effects by heteronuclear decoupling, with application to phage lambda repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1325–1329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


