These patients likely play a role in transmission of these organisms into hospitals.
Keywords: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, community-associated MRSA, hospital-associated MRSA, phenotypic susceptibility, outpatients, staphylococci, bacteria, CME, research
Abstract
Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) has become a major problem in US hospitals already dealing with high levels of hospital-associated MRSA (HA-MRSA). Using antimicrobial drug susceptibility data for 1999–2006 from The Surveillance Network, we characterized the relationship between outpatient and inpatient levels of CA-MRSA nationally. In outpatients, the frequency of CA-MRSA isolates has increased >7× during 1999–2006, which suggests that outpatients have become a major reservoir for CA-MRSA. However, contrary to results in other reports, although CA-MRSA increases are associated with decreases in the frequency of HA-MRSA in hospitals, the decreases are only modest. This finding suggests that instead of replacing HA-MRSA in the hospital, CA-MRSA is adding to the overall presence of MRSA already found within the hospital population.
CME ACTIVITY
MedscapeCME is pleased to provide online continuing medical education (CME) for this journal article, allowing clinicians the opportunity to earn CME credit. This activity has been planned and implemented in accordance with the Essential Areas and policies of the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education through the joint sponsorship of MedscapeCME and Emerging Infectious Diseases. MedscapeCME is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) to provide continuing medical education for physicians. MedscapeCME designates this educational activity for a maximum of 0.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™. Physicians should only claim credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity. All other clinicians completing this activity will be issued a certificate of participation. To participate in this journal CME activity: (1) review the learning objectives and author disclosures; (2) study the education content; (3) take the post-test and/or complete the evaluation at http://www.medscape.com/cme/eid; (4) view/print certificate.
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this activity, participants will be able to:
Specify characteristics of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) compared with hospital-acquired MRSA
Recognize recent trends in MRSA among outpatients
Identify anatomic sites most commonly associated with infection with MRSA resistant only to oxacillin
Recognize recent trends in MRSA among inpatients
Describe the most common treatment for rickettsial diseases.
Editor
Thomas Gryczan, Technical Writer-Editor, Emerging Infectious Diseases. Disclosure: Thomas Gryczan has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
CME AUTHOR
Charles P. Vega, MD, Associate Professor; Residency Director, Department of Family Medicine, University of California, Irvine. Disclosure: Charles P. Vega, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
AUTHORS
Disclosures: Eili Klein, MA; David L. Smith, PhD; and Ramanan Laxminarayan, PhD, MPH, have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Earning CME Credit
To obtain credit, you should first read the journal article. After reading the article, you should be able to answer the following, related, multiple-choice questions. To complete the questions and earn continuing medical education (CME) credit, please go to http://www.medscape.com/cme/eid. Credit cannot be obtained for tests completed on paper, although you may use the worksheet below to keep a record of your answers. You must be a registered user on Medscape.com. If you are not registered on Medscape.com, please click on the New Users: Free Registration link on the left hand side of the website to register. Only one answer is correct for each question. Once you successfully answer all post-test questions you will be able to view and/or print your certificate. For questions regarding the content of this activity, contact the accredited provider, CME@medscape.net. For technical assistance, contact CME@webmd.net. American Medical Association’s Physician’s Recognition Award (AMA PRA) credits are accepted in the US as evidence of participation in CME activities. For further information on this award, please refer to http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/category/2922.html. The AMA has determined that physicians not licensed in the US who participate in this CME activity are eligible for AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™. Through agreements that the AMA has made with agencies in some countries, AMA PRA credit is acceptable as evidence of participation in CME activities. If you are not licensed in the US and want to obtain an AMA PRA CME credit, please complete the questions online, print the certificate and present it to your national medical association.
Article Title: Community-associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Outpatients, United States, 1999–2006
CME Questions
-
Which of the following characteristics helps to differentiate community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) from hospital-associated (HA)–MRSA?
A. Resistance to fluoroquinolones
B. Resistance to a higher number of antibiotics
C. Resistance to vancomycin
D. Resistance to beta-lactam and erythromycin only
-
Which of the following trends were noted in the epidemiology of outpatient MRSA in the current study?
A. The presence of MRSA was stable over the study period
B. The number of MRSA isolates resistant to at least 1 other drug increased significantly
C. S aureus infections that were MRSA nearly doubled
D. HA-MRSA accounted for the majority of change in the prevalence of MRSA among outpatients
-
The number of S aureus isolates resistant only to oxacillin increased most significantly from which anatomic site?
A. Lung
B. Blood
C. Skin and soft tissue
D. Genitourinary tract
-
Which of the following statements about the epidemiology of MRSA among inpatients is most accurate?
A. The proportion of S aureus infections that were MRSA increased by 25%
B. The prevalence of S aureus isolates resistant only to oxacillin decreased
C. The prevalence of HA-MRSA isolates fell sharply as CA-MRSA increased
D. There was a significant increase in lung infections with multiple-drug resistant MRSA
Activity Evaluation
| 1. The activity supported the learning objectives. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strongly Disagree | Strongly Agree | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 2. The material was organized clearly for learning to occur. | ||||
| Strongly Disagree | Strongly Agree | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 3. The content learned from this activity will impact my practice. | ||||
| Strongly Disagree | Strongly Agree | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 4. The activity was presented objectively and free of commercial bias. | ||||
| Strongly Disagree | Strongly Agree | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
Community-associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Outpatients, United States, 1999–2006
The past decade has seen a large increase in infections with hospital-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (HA-MRSA) (1). MRSA is one of the most common causes of nosocomial infections, especially invasive bacterial infections (2), and is now endemic and even epidemic to many US hospitals, long-term care facilities (3), and communities (4–6). Although community-associated MRSA (CA-MRSA) strains have been recognized as a leading cause of skin and soft tissue infections (1,6), especially in patients with no established healthcare risk factors (7,8), they also cause severe invasive infections (9,10). Recent reports based on genotypic evidence have suggested that CA-MRSA is likely spreading within hospitals as well, blurring the line between CA-MRSA and HA-MRSA infections (11).
Molecular typing studies have identified 2 MRSA clones, USA300 and USA400, as the primary types that cause CA-MRSA infections (12). Evidence suggests that emergence of these strains was independent of hospital strains (13). Thus, understanding the role of outpatients, who are among the likely carriers of CA-MRSA into a hospital, is useful for understanding the changing epidemiology of MRSA in hospitals. Outpatients, who outnumber inpatients by ≈3:1, may play a major role in the spread of CA-MRSA strains from the community to the hospital through their interaction with hospital staff or use of similar hospital resources, such as surgical rooms. However, limited information hinders understanding of long-term trends in CA-MRSA in outpatients in the context of changing epidemiology of inpatients. This lack of information hinders the ability to evaluate infection control methods in the face of a possible emerging epidemic of nosocomial infections caused by CA-MRSA.
Knowledge of trends in antimicrobial drug resistance rates for emerging pathogens are useful to clinicians to ensure high-quality care, which is essential for antimicrobial drug therapy, in which different drugs can have different costs and effectiveness. These trends can also help hospital administrators and policy makers make infection control investments to address the role that large influxes of outpatients with CA-MRSA infections may play with regard to overall MRSA infection rates in the hospital.
Methods
To analyze trends in frequency of CA-MRSA and HA-MRSA, we studied changes in the proportion of isolates of each type that were found in inpatient and outpatient settings from a nationally representative sample of US hospitals during 1999–2006. Although genotypic analysis is the most reliable way of identifying MRSA strains, historical genotypic data on isolates are not available at the national level. An alternative approach is to ascertain strain type by using phenotypic susceptibility profiles. S. aureus susceptibility profiles are determined by the staphylococcal cassette chromosome (SCC) types on which the methicillin resistance gene, mecA, is carried. Because CA-MRSA and HA-MRSA strains typically have different SCCmec types, rules have been developed for determining the likely genetic makeup of an isolate on the basis of susceptibility results (11,14–16).
Phenotypic susceptibility results were obtained from The Surveillance Network (TSN) Database-USA (Focus Diagnostics, Herndon, VA, USA). TSN is an electronic repository of antimicrobial drug susceptibility data from a national network of >300 microbiology laboratories in the United States. Participating laboratories are geographically dispersed and make up a nationally representative sample based on patient population and number of beds. Patient isolates are tested on site as part of routine diagnostic testing for susceptibility to different antimicrobial agents by using standards established by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (17) and approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. Results are then filtered to remove repeat isolates and identify microbiologically atypical results for confirmation or verification before being included in the TSN database. Data from the database have been used extensively to evaluate antimicrobial drug resistance patterns and trends (1,18–22).
Genotypic analysis of phenotypically defined strains has found that in general, isolates of the USA300 strain, the one most commonly associated with CA-MRSA infections, are resistant to fewer antimicrobial drugs (14–16). Naimi et al. (15) tested genetically determined CA-MRSA isolates against several antimicrobial drugs and found that they were typically susceptible to ciprofloxacin (79%) and clindamycin (83%). Similarly, King et al. (14) found that 88% of CA-MRSA strains were resistant only to a β-lactam and erythromycin or a β-lactam only. Popovich et al. (16) also found that susceptibility to a fluoroquinolone had a 90% positive predictive value for predicting a community-associated strain. Additionally, the number of antimicrobial drugs to which an isolate was susceptible was a reliable predictor of the genotype (16).
We analyzed S. aureus isolates that were tested for susceptibility to oxacillin (a proxy for all β-lactam antimicrobial drugs). Isolates classified as resistant according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute breakpoint criteria were considered MRSA (<0.01% had intermediate resistance and were classified as susceptible). MRSA isolates, regardless of source (outpatient or inpatient), that were tested against ciprofloxacin or clindamycin, and >3 other drugs and found to be resistant only to oxacillin were classified as CA-MRSA strains. Isolates resistant to oxacillin and >1 other drug were assumed to be HA-MRSA strains. Other drugs tested were gentamicin, tetracycline, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, and vancomycin.
Using this framework, we determined that the mean number of outpatient isolates analyzed annually was >50,000. Isolates were stratified on the basis of source (blood, lungs, skin, and other organs). Confidence intervals (CIs) for TSN data were calculated by using the Wilson score method incorporating continuity correction as detailed by Newcombe (23). Statistical analysis was performed by using Stata version 10 software (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA).
Results
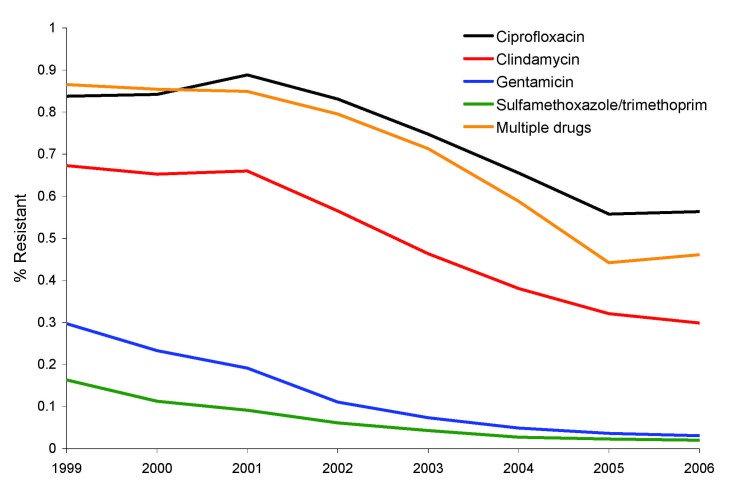
Susceptibility to clindamycin, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin, tetracycline, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, and vancomycin was used to infer genotypes of MRSA isolates during 1999–2006. During this period, there was a statistically significant reduction (p<0.001) in the number of MRSA isolates in outpatient areas resistant to ciprofloxacin (84% to 56%), clindamycin (67% to 30%), gentamicin (30% to 3%), and sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim (16% to 2%). Our phenotypic rule, which was based on susceptibility to all drugs, found qualitatively similar results, with the number of MRSA isolates resistant to >1 other drug decreasing from 87% to 46% during the period (Figure).
Figure.
Resistance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates to clindamycin, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin, and sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim in outpatient areas of hospitals, United States, 1999–2006. Multiple drugs indicates isolates that were tested against ciprofloxacin or clindamycin and >3 other drugs and found to resistant only to oxacillin. The p values were calculated by using the χ2 test. Differences in all comparisons were significant (p<0.001).
For outpatient data, the proportion of all S. aureus infections that were MRSA infections nearly doubled, from 26.8% (95% CI 26.3%–27.3%) to 52.4% (95% CI 52.0%–52.9%), over the study period. This increase was caused almost entirely by increases in isolates resistant only to oxacillin, which increased >7× from 3.6% (95% CI 3.5%–3.7%) to 28.2% (95% CI 28.0%–28.5%). The proportion of isolates resistant only to oxacillin increased for skin and soft tissue infections. However, increases were also observed in invasive blood and lung infections and other infections. Isolates resistant to >1 other drug increased ≈5% during 1999–2001 from 23.2% (95% CI 23.0%–23.5%) to 28.2% (95% CI 28.0%–28.5%) before reaching a plateau. In 2005, the proportion of isolates resistant to oxacillin and 1 other drug then decreased back to almost the same percentage it started at. This pattern was driven by overall increases at all infection sites during 1999–2001 and later decreases at all collection sites except skin infections (Table).
Table. Frequency of MRSA in hospitals, by unit, United States, 1999–2006*.
| Unit | % Patients (95% confidence interval) |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006† | |
| Outpatient | ||||||||
| All MRSA | 26.8 (26.3–27.3) | 29.4 (29.0–29.9) | 33.4 (33.0–33.9) | 35.7 (35.3–36.2) | 40.7 (40.2–41.2) | 47.7 (47.3–48.1) | 52.7 (52.3–53.1) | 52.4 (52.0–52.9) |
| HA-MRSA | 23.2 (23.0–23.5) | 25.1 (24.9–25.4) | 28.2 (28.0–28.5) | 28.4 (28.2–28.7) | 29.3 (29.0–29.5) | 28.4 (28.2–28.7) | 24.1 (23.8–24.3) | 24.2 (24.0–24.5) |
| Blood | 2.7 | 2.8 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 3.1 | 2.8 | 2.1 | 1.9 |
| Lungs | 4.7 | 5.3 | 6.5 | 5.5 | 5.4 | 4.2 | 3.5 | 2.9 |
| Skin | 9.3 | 10.6 | 10.1 | 11.6 | 13.8 | 15.5 | 14.2 | 15.5 |
| Other source | 6.4 | 6.5 | 7.6 | 7.7 | 7.0 | 6.0 | 4.2 | 4.0 |
| CA-MRSA | 3.6 (3.5–3.7) | 4.3 (4.2–4.4) | 5.2 (5.1–5.4) | 7.3 (7.1–7.5) | 11.4 (11.3–11.6) | 19.3 (19.1–19.5) | 28.7 (28.4–28.9) | 28.2 (28.0–28.5) |
| Blood | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| Lungs | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| Skin | 2.3 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 4.8 | 9.0 | 16.6 | 25.3 | 25.4 |
| Other source |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.8 |
0.9 |
1.0 |
1.3 |
1.6 |
1.4 |
| Inpatient | ||||||||
| All MRSA | 46.7 (46.2–47.2) | 47.6 (47.2–48.1) | 50.0 (49.6–50.4) | 52.2 (51.8–52.6) | 54.9 (54.6–55.3) | 58.3 (57.9–58.6) | 59.5 (59.2–59.9) | 58.5 (58.0–58.9) |
| HA-MRSA | 43.4 (43.0–43.9) | 43.2 (42.8–43.6) | 44.1 (43.7–44.5) | 43.9 (43.5–44.3) | 44.1 (43.7–44.5) | 41.9 (41.6–42.3) | 38.5 (38.2–38.9) | 38.7 (38.3–39.1) |
| Blood | 7.1 | 7.2 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.0 | 6.2 | 6.3 |
| Lungs | 21.4 | 19.9 | 19.2 | 18.5 | 17.6 | 16.5 | 14.7 | 14.5 |
| Skin | 9.3 | 10.5 | 11.4 | 12.0 | 12.9 | 13.1 | 13.0 | 13.1 |
| Other source | 5.6 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 5.9 | 6.1 | 5.3 | 4.5 | 4.7 |
| CA-MRSA | 3.3 (3.1–3.4) | 4.5 (4.3–4.6) | 5.8 (5.6–6.0) | 8.4 (8.2–8.6) | 10.9 (10.6–11.1) | 16.3 (16.1–16.6) | 21.0 (20.7–21.3) | 19.8 (19.4–20.1) |
| Blood | 0.6 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 2.0 |
| Lungs | 1.2 | 1.6 | 2.1 | 2.3 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 3.3 | 3.8 |
| Skin | 1.1 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 4.0 | 6.6 | 10.9 | 14.4 | 12.8 |
| Other source | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.2 |
*MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; HA-MRSA, hospital-associated MRSA; CA-MRSA, community-associated MRSA. †Data through October only. Data for blood, lungs, skin, and other source refer to the percentage of each source tested that was estimated to be CA-MRSA or HA-MRSA.
Among inpatients, the proportion of S. aureus isolates that were MRSA increased 25% from 46.7% (95% CI 46.2%–47.2%) to 58.5% (95% CI 58.0%–58.9%). Again, the increase was driven primarily by increases in the rate of isolates resistant only to oxacillin, which increased >7× from 3.3% (95% CI 3.1%–3.4%) to 19.8% (95% CI 19.4%–20.1%). Similar to outpatient data, the frequency of skin and soft tissue infections increased for isolates resistant only to oxacillin, although increases in blood, lung, and other infections were also observed. For isolates resistant to >1 other drug, a slightly different pattern was observed than for the pattern of outpatient isolate resistance. Instead of a large increase, the proportion of MRSA isolates resistant to >1 drug remained the same (≈43%–44%) until 2003 before decreasing >5% from 44.1% (95% CI 43.7%–44.5%) to 38.5% (95% CI 38.2%–38.9%) during 2003–2005. This decrease was largely caused by reductions in lung infections, although decreases were also seen in blood and other infections. Also different was the increase in MRSA skin isolates resistant to multiple drugs. There was an increase from 1999, but the increase was less (only 3%–4%) and appeared to plateau at ≈12%–13%.
Discussion
We found during 1999–2006 that the percentage of S. aureus infections resistant to methicillin increased >90%, or ≈10% a year, in outpatients admitted to US hospitals. This increase was caused almost entirely by CA-MRSA strains, which increased >33% annually. Increases in the proportion of HA-MRSA isolates among outpatients were more variable, increasing ≈10% per year during 1999–2001 before the increase slowed; the proportion then decreased over the second half of the study period. This reduction in the growth of HA-MRSA isolates corresponds to a steep increase in the frequency of CA-MRSA skin and soft tissue infections among outpatients over an extremely short period, mostly during 2003–2005.
The frequency of CA-MRSA among inpatients increased nearly in conjunction with outpatient rates, overall and at each infection site. However, increases in blood and lung infections increased more among inpatients than in outpatients, which likely reflected the more severe status and increased likelihood of open wounds in inpatients. During this same period, rates of HA-MRSA decreased only ≈10%. Most of this decrease occurred during 2003–2005 and was mainly the result of a decrease in the frequency of HA-MRSA lung infections. This decrease was more likely the result of changes in empirical antimicrobial drug therapy for ventilator-associated pneumonia (24) than a consequence of any changes in the epidemiology of MRSA.
Despite increases in the proportion of CA-MRSA strains among inpatients, the continuing high level of HA-MRSA suggests that in contrast to reports from local institutions (11), CA-MRSA strains are adding to the problem of MRSA rather than replacing HA-MRSA strains. The fact that the frequency of HA-MRSA has decreased implies that some crowding out of HA-MRSA strains within the hospital may be occurring. However, lack of a decrease suggests that within the hospital, HA-MRSA strains may be more fit, and thus CA-MRSA strains are unable to replace them fully. The result is a coexistence of both strains in the hospital and maintenance of CA-MRSA because of the large influx of colonized and infected patients.
This finding is consistent with the biology of the 2 strains, which suggests differential fitness on the basis of the size of SCCmec. In CA-MRSA strains, the predominant SCCmec elements are types IV and V, which are smaller than the SCCmec types typically found in HA-MRSA strains. These smaller genetic elements may increase the fitness of CA-MRSA strains outside hospital-related antimicrobial drug pressures, presumably by increasing mobility and growth potential (25). However, their increased susceptibility to antibacterial agents in the hospital leaves them at a fitness disadvantage. The result is that although the community has effectively become a reservoir for the CA-MRSA strains that are continually introduced into the hospital population without genetic changes, they are unlikely to replace HA-MRSA strains in the hospital.
The large proportion of infections caused by CA-MRSA strains in hospitals with high frequencies of HA-MRSA has implications for drug-prescribing patterns within hospitals. Because CA-MRSA strains are generally susceptible to more antimicrobial drugs, persons with these infections may be able to be treated with less expensive antimicrobial drugs with fewer adverse outcomes. Moreover, appropriate therapy can reduce the likelihood of emergence of other resistant pathogens, such as vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Initial empiric therapy of infections with the suspected etiology of CA-MRSA must be tailored to antimicrobial drug susceptibility patterns within the local community and be based on efficacy studies that suggest specific effectiveness targets.
Kaplan suggested that empiric therapy should be modified if >10%–15% of CA-MRSA isolates become resistant to a specific empiric therapy (26). Conversely, it may be appropriate to reintroduce a specific agent when susceptibility levels increase above a threshold. However, cycling strategies may not always be optimal (27), and no efficacy studies have been conducted to establish this target. In addition, we urge caution in applying national results to the CA-MRSA antibiogram of a specific area. Although results showed an overall trend at the national level, specific results at individual testing centers tended to be more variable. Moreover, local health officials and hospitals should coordinate their efforts to identify susceptibility patterns at the community level, rather than at the hospital level, to optimize the gains from investments in infection control (28).
The results of our study should be interpreted with caution because TSN provides information concerning only the site of isolate collection and not the infection. In addition, TSN only provides information on the collection location (i.e., outpatient or inpatient) and not case histories. Thus, some isolates may be difficult to classify in situations such as when an isolate was collected in the emergency department and then the patient was admitted or the patient was discharged and then returned as an outpatient. However, the effect of these situations is likely to be small because most isolates are from patients who can be classified as inpatients or outpatients.
A further limitation of the study is that although CA-MRSA isolate drug susceptibility patterns are technically genetically determined, the data enabled only phenotypic classification of isolates. In addition, as with any large time-series database, changes in surveillance or bias in the types of infections cultured over time, such as more severe or unusual infections, could alter the results. These findings suggest that more complicated bacteriology could alter the results. However, no general trend in the number of isolates collected was seen at individual testing centers, and resistance results from the TSN database were comparable to results of other national studies (1). Furthermore, the striking increases over the study period suggest that the trends are likely robust to any bias.
In summary, we examined the frequency of CA-MRSA and HA-MRSA in inpatient and outpatient settings. Our results indicate that outpatients may be a major reservoir of CA-MRSA, which will continue to enter hospitals, exacerbating the problem of MRSA. However, although CA-MRSA isolates have undoubtedly spread within hospitals and are likely to continue to do so, without changes in the fitness of different strains, CA-MRSA strains are unlikely to displace HA-MRSA strains within the hospital.
Our findings have implications for local and national policies aimed at containing and preventing MRSA. More rapid diagnostic methods are urgently needed to better aid physicians in determining appropriate empiric therapy. Strategies for prevention of infection and treatment of patients with CA-MRSA within healthcare settings should be coordinated primarily at the local level in accordance with local susceptibility profiles. Lastly, infection control policies should take into account the role that outpatients likely play in the spread of MRSA and promote interventions that could prevent spread of MRSA from outpatient areas to inpatient areas.
Acknowledgments
E.K. and R.L. were supported by a Pioneer Portfolio grant from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. D.L.S. conducted this research while an employee of the Fogarty International Center, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA.
Biography
Mr Klein is pursuing a PhD in ecology and evolutionary biology at Princeton University. His research interests include the ecology and epidemiology of resistance to antimicrobial drugs and policies to prevent the emergence and spread of drug resistance.
Footnotes
Suggested citation for this article: Klein E, Smith DL, Laxminarayan R. Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in outpatients, United States, 1999–2006. Emerg Infect Dis [serial on the Internet]. 2009 Dec [date cited]. Available from http://www.cdc.gov/EID/content/15/12/1925.htm
References
- 1.Klein E, Smith DL, Laxminarayan R. Hospitalizations and deaths caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, United States, 1999–2005. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1840–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Klevens RM, Morrison MA, Nadle J, Petit S, Gershman K, Ray S, et al. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298:1763–71. 10.1001/jama.298.15.1763 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Strausbaugh LJ, Crossley KB, Nurse BA, Thrupp LD. Antimicrobial resistance in long-term-care facilities. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1996;17:129–40. 10.1086/647257 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Crum NF, Lee RU, Thornton SA, Stine OC, Wallace MR, Barrozo C, et al. Fifteen-year study of the changing epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Med. 2006;119:943–51. 10.1016/j.amjmed.2006.01.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lowy FD. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:520–32. 10.1056/NEJM199808203390806 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moran GJ, Krishnadasan A, Gorwitz RJ, Fosheim GE, McDougal LK, Carey RB, et al. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus infections among patients in the emergency department. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:666–74. 10.1056/NEJMoa055356 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Campbell KM, Vaughn AF, Russell KL, Smith B, Jimenez DL, Barrozo CP, et al. Risk factors for community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in an outbreak of disease among military trainees in San Diego, California, in 2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:4050–3. 10.1128/JCM.42.9.4050-4053.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Herold BC, Immergluck LC, Maranan MC, Lauderdale DS, Gaskin RE, Boyle-Vavra S, et al. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in children with no identified predisposing risk. JAMA. 1998;279:593–8. 10.1001/jama.279.8.593 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Francis JS, Doherty MC, Lopatin U, Johnston CP, Sinha G, Ross T, et al. Severe community-onset pneumonia in healthy adults caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying the Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40:100–7. 10.1086/427148 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Miller LG, Perdreau-Remington F, Rieg G, Mehdi S, Perlroth J, Bayer AS, et al. Necrotizing fasciitis caused by community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Los Angeles. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1445–53. 10.1056/NEJMoa042683 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Popovich KJ, Weinstein RA, Hota B. Are community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains replacing traditional nosocomial MRSA strains? Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:787–94. 10.1086/528716 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.McDougal LK, Steward CD, Killgore GE, Chaitram JM, McAllister SK, Tenover FC. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis typing of oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from the United States: establishing a national database. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:5113–20. 10.1128/JCM.41.11.5113-5120.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fey PD, Said-Salim B, Rupp ME, Hinrichs SH, Boxrud DJ, Davis CC, et al. Comparative molecular analysis of community- or hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003;47:196–203. 10.1128/AAC.47.1.196-203.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.King MD, Humphrey BJ, Wang YF, Kourbatova EV, Ray SM, Blumberg HM. Emergence of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA 300 clone as the predominant cause of skin and soft-tissue infections. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:309–17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Naimi TS, LeDell KH, Como-Sabetti K, Borchardt SM, Boxrud DJ, Etienne J, et al. Comparison of community-and health care-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. JAMA. 2003;290:2976–84. 10.1001/jama.290.22.2976 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Popovich K, Hota B, Rice T, Aroutcheva A, Weinstein RA. Phenotypic prediction rule for community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus? J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:2293–5. 10.1128/JCM.00044-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; Supplement M100–S14. Wayne (PA): The Institute; 2005.
- 18.Flamm RK, Weaver MK, Thornsberry C, Jones ME, Karlowsky JA, Sahm DF. Factors associated with relative rates of antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates tested in clinical laboratories in the United States from 1999 to 2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:2431–6. 10.1128/AAC.48.7.2431-2436.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jones ME, Mayfield DC, Thornsberry C, Karlowsky JA, Sahm DF, Peterson D. Prevalence of oxacillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus among inpatients and outpatients in the United States during 2000. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46:3104–5. 10.1128/AAC.46.9.3104-3105.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Karlowsky JA, Draghi DC, Jones ME, Thornsberry C, Friedland IR, Sahm DF. Surveillance for antimicrobial susceptibility among clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii from hospitalized patients in the United States, 1998 to 2001. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003;47:1681–8. 10.1128/AAC.47.5.1681-1688.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sahm DF, Marsilio MK, Piazza G. Antimicrobial resistance in key bloodstream bacterial isolates: electronic surveillance with the surveillance network database–USA. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;29:259–63. 10.1086/520195 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Styers D, Sheehan DJ, Hogan P, Sahm DF. Laboratory-based surveillance of current antimicrobial resistance patterns and trends among Staphylococcus aureus: 2005 status in the United States. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2006;5:2. 10.1186/1476-0711-5-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Newcombe RG. Two-sided confidence intervals for the single proportion: comparison of seven methods. Stat Med. 1998;17:857–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Chastre J, Wolff M, Fagon JY, Chevret S, Thomas F, Wermert D, et al. Comparison of 8 vs 15 days of antibiotic therapy for ventilator-associated pneumonia in adults: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2003;290:2588–98. 10.1001/jama.290.19.2588 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lee SM, Ender M, Adhikari R, Smith JMB, Berger-Bachi B, Cook GM. Fitness cost of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by way of continuous culture. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51:1497–9. 10.1128/AAC.01239-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kaplan SL. Treatment of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005;24:457–8. 10.1097/01.inf.0000164162.00163.9d [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bonhoeffer S, Lipsitch M, Levin BR. Evaluating treatment protocols to prevent antibiotic resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:12106–11. 10.1073/pnas.94.22.12106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Smith DL, Levin SA, Laxminarayan R. Strategic interactions in multi-institutional epidemics of antibiotic resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:3153–8. 10.1073/pnas.0409523102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]