Abstract
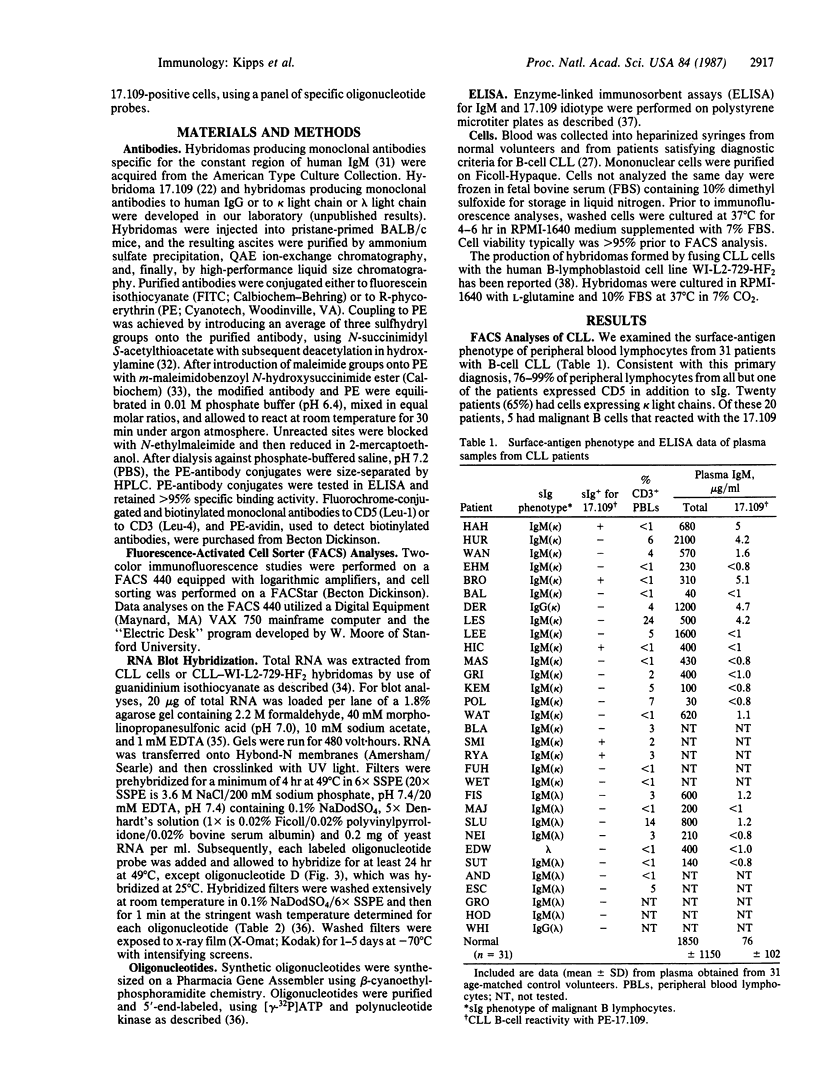
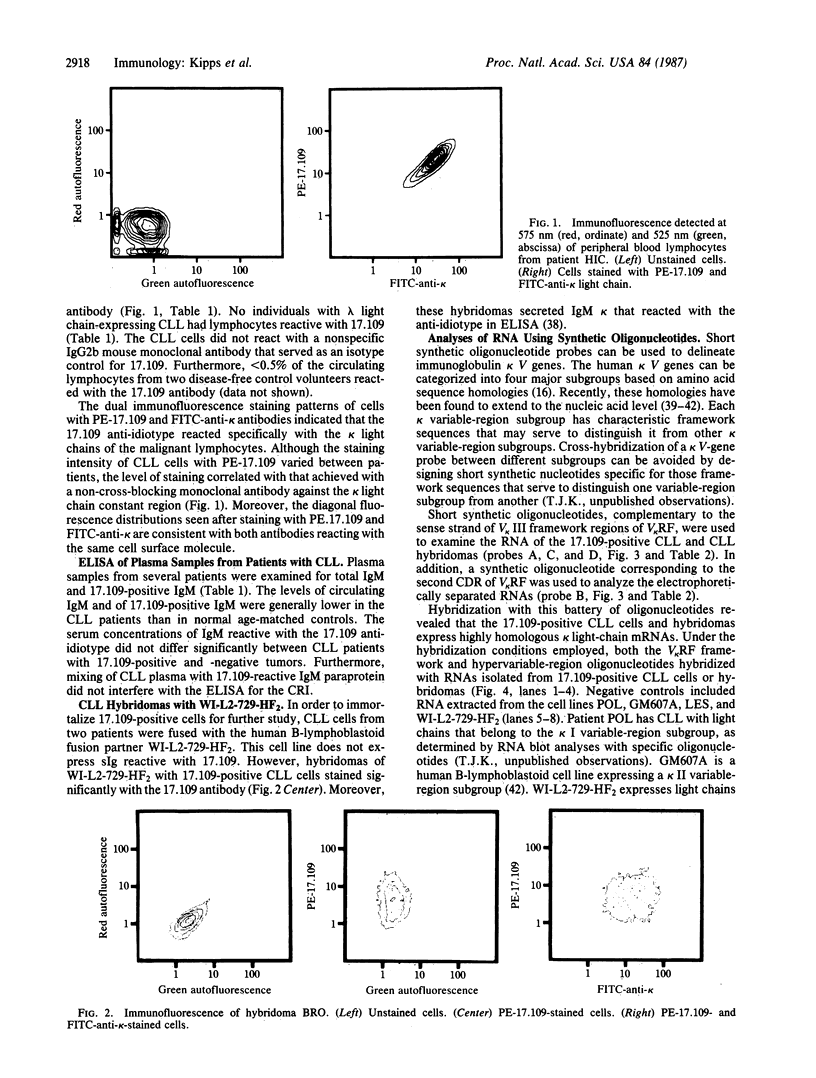
Malignant B lymphocytes from several patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) were examined for reactivity with murine monoclonal antibody 17.109. This antibody, prepared against the rheumatoid factor (RF) paraprotein Sie, recognizes a crossreactive idiotype on 48% of human IgM RF paraproteins, but does not react with IgM paraproteins without RF activity or substantially with normal pooled immunoglobulin. The 17.109-reactive idiotype is a marker for a kappa III variable-region gene, designated V kappa RF, that is conserved in outbred human populations. In a limited study of 31 CLL patients, the leukemic cells from 5 of 20 patients with kappa light chain-expressing CLL were recognized by the 17.109 monoclonal antibody. Despite having malignant cells specifically reactive with this antibody, patients with 17.109-positive CLL did not have elevated serum levels of circulating antibody bearing 17.109-reactive determinants. Total RNAs isolated from the CLL B lymphocytes, or from hybridomas produced by fusing the CLL cells with the WI-L2-729-HF2 cell line, were fractionated electrophoretically and examined by blot hybridization. Under stringent hybridization conditions capable of discerning a single base-pair mismatch, RNA from the 17.109-idiotype-positive CLL cells hybridized to synthetic oligonucleotide probes corresponding to framework and complementary-determining regions in the V kappa RF gene. The high frequency of the 17.109-associated idiotype and the V kappa RF gene in CLL suggests that the disease may arise from B lymphocytes that express a restricted set of inherited immunoglobulin variable-region genes with little or no somatic mutation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews D. W., Capra J. D. Complete amino acid sequence of variable domains from two monoclonal human anti-gamma globulins of the Wa cross-idiotypic group: suggestion that the J segments are involved in the structural correlate of the idiotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3799–3803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L. Most kappa immunoglobulin mRNA in human lymphocytes is homologous to a small family of germ-line V genes. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):77–80. doi: 10.1038/307077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Rabbitts T. H. Human V kappa immunoglobulin gene number: implications for the origin of antibody diversity. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):613–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Rabbitts T. H. Human V kappa immunoglobulin gene number: implications for the origin of antibody diversity. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):613–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell A. L., Paskind M., Reth M., Imanishi-Kari T., Rajewsky K., Baltimore D. Heavy chain variable region contribution to the NPb family of antibodies: somatic mutation evident in a gamma 2a variable region. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):625–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Structure of antibodies with shared idiotypy: the complete sequence of the heavy chain variable regions of two immunoglobulin M anti-gamma globulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4032–4036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll W. L., Lowder J. N., Streifer R., Warnke R., Levy S., Levy R. Idiotype variant cell populations in patients with B cell lymphoma. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1566–1580. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Fong S. A common idiotope on human rheumatoid factors identified by a hybridoma antibody. Mol Immunol. 1983 Oct;20(10):1081–1087. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90116-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Meeker T. C., Levy S., Lee E., Trela M., Sklar J., Levy R. Clustering of extensive somatic mutations in the variable region of an immunoglobulin heavy chain gene from a human B cell lymphoma. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90488-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R. J., Weston P. D., Wrigglesworth R. A new reagent which may be used to introduce sulfhydryl groups into proteins, and its use in the preparation of conjugates for immunoassay. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):68–73. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90426-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong S., Chen P. P., Gilbertson T. A., Fox R. I., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Structural similarities in the kappa light chains of human rheumatoid factor paraproteins and serum immunoglobulins bearing a cross-reactive idiotype. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1955–1960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong S., Chen P. P., Gilbertson T. A., Weber J. R., Fox R. I., Carson D. A. Expression of three cross-reactive idiotypes on rheumatoid factor autoantibodies from patients with autoimmune diseases and seropositive adults. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):122–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong S., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Two different rheumatoid factor-producing cell populations distinguished by the mouse erythrocyte receptor and responsiveness to polyclonal B cell activators. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):162–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. I., Chen P., Carson D. A., Fong S. Expression of a cross-reactive idiotype on rheumatoid factor in patients with Sjogren's syndrome. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):477–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearhart P. J., Bogenhagen D. F. Clusters of point mutations are found exclusively around rearranged antibody variable genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3439–3443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfien R. D., Chen P. J., Kipps T. J., Starkebaum G., Heitzmann J. G., Radoux V., Fong S., Carson D. A. Genetic analysis of human B cell hybridomas expressing a cross-reactive idiotype. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):940–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirik F. R., Sorge J., Fong S., Heitzmann J. G., Curd J. G., Chen P. P., Goldfien R., Carson D. A. Cloning and sequence determination of a human rheumatoid factor light-chain gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2195–2199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch I. R., Morton C. C., Nakahara K., Leder P. Human immunoglobulin heavy chain genes map to a region of translocations in malignant B lymphocytes. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):301–303. doi: 10.1126/science.6801764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa T., Aikawa T. Enzyme coupled immunoassay of insulin using a novel coupling reagent. J Biochem. 1976 Jan;79(1):233–236. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobeck H. G., Solomon A., Zachau H. G. Contribution of human V kappa II germ-line genes to light-chain diversity. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):73–76. doi: 10.1038/309073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Agnello V., Joslin F. G., Winchester R. J., Capra J. D. Cross-idiotypic specificity among monoclonal IgM proteins with anti- -globulin activity. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):331–342. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Winchester R. J., Joslin F. G., Capra J. D. Similarities in the light chains of anti-gamma-globulins showing cross-idiotypic specificities. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):128–136. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P. The genetics of antibody diversity. Sci Am. 1982 May;246(5):102–115. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0582-102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm S., Barton P., Murphy C., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Bentley D. L., Rabbitts T. H. Localization of human immunoglobulin kappa light chain variable region genes to the short arm of chromosome 2 by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4957–4961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama S., Kubagawa H., Cooper M. D. Activation of human B cells and inhibition of their terminal differentiation by monoclonal anti-mu antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Hieter P. A., Hollis G. F., Swan D., Otey M. C., Leder P. Chromosomal location of human kappa and lambda immunoglobulin light chain constant region genes. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1480–1490. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean D., Huppi K., Bell M., Staudt L., Gerhard W., Weigert M. Generation of antibody diversity in the immune response of BALB/c mice to influenza virus hemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C. Linked groups of residues in immunoglobulin k chains. Nature. 1967 Oct 28;216(5113):330–332. doi: 10.1038/216330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pech M., Höchtl J., Schnell H., Zachau H. G. Differences between germ-line and rearranged immunoglobulin V kappa coding sequences suggest a localized mutation mechanism. Nature. 1981 Jun 25;291(5817):668–670. doi: 10.1038/291668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pech M., Jaenichen H. R., Pohlenz H. D., Neumaier P. S., Klobeck H. G., Zachau H. G. Organization and evolution of a gene cluster for human immunoglobulin variable regions of the kappa type. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 25;176(2):189–204. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pech M., Zachau H. G. Immunoglobulin genes of different subgroups are interdigitated within the VK locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9229–9236. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Crews S. T., Douglas R., Sorensen G., Johnson N., Nivera N., Gearhart P. J., Hood L. The generation of diversity in phosphorylcholine-binding antibodies. Adv Immunol. 1984;35:1–37. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60572-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons-Estel B., Goñi F., Solomon A., Frangione B. Sequence similarities among kappa IIIb chains of monoclonal human IgM kappa autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):893–904. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preud'homme J. L., Seligmann M. Anti-human immunoglobulin G activity of membrane-bound monoclonal immunoglobulin M in lymphoproliferative disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2132–2135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radoux V., Chen P. P., Sorge J. A., Carson D. A. A conserved human germline V kappa gene directly encodes rheumatoid factor light chains. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2119–2124. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin E. M., Hekman A. Shared idiotypes among surface immunoglobulins in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 16;311(7):470–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royston I., Majda J. A., Baird S. M., Meserve B. L., Griffiths J. C. Human T cell antigens defined by monoclonal antibodies: the 65,000-dalton antigen of T cells (T65) is also found on chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells bearing surface immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):725–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekevitz M., Huang S. Y., Gefter M. L. The genetic basis of antibody production: a single heavy chain variable region gene encodes all molecules bearing the dominant anti-arsonate idiotype in the strain A mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Feb;13(2):123–132. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims J., Rabbitts T. H., Estess P., Slaughter C., Tucker P. W., Capra J. D. Somatic mutation in genes for the variable portion of the immunoglobulin heavy chain. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):309–311. doi: 10.1126/science.6801765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson F. K., Wrightham M., Glennie M. J., Jones D. B., Cattan A. R., Feizi T., Hamblin T. J., Stevenson G. T. Antibodies to shared idiotypes as agents for analysis and therapy for human B cell tumors. Blood. 1986 Aug;68(2):430–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Good R. A., Ammirati P., Dymbort G., Evans R. L. Identification of a p69,71 complex expressed on human T cells sharing determinants with B-type chronic lymphatic leukemic cells. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1539–1544. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



