Abstract
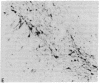
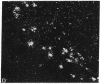
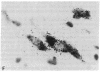
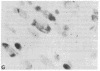
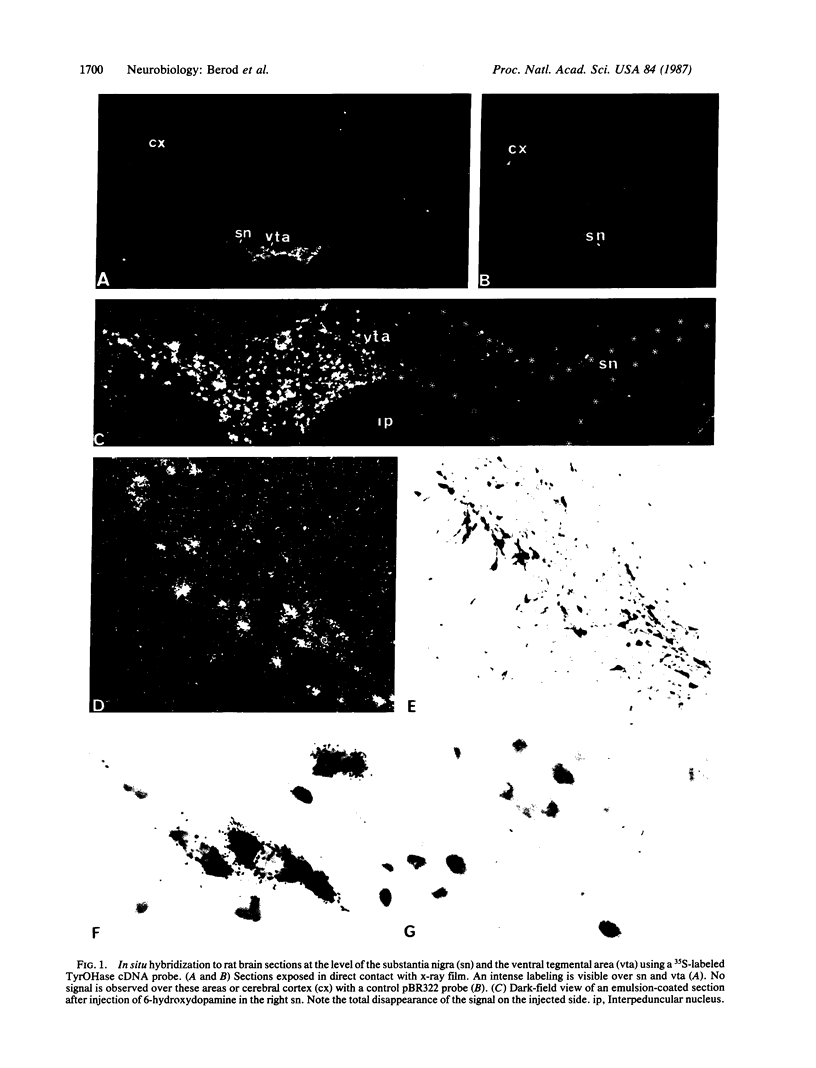
A rat tyrosine hydroxylase [TyrOHase; tyrosine 3-monooxygenase; L-tyrosine, tetrahydropteridine:oxygen oxidoreductase (3-hydroxylating); EC 1.14.16.2] cDNA probe was used for in situ hybridization studies on histological sections through the locus coeruleus, substantia nigra, and the ventral tegmental area of the rat brain. Experimental conditions were established that yielded no background and no signal when pBR322 was used as a control probe. Using the tyrosine hydroxylase probe, we ascertained the specificity of the labeling over catecholaminergic cells by denervation experiments and comparison of the hybridization pattern with that of immunoreactivity. The use of 35S-labeled probe enabled the hybridization signal to be resolved at the cellular level. A single injection of reserpine into the rat led to an increase of the intensity of the autoradiographic signal over the locus coeruleus area, confirming an RNA gel blot analysis. The potential of in situ hybridization to analyze patterns of modulation of gene activity as a result of nervous activity is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berod A., Chat M., Paut L., Tappaz M. Catecholaminergic and GABAergic anatomical relationship in the rat substantia nigra, locus coeruleus, and hypothalamic median eminence: immunocytochemical visualization of biosynthetic enzymes on serial semithin plastic-embedded sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Dec;32(12):1331–1338. doi: 10.1177/32.12.6150057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berod A., Hartman B. K., Keller A., Joh T. H., Pujol J. F. A new double labeling technique using tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase immunohistochemistry: evidence for dopaminergic cells lying in the pons of the beef brain. Brain Res. 1982 May 27;240(2):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90219-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biguet N. F., Buda M., Lamouroux A., Samolyk D., Mallet J. Time course of the changes of TH mRNA in rat brain and adrenal medulla after a single injection of reserpine. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):287–291. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björklund H., Hökfelt T., Goldstein M., Terenius L., Olson L. Appearance of the noradrenergic markers tyrosine hydroxylase and neuropeptide Y in cholinergic nerves of the iris following sympathectomy. J Neurosci. 1985 Jun;5(6):1633–1640. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-06-01633.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black I. B., Adler J. E., Dreyfus C. F., Jonakait G. M., Katz D. M., LaGamma E. F., Markey K. M. Neurotransmitter plasticity at the molecular level. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1266–1270. doi: 10.1126/science.6147894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black I. B., Chikaraishi D. M., Lewis E. J. Trans-synaptic increase in RNA coding for tyrosine hydroxylase in a rat sympathetic ganglion. Brain Res. 1985 Jul 22;339(1):151–153. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90635-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buda M., Gonon F., Cespuglio R., Jouvet M., Pujol J. F. In vivo electrochemical detection of catechols in several dopaminergic brain regions of anaesthetized rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furshpan E. J., Landis S. C., Matsumoto S. G., Potter D. D. Synaptic functions in rat sympathetic neurons in microcultures. I. Secretion of norepinephrine and acetylcholine. J Neurosci. 1986 Apr;6(4):1061–1079. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-04-01061.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grima B., Lamouroux A., Blanot F., Biguet N. F., Mallet J. Complete coding sequence of rat tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):617–621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Weintraub H. Propagation of globin DNAase I-hypersensitive sites in absence of factors required for induction: a possible mechanism for determination. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Costa E. Commentary: Trans-synaptic regulation of typrosine 3-mono-oxygenase biosynthesis in rat adrenal medulla. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 May 1;26(9):817–823. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90393-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Fuxe K., Goldstein M., Park D. Immunohistochemical studies on the localization and distribution of monoamine neuron systems in the rat brain. I. Tyrosine hydroxylase in the mes- and diencephalon. Med Biol. 1976 Dec;54(6):427–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joh T. H., Geghman C., Reis D. Immunochemical demonstration of increased accumulation of tyrosine hydroxylase protein in sympathetic ganglia and adrenal medulla elicited by reserpine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2767–2771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallet J., Faucon Biguet N., Buda M., Lamouroux A., Samolyk D. Detection and regulation of the tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA levels in rat adrenal medulla and brain tissues. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 1):305–308. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. Y., Bloom F. E. Central catecholamine neuron systems: anatomy and physiology of the dopamine systems. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1978;1:129–169. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.01.030178.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. Y., Bloom F. E. Central catecholamine neuron systems: anatomy and physiology of the norepinephrine and epinephrine systems. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1979;2:113–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.02.030179.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson P. H. Environmental determination of autonomic neurotransmitter functions. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1978;1:1–17. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.01.030178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis D. J., Joh T. H., Ross R. A., Pickel V. M. Reserpine selectively increases tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase enzyme protein in central noradrenergic neurons. Brain Res. 1974 Dec 6;81(2):380–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90956-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H. Trans-synaptic enzyme induction. Life Sci. 1974 Jan 16;14(2):223–235. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond R. E., Schon F., Iversen L. L. Increased tyrosine hydroxylase activity in the locus coeruleus of rat brain stem after reserpine treatment and cold stress. Brain Res. 1974 Apr 26;70(3):547–552. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond R. E. Tyrosine hydroxylase activity in noradrenergic neurons of the locus coeruleus after reserpine administration: sequential increase in cell bodies and nerve terminals. J Neurochem. 1979 Jan;32(1):23–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]