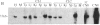Abstract
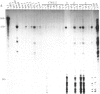
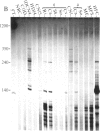
Type II collagen is crucial to the development of form in vertebrates as it is the major protein of cartilage. To study the factors regulating its expression we introduced a cosmid containing the human type II collagen gene, including 4.5 kilobases of 5' and 2.2 kilobases of 3' flanking DNA, into embryonic stem cells in vitro. The transformed cells contribute to all tissues in chimeric mice allowing the expression of the exogenous gene to be studied in vivo. Human type II collagen mRNA is restricted to tissues showing transcription from the endogenous gene and human type II collagen is found in extracellular matrix surrounding chondrocytes in cartilage. The results indicate that the cis-acting requirements for correct temporal and spatial regulation of the gene are contained within the introduced DNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. L., Boettiger D., Focht R. J., Holtzer H., Pacifici M. Regulation of the synthesis of extracellular matrix components in chondroblasts transformed by a temperature-sensitive mutant of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90235-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benya P. D., Shaffer J. D. Dedifferentiated chondrocytes reexpress the differentiated collagen phenotype when cultured in agarose gels. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley A., Evans M., Kaufman M. H., Robertson E. Formation of germ-line chimaeras from embryo-derived teratocarcinoma cell lines. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):255–256. doi: 10.1038/309255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley A., Robertson E. Embryo-derived stem cells: a tool for elucidating the developmental genetics of the mouse. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1986;20:357–371. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60675-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chada K., Magram J., Raphael K., Radice G., Lacy E., Costantini F. Specific expression of a foreign beta-globin gene in erythroid cells of transgenic mice. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):377–380. doi: 10.1038/314377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah K. S. Collagen genes and inherited connective tissue disease. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):287–303. doi: 10.1042/bj2290287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah K. S., Stoker N. G., Griffin J. R., Grosveld F. G., Solomon E. Identification and characterization of the human type II collagen gene (COL2A1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2555–2559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Kaufman M. H. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):154–156. doi: 10.1038/292154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossler A., Doetschman T., Korn R., Serfling E., Kemler R. Transgenesis by means of blastocyst-derived embryonic stem cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9065–9069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumpel-Pinot M. Ectoderm-mesoderm interactions in relation to limb-bud chondrogenesis in the chick embryo: transfilter cultures and ultrastructural studies. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1981 Oct;65:73–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister D. W., Sakai L. Y., Morris N. P., Shimono L. H., Burgeson R. E. Production and characterization of hybridoma antibody to native human type II collagen. Coll Relat Res. 1982;2(3):197–210. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(82)80014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh H., Takahashi Y., Okada T. S. Differentiation-dependent expression of the chicken delta-crystallin gene introduced into mouse teratocarcinoma stem cells. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2009–2014. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02083.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kravis D., Upholt W. B. Quantitation of type II procollagen mRNA levels during chick limb cartilage differentiation. Dev Biol. 1985 Mar;108(1):164–172. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R., Hammer R. E., Tilghman S. M., Brinster R. L. Developmental regulation of alpha-fetoprotein genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1639–1648. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovell-Badge R. H., Bygrave A. E., Bradley A., Robertson E., Evans M. J., Cheah K. S. Transformation of embryonic stem cells with the human type-II collagen gene and its expression in chimeric mice. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:707–711. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. Isolation of a pluripotent cell line from early mouse embryos cultured in medium conditioned by teratocarcinoma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7634–7638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Palmiter R. D., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Swift G. H., MacDonald R. J. Specific expression of an elastase-human growth hormone fusion gene in pancreatic acinar cells of transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):600–602. doi: 10.1038/313600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prockop D. J., Kivirikko K. I. Heritable diseases of collagen. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 9;311(6):376–386. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408093110606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson E., Bradley A., Kuehn M., Evans M. Germ-line transmission of genes introduced into cultured pluripotential cells by retroviral vector. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):445–448. doi: 10.1038/323445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Wright S., Cedar H., Flavell R., Grosveld F. Regulated expression of an introduced MHC H-2K bm1 gene in murine embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):415–418. doi: 10.1038/310415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandell L. J., Prentice H. L., Kravis D., Upholt W. B. Structure and sequence of the chicken type II procollagen gene. Characterization of the region encoding the carboxyl-terminal telopeptide and propeptide. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7826–7834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. W., Vogt T. F., Croke M. E., Tilghman S. M. Tissue-specific activation of a cloned alpha-fetoprotein gene during differentiation of a transfected embryonal carcinoma cell line. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):562–567. doi: 10.1038/310562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. L., Vanek M., Wagner E. F. Expression of foreign genes from retroviral vectors in mouse teratocarcinoma chimaeras. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3701–3709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04138.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker N. G., Cheah K. S., Griffin J. R., Pope F. M., Solomon E. A highly polymorphic region 3' to the human type II collagen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4613–4622. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swimmer C., Shenk T. Selection of sequence elements that substitute for the standard AATAAA motif which signals 3' processing and polyadenylation of late simian virus 40 mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8053–8063. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachtler F., Christ B., Jacob H. J. On the determination of mesodermal tissues in the avian embryonic wing bud. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1981;161(3):283–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00301826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. F., Mintz B. Transfer of nonselectable genes into mouse teratocarcinoma cells and transcription of the transferred human beta-globin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):190–198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw E., Proudfoot N. J. Transcriptional activity of the human pseudogene psi alpha globin compared with alpha globin, its functional gene counterpart. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7717–7733. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K., von der Mark H., Gay S. Study of differential collagen synthesis during development of the chick embryo by immunofluroescence. II. Localization of type I and type II collagen during long bone development. Dev Biol. 1976 Oct 15;53(2):153–170. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90220-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]