Abstract
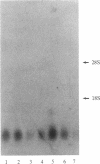
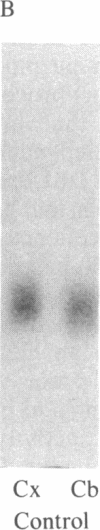
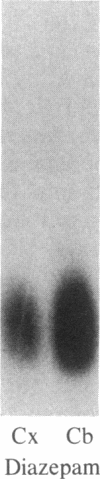
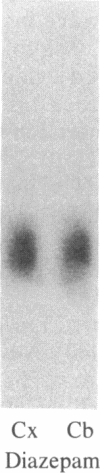
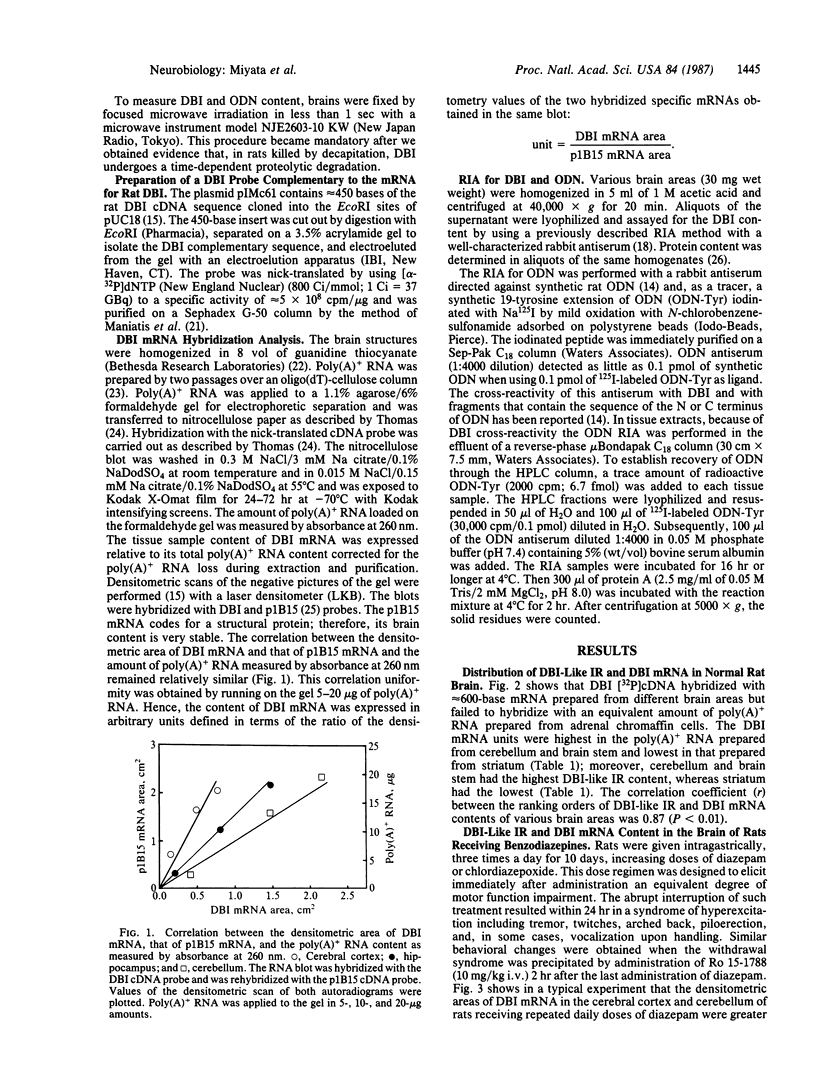
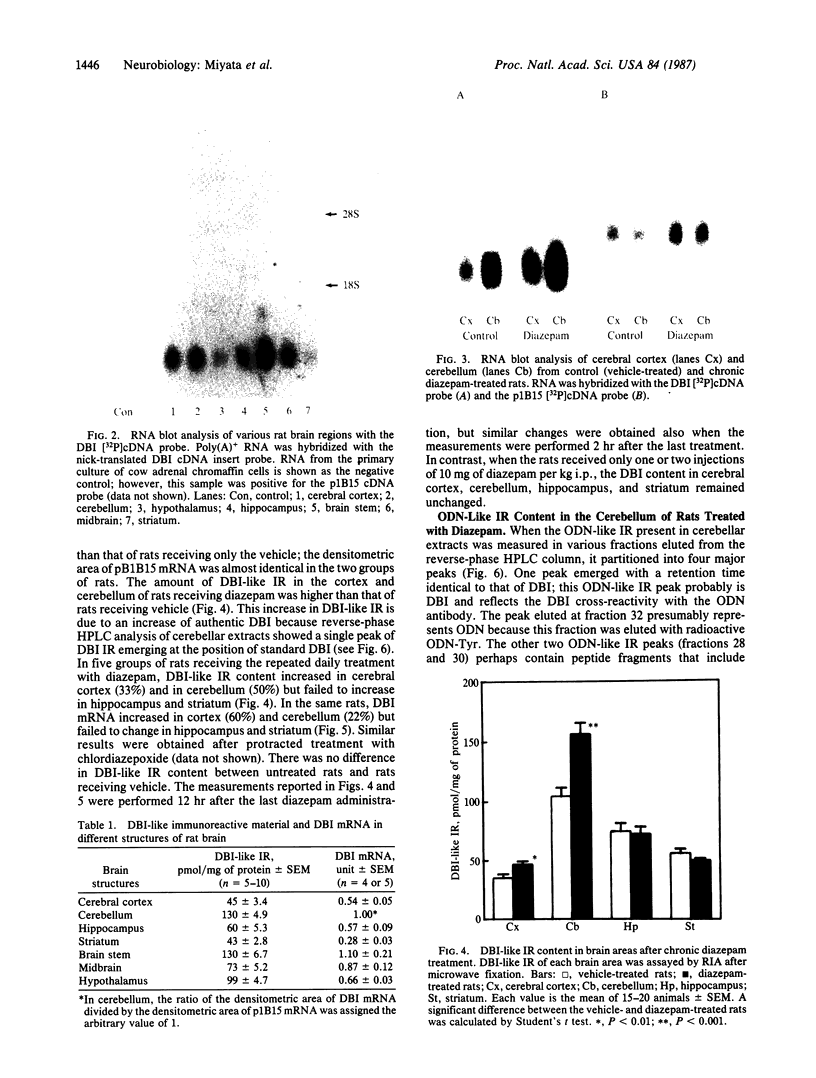
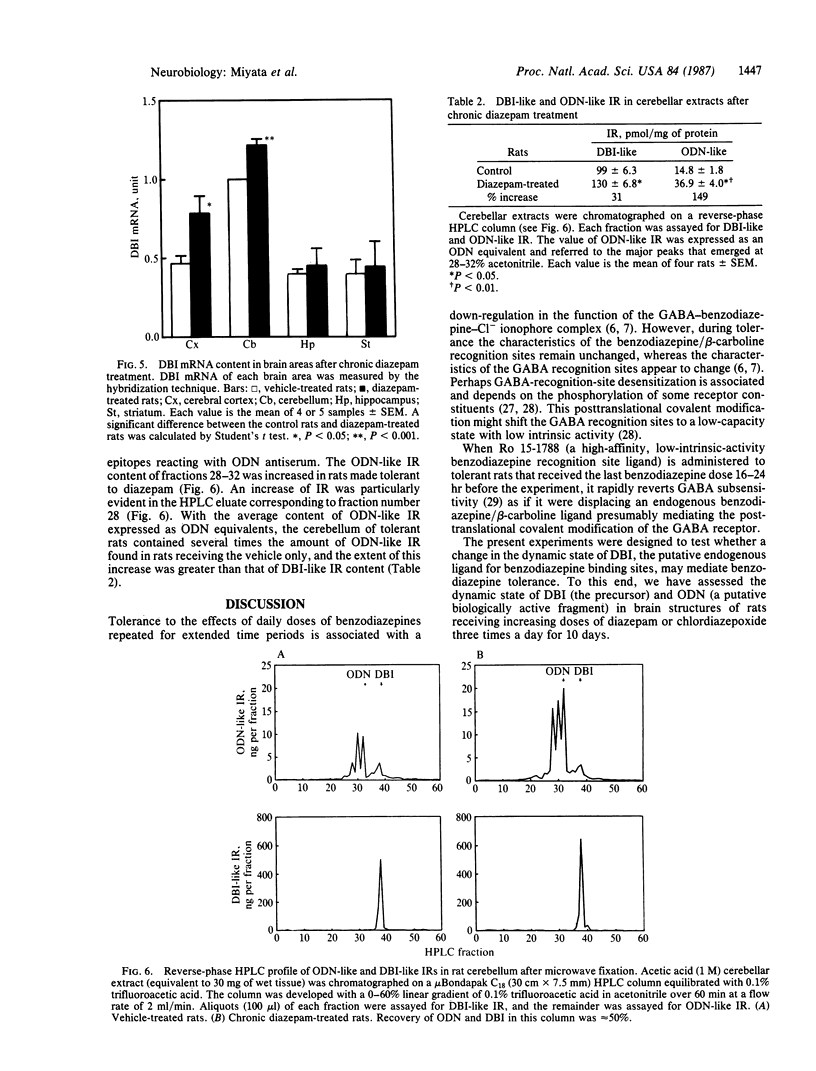
DBI (diazepam-binding inhibitor) is a putative neuromodulatory peptide isolated from rat brain that acts on gamma-aminobutyric acid-benzodiazepine-Cl- ionophore receptor complex inducing beta-carboline-like effects. We used a cDNA probe complementary to DBI mRNA and a specific antibody for rat DBI to study in rat brain how the dynamic state of DBI can be affected after protracted (three times a day for 10 days) treatment with diazepam and chlordiazepoxide by oral gavage. Both the content of DBI and DBI mRNA increased in the cerebellum and cerebral cortex but failed to change in the hippocampus and striatum of rats receiving this protracted benzodiazepine treatment. Acute treatment with diazepam did not affect the dynamic state of brain DBI. An antibody was raised against a biologically active octadecaneuropeptide (Gln-Ala-Thr-Val-Gly-Asp-Val-Asn-Thr-Asp-Arg-Pro-Gly-Leu-Leu-Asp-Leu-Lys ) derived from the tryptic digestion of DBI. The combined HPLC/RIA analysis of rat cerebellar extracts carried out with this antibody showed that multiple molecular forms of the octadecaneuropeptide-like reactivity are present and all of them are increased in rats receiving repeated daily injections of diazepam. It is inferred that tolerance to benzodiazepines is associated with an increase in the turnover rate of DBI, which may be responsible for the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor desensitization that occurs after protracted benzodiazepine administration.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alho H., Costa E., Ferrero P., Fujimoto M., Cosenza-Murphy D., Guidotti A. Diazepam-binding inhibitor: a neuropeptide located in selected neuronal populations of rat brain. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):179–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3892688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann J., Ferrero P., Guidotti A., Costa E. Neuropeptide modulation of GABA receptor C1- channels. Regul Pept Suppl. 1985;4:33–38. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(85)90215-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Schmiechen R., Neef G., Nielsen M., Petersen E. N. Interaction of convulsive ligands with benzodiazepine receptors. Science. 1982 Jun 11;216(4551):1241–1243. doi: 10.1126/science.6281892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Alho H., Santi M. R., Ferrero P., Guidotti A. Cotransmission at GABAergic synapses. Prog Brain Res. 1986;68:343–356. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero P., Santi M. R., Conti-Tronconi B., Costa E., Guidotti A. Study of an octadecaneuropeptide derived from diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI): biological activity and presence in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):827–831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallager D. W., Lakoski J. M., Gonsalves S. F., Rauch S. L. Chronic benzodiazepine treatment decreases postsynaptic GABA sensitivity. Nature. 1984 Mar 1;308(5954):74–77. doi: 10.1038/308074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallager D. W., Rauch S. L., Malcolm A. B. Alterations in a low affinity GABA recognition site following chronic benzodiazepine treatment. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Feb 10;98(1):159–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Iversen L. L. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):655–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonsalves S. F., Gallager D. W. Spontaneous and RO 15-1788-induced reversal of subsensitivity to GABA following chronic benzodiazepines. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr 2;110(2):163–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Glaister D., Seeburg P. H., Guidotti A., Costa E. Cloning and expression of cDNA for human diazepam binding inhibitor, a natural ligand of an allosteric regulatory site of the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7547–7551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Shader R. I. Dependence, tolerance, and addiction to benzodiazepines: clinical and pharmacokinetic considerations. Drug Metab Rev. 1978;8(1):13–28. doi: 10.3109/03602537808993775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Forchetti C. M., Corda M. G., Konkel D., Bennett C. D., Costa E. Isolation, characterization, and purification to homogeneity of an endogenous polypeptide with agonistic action on benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3531–3535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häring P., Stähli C., Schoch P., Takács B., Staehelin T., Möhler H. Monoclonal antibodies reveal structural homogeneity of gamma-aminobutyric acid/benzodiazepine receptors in different brain areas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4837–4841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Todaro G. J., Shoyab M. Complete amino acid sequences of bovine and human endozepines. Homology with rat diazepam binding inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9727–9731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicholas L. F., Martin W. R., Cherian S. Physical dependence on diazepam and lorazepam in the dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Sep;226(3):783–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. Gene expression in rat brain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5497–5520. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocchetti I., Einstein R., Brosius J. Putative diazepam binding inhibitor peptide: cDNA clones from rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7221–7225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevnick J. S., Jasinski D. R., Haertzen C. A. Abrupt withdrawal from therapeutically administered diazepam. Report of a case. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1978 Aug;35(8):995–998. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1978.01770320089008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan G. P., Boisse N. R. Benzodiazepine tolerance, physical dependence and withdrawal: electrophysiological study of spinal reflex function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Nov;231(2):464–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan G. P., Boisse N. R. Experimental induction of benzodiazepine tolerance and physical dependence. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jul;226(1):100–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Study R. E., Barker J. L. Diazepam and (--)-pentobarbital: fluctuation analysis reveals different mechanisms for potentiation of gamma-aminobutyric acid responses in cultured central neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7180–7184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang F., Costa E., Schwartz J. P. Increase of proenkephalin mRNA and enkephalin content of rat striatum after daily injection of haloperidol for 2 to 3 weeks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3841–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicini S., Mienville J. M., Costa E. Flunitrazepam action on the GABA-Cl ionophore complex in rat cortical neurons in culture: a patch-clamp study. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1986;9 (Suppl 4):395–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]