Abstract
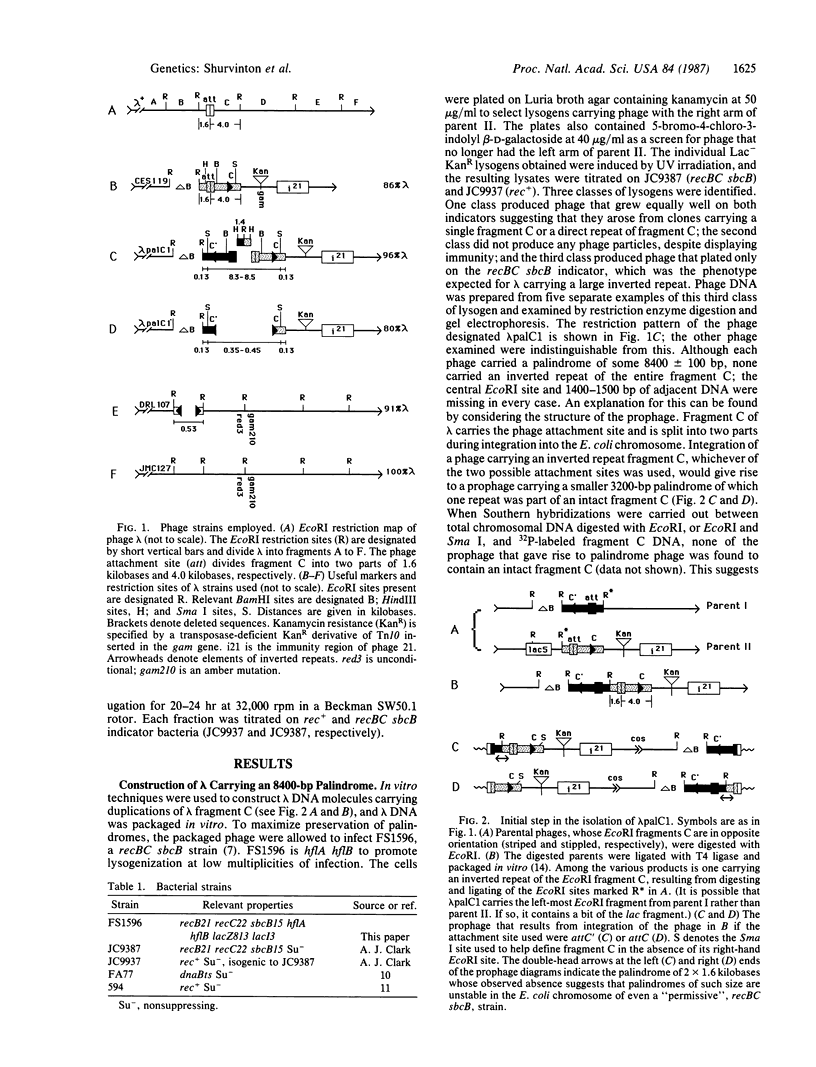
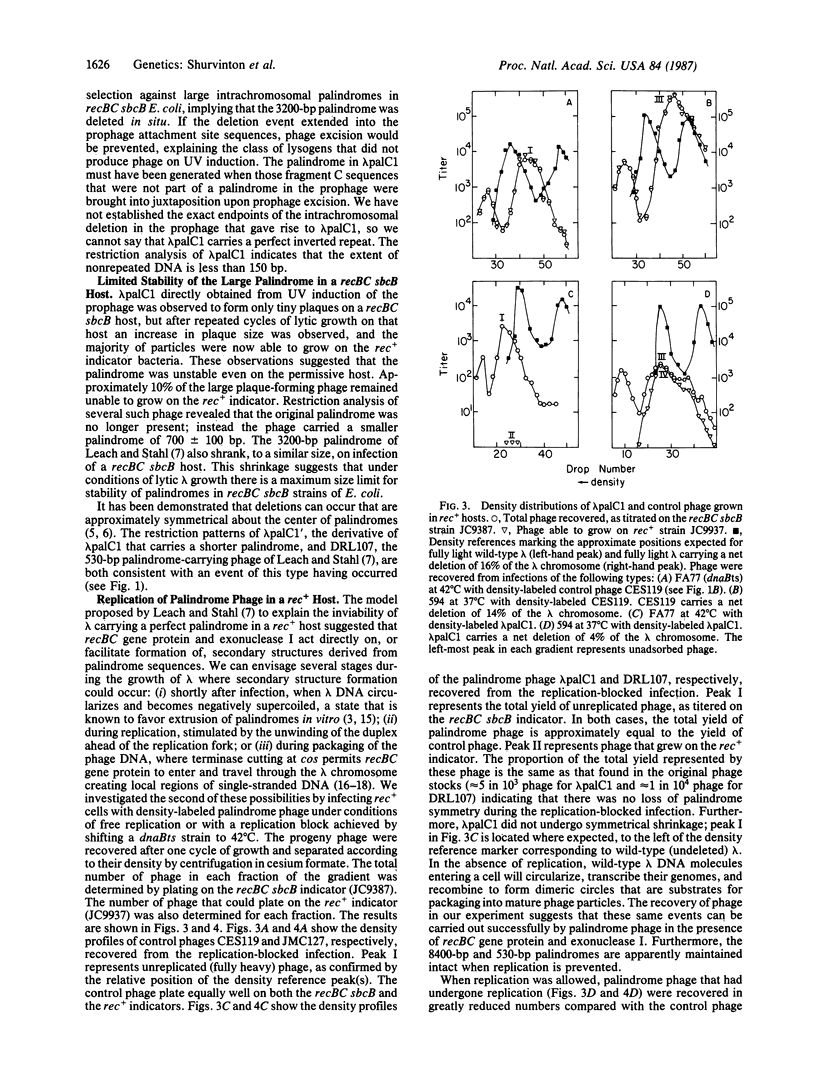
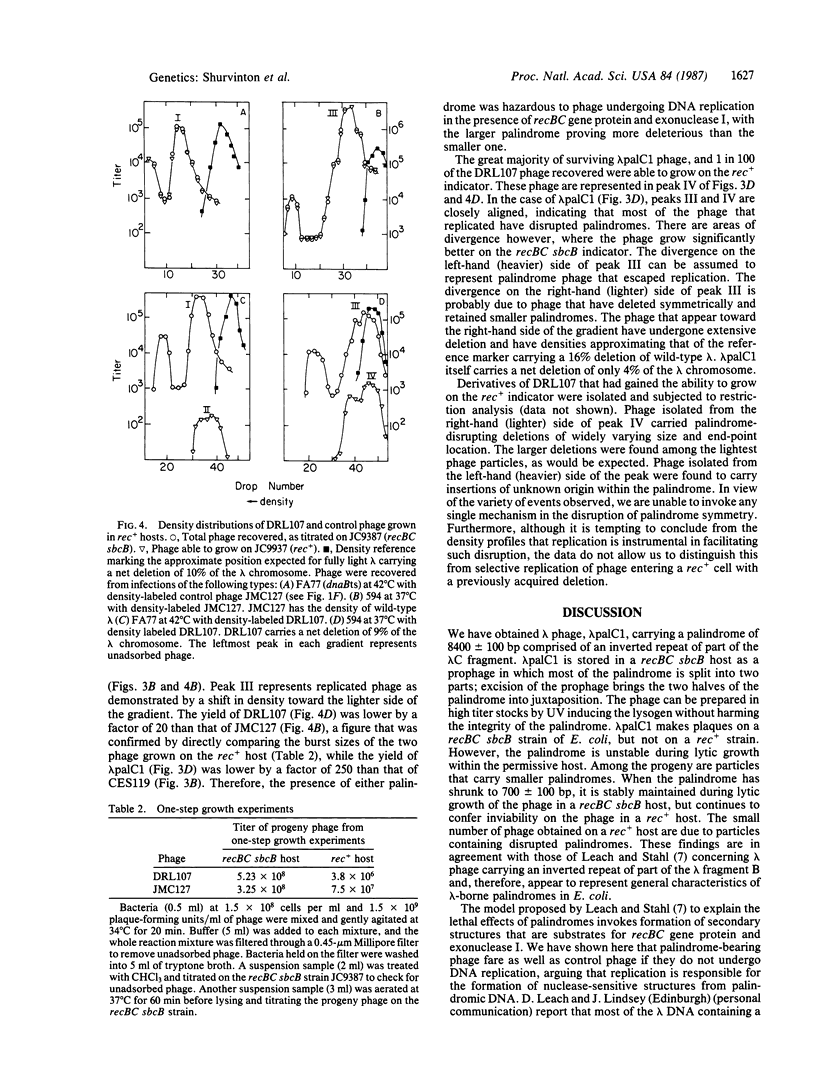
A large palindrome carried by phage lambda has been shown to prevent growth of the phage on a rec+ strain of Escherichia coli. The phage do form plaques on recBC sbcB strains, but the palindrome is not stable--deletions that either destroy the palindrome or diminish its size overgrow the original engineered palindrome-containing phage. We have prepared stocks of lambda carrying a palindrome that is 2 X 4200 base pairs long. These phage stocks are produced by induction of a lysogen in which the two halves of the palindrome are stored at opposite ends of the prophage and are of sufficient titer (10(9) phage per ml) to enable one-step growth experiments with replication-blocked phage. We find that the large palindrome as well as a lesser palindrome of 2 X 265 base pairs are recovered intact among particles carrying unreplicated chromosomes following such an infection of a rec+ host. We propose that DNA replication drives the extrusion of palindromic sequences in vivo, forming secondary structures that are substrates for the recBC and sbcB gene products.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banuett F., Hoyt M. A., McFarlane L., Echols H., Herskowitz I. hflB, a new Escherichia coli locus regulating lysogeny and the level of bacteriophage lambda cII protein. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90229-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. Instability of palindromic DNA in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):409–416. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Volckaert G., Nevers P. Precise and nearly-precise excision of the symmetrical inverted repeats of Tn5; common features of recA-independent deletion events in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):139–146. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Wang J. C. Cruciform formation in a negatively supercoiled DNA may be kinetically forbidden under physiological conditions. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Ohmori H., Tomizawa J. DNA gyrase and DNA supercoiling. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):35–40. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan C. E., Warren G. J. Lethality of palindromic DNA and its use in selection of recombinant plasmids. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90199-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan C. E., Warren G. J. Viability of palindromic DNA is restored by deletions occurring at low but variable frequency in plasmids of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi I., Stahl M. M., Stahl F. W. The mechanism of the chi-cos interaction in RecA-RecBC-mediated recombination in phage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:497–506. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaDuca R. J., Fay P. J., Chuang C., McHenry C. S., Bambara R. A. Site-specific pausing of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis catalyzed by four forms of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase III. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 25;22(22):5177–5188. doi: 10.1021/bi00291a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach D. R., Stahl F. W. Viability of lambda phages carrying a perfect palindrome in the absence of recombination nucleases. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):448–451. doi: 10.1038/305448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. In vivo consequences of plasmid topology. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):380–382. doi: 10.1038/292380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Mizuuchi M., Gellert M. Cruciform structures in palindromic DNA are favored by DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 5;156(2):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosamond J., Telander K. M., Linn S. Modulation of the action of the recBC enzyme of Escherichia coli K-12 by Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8646–8652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. M., Stahl M. M., Kobayashi I., Stahl F. W. Improved in vitro packaging of coliphage lambda DNA: a one-strain system free from endogenous phage. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Broyles S. S., Pettijohn D. E. Perfect palindromic lac operator DNA sequence exists as a stable cruciform structure in supercoiled DNA in vitro but not in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1797–1801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Smith G. R. Unwinding and rewinding of DNA by the RecBC enzyme. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle J. Assembly of phage lambda in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1462–1466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


