Abstract
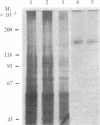
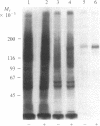
Colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1) regulates the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes. The CSF-1 receptor was purified from cell membranes of the J774.2 mouse macrophage cell line by solubilization with Triton X-100, CSF-1 affinity chromatography, and gel filtration. The purified receptor is a protein or glycoprotein of 165 kDa comprising a single polypeptide chain that is not covalently associated, either as a homopolymer, or with any other protein. CSF-1 stimulated autophosphorylation of the purified receptor in tyrosine residues. Casein but not histone was shown to act as a substrate for the tyrosine protein kinase activity of purified receptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assimeh S. N., Bing D. H., Painter R. H. A simple method for the isolation of the subcomponents of the first component of complement by affinity chromatography. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):225–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne P. V., Guilbert L. J., Stanley E. R. Distribution of cells bearing receptors for a colony-stimulating factor (CSF-1) in murine tissues. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):848–853. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Fava R. A., Sawyer S. T. Purification and characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor/protein kinase from normal mouse liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6237–6241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Isolation of the insulin receptor of liver and fat-cell membranes (detergent-solubilized-( 125 I)insulin-polyethylene glycol precipitation-sephadex). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):318–322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch P. J., Rosen O. M., Rubin C. S. Identification and characterization of a latent pool of insulin receptors in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5350–5358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Bloom B. R., Scharff M. D. The Fc receptors of primary and cultured phagocytic cells studied with homogeneous antibodies. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1329–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. A., Gabrilove J. L., Tam J. P., Moore M. A., Hanafusa H. Specific expression of the human cellular fps/fes-encoded protein NCP92 in normal and leukemic myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2379–2383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilbert L. J., Stanley E. R. Specific interaction of murine colony-stimulating factor with mononuclear phagocytic cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Apr;85(1):153–159. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilbert L. J., Stanley E. R. The interaction of 125I-colony-stimulating factor-1 with bone marrow-derived macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4024–4032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilbert L. J., Tynan P. W., Stanley E. R. Uptake and destruction of 125I-CSF-1 by peritoneal exudate macrophages. J Cell Biochem. 1986;31(3):203–216. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240310303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Ek B., Rönnstrand L. Characterization of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor on human fibroblasts. Demonstration of an intimate relationship with a 185,000-Dalton substrate for the platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10054–10061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C. J., Stanley E. R. Chemical crosslinking of the mononuclear phagocyte specific growth factor CSF-1 to its receptor at the cell surface. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91614-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Prichard J., Cohn M. Reticulum cell sarcoma: an effector cell in antibody-dependent cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):898–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Furman W. L., Roussel M. F., Holt J. T., Nienhuis A. W., Stanley E. R., Sherr C. J. Expression of the human c-fms proto-oncogene product (colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor) on peripheral blood mononuclear cells and choriocarcinoma cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1740–1746. doi: 10.1172/JCI112496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacca R., Stanley E. R., Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W. Specific binding of the mononuclear phagocyte colony-stimulating factor CSF-1 to the product of the v-fms oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3331–3335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Roussel M. F., Look A. T., Stanley E. R. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):665–676. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Guilbert L. J. Methods for the purification, assay, characterization and target cell binding of a colony stimulating factor (CSF-1). J Immunol Methods. 1981;42(3):253–284. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Guilbert L. J., Tushinski R. J., Bartelmez S. H. CSF-1--a mononuclear phagocyte lineage-specific hemopoietic growth factor. J Cell Biochem. 1983;21(2):151–159. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240210206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Heard P. M. Factors regulating macrophage production and growth. Purification and some properties of the colony stimulating factor from medium conditioned by mouse L cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4305–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Jubinsky P. T. Factors affecting the growth and differentiation of haemopoietic cells in culture. Clin Haematol. 1984 Jun;13(2):329–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung Y. G., Jubinsky P. T., Stanley E. R. Solubilization and assay of a colony-stimulating factor receptor from murine macrophages. J Cell Biochem. 1986;31(4):259–269. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240310403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]