Abstract
Immunocytochemical studies with a monoclonal antibody show that acetylcholinesterase (AcChoEase; EC 3.1.1.7) is distributed in clusters along the fibers of cultured sympathetic neurons but is essentially absent from cell bodies. Although tissue-cultured sympathetic neurons synthesize several oligomeric forms of AcChoEase, only the hydrophobic globular (G4) form of AcChoEase is present within these clusters. This G4 form is asymmetrically distributed within neurons and is transported preferentially into nerve fibers following its synthesis in the cell bodies. Thus G4 is found in clusters on neurons and is readily distinguishable from the hydrophilic forms on the surfaces of myotubes. The association of a specialized form of AcChoEase in densities on neurons in culture indicates that neurons and myotubes have distinct mechanisms for localizing AcChoEase molecules on their surfaces and suggests that these two types of electrically excitable cells have different requirements for organizing synaptic components on their plasma membranes.
Full text
PDF

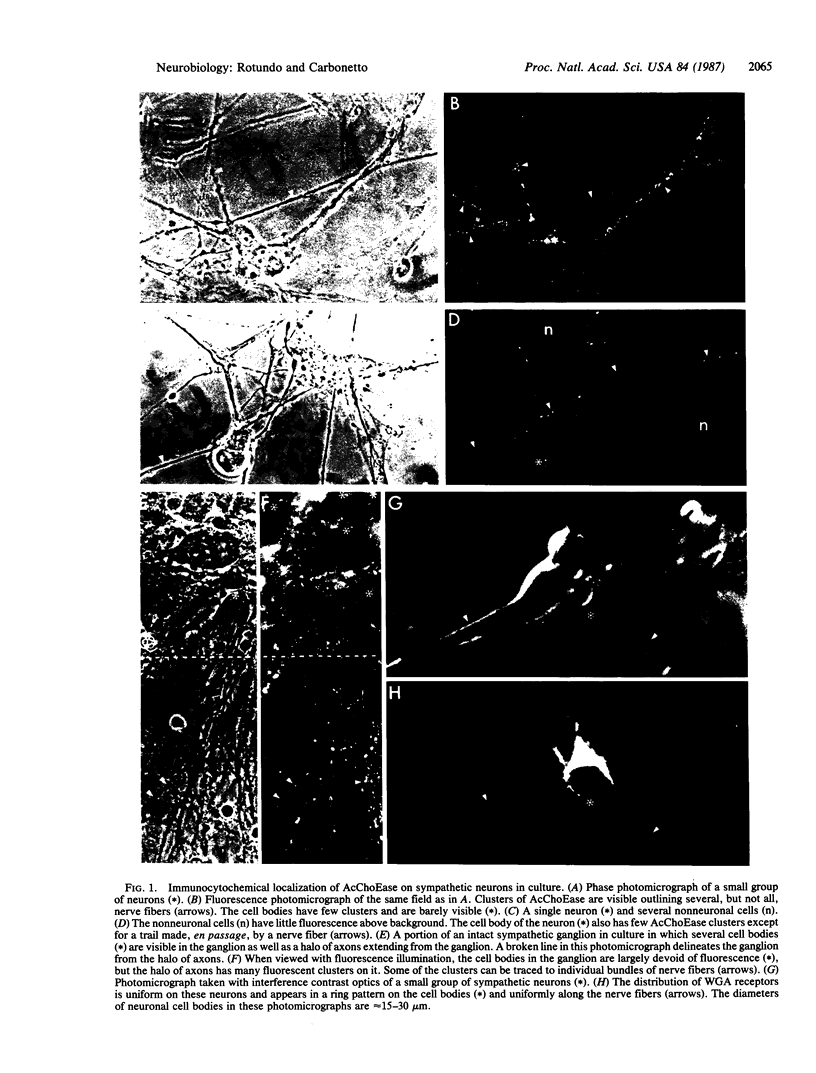
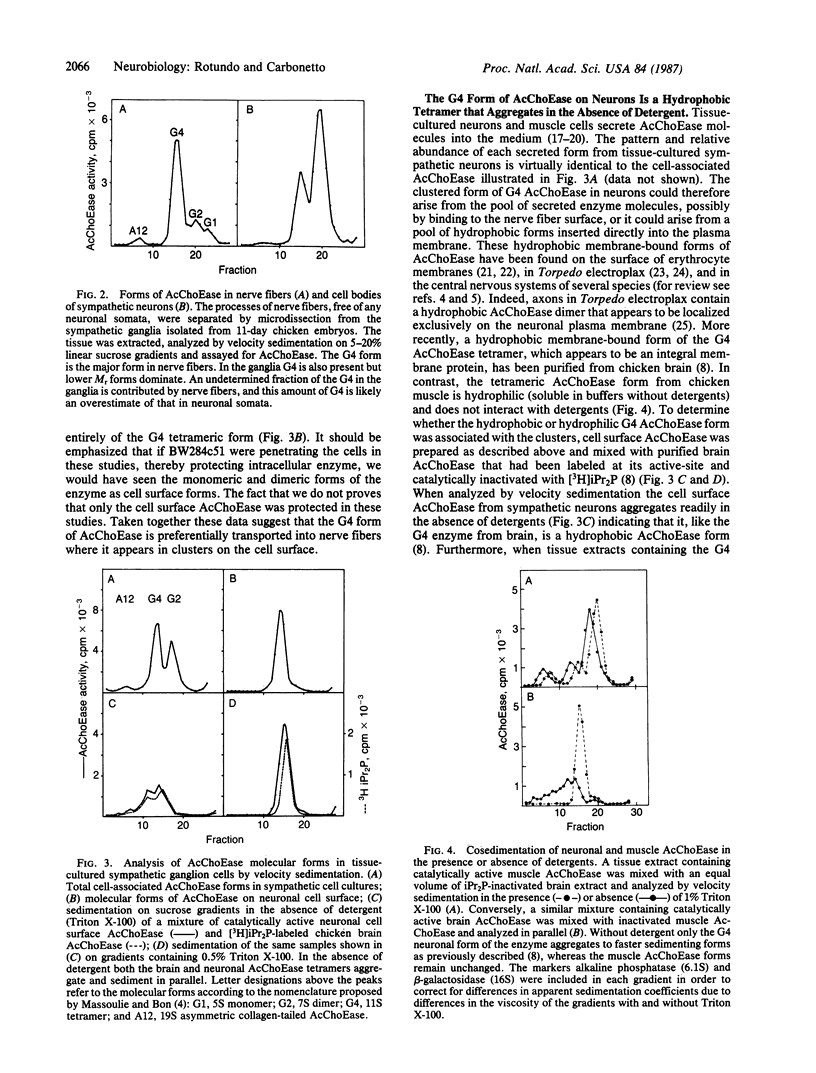

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betz W., Sakmann B. Effects of proteolytic enzymes on function and structure of frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):673–688. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandan E., Maldonado M., Garrido J., Inestrosa N. C. Anchorage of collagen-tailed acetylcholinesterase to the extracellular matrix is mediated by heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):985–992. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimijoin S. Molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase in brain, nerve and muscle: nature, localization and dynamics. Prog Neurobiol. 1983;21(4):291–322. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(83)90015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursztajn S., Berman S. A., McManaman J. L., Watson M. L. Insertion and internalization of acetylcholine receptors at clustered and diffuse domains on cultured myotubes. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):104–111. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonetto S., Argon Y. Lectins induce the redistribution and internalization of receptors on the surface of cultured neurons. Dev Biol. 1980 Dec;80(2):364–378. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90411-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonetto S., Fambrough D. M. Synthesis, insertion into the plasma membrane, and turnover of alpha-bungarotoxin receptors in chick sympathetic neurons. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):555–569. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta-Choudhury T. A., Rosenberry T. L. Human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase is an amphipathic protein whose short membrane-binding domain is removed by papain digestion. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5653–5660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M. Control of acetylcholine receptors in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jan;59(1):165–227. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank E., Fischbach G. D. Early events in neuromuscular junction formation in vitro: induction of acetylcholine receptor clusters in the postsynaptic membrane and morphology of newly formed synapses. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):143–158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W., Kelly R. B. Enzymatic detachment of endplate acetylcholinesterase from muscle. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 14;232(28):62–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio232062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inestrosa N. C., Silberstein L., Hall Z. W. Association of the synaptic form of acetylcholinesterase with extracellular matrix in cultured mouse muscle cells. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. D., Russell R. L. A rapid, simple radiometric assay for cholinesterase, suitable for multiple determinations. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliana T. H., Chyu J. Y., Max S. R. Release of acetylcholinesterase by cultured spinal cord cells. J Neurobiol. 1977 Sep;8(5):469–476. doi: 10.1002/neu.480080507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig J. Formation de jonctions neuromusculaires dans des cultures cellulaires embryonnaires de rat. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1978 May 22;286(20):1451–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. L., Camp S. J., Taylor P. Characterization of a hydrophobic, dimeric form of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12302–12309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. Y., Bon C. Presence of a membrane-bound acetylcholinesterase form in a preparation of nerve endings from Torpedo marmorata electric organ. J Neurochem. 1983 Feb;40(2):338–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb11288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié J., Bon S. The molecular forms of cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in vertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1982;5:57–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.05.030182.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McISAAC R. J., KOELLE G. B. Comparison of the effects of inhibition of external, internal and total acetylcholinesterase upon ganglionic transmission. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 May;126(1):9–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan U. J., Sanes J. R., Marshall L. M. Cholinesterase is associated with the basal lamina at the neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1978 Jan 12;271(5641):172–174. doi: 10.1038/271172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody-Corbett F., Cohen M. W. Influence of nerve on the formation and survival of acetylcholine receptor and cholinesterase patches on embryonic Xenopus muscle cells in culture. J Neurosci. 1982 May;2(5):633–646. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-05-00633.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody-Corbett F., Cohen M. W. Localization of cholinesterase at sites of high acetylcholine receptor density on embryonic amphibian muscle cells cultured without nerve. J Neurosci. 1981 Jun;1(6):596–605. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-06-00596.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott P., Jenny B., Brodbeck U. Multiple molecular forms of purified human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):469–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poo M. M. Mobility and localization of proteins in excitable membranes. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1985;8:369–406. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.08.030185.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Fields K. L., Hakomori S. I., Mirsky R., Pruss R. M., Winter J. Cell-type-specific markers for distinguishing and studying neurons and the major classes of glial cells in culture. Brain Res. 1979 Oct 5;174(2):283–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90851-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranscht B., Moss D. J., Thomas C. A neuronal surface glycoprotein associated with the cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1803–1813. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L. Acetylcholinesterase biosynthesis and transport in tissue culture. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:353–367. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L., Fambrough D. M. Molecular forms of chicken embryo acetylcholinesterase in vitro and in vivo. Isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4790–4799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L., Fambrough D. M. Secretion of acetylcholinesterase: relation to acetylcholine receptor metabolism. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90369-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L., Fambrough D. M. Synthesis, transport and fate of acetylcholinesterase in cultured chick embryos muscle cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):583–594. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90368-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L. Purification and properties of the membrane-bound form of acetylcholinesterase from chicken brain. Evidence for two distinct polypeptide chains. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13186–13194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. L., Schuetze S. M., Fischbach G. D. Accumulation of acetylcholinesterase at newly formed nerve--muscle synapases. Dev Biol. 1979 Mar;69(1):46–58. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. L., Schuetze S. M., Weill C. L., Fischbach G. D. Regulation of acetylcholinesterase appearance at neuromuscular junctions in vitro. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):264–267. doi: 10.1038/283264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Unanue E. R. Membrane and cytoplasmic changes in B lymphocytes induced by ligand-surface immunoglobulin interaction. Adv Immunol. 1976;24:37–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small R. K., Blank M., Ghez R., Pfenninger K. H. Components of the plasma membrane of growing axons. II. Diffusion of membrane protein complexes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1434–1443. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. B., Rieger F., Shelanski M. L., Greene L. A. Cellular localization of the multiple molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase in cultured neuronal cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3827–3830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villegas J. Axon/Schwann-cell relationships in the giant nerve fibre of the squid. J Exp Biol. 1981 Dec;95:135–151. doi: 10.1242/jeb.95.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viratelle O. M., Bernhard S. A. Major component of acetylcholinesterase in Torpedo electroplax is not basal lamina associated. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 28;19(22):4999–5007. doi: 10.1021/bi00563a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. G., Nitkin R. M., Reist N. E., Fallon J. R., Moayeri N. N., McMahan U. J. Aggregates of acetylcholinesterase induced by acetylcholine receptor-aggregating factor. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):574–577. doi: 10.1038/315574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. W., Nieberg P. S., Walker C. R., Linkhart T. A., Fry D. M. Production and release of acetylcholinesterase by cultured chick embryo muscle. Dev Biol. 1973 Aug;33(2):285–299. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90138-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



