Abstract
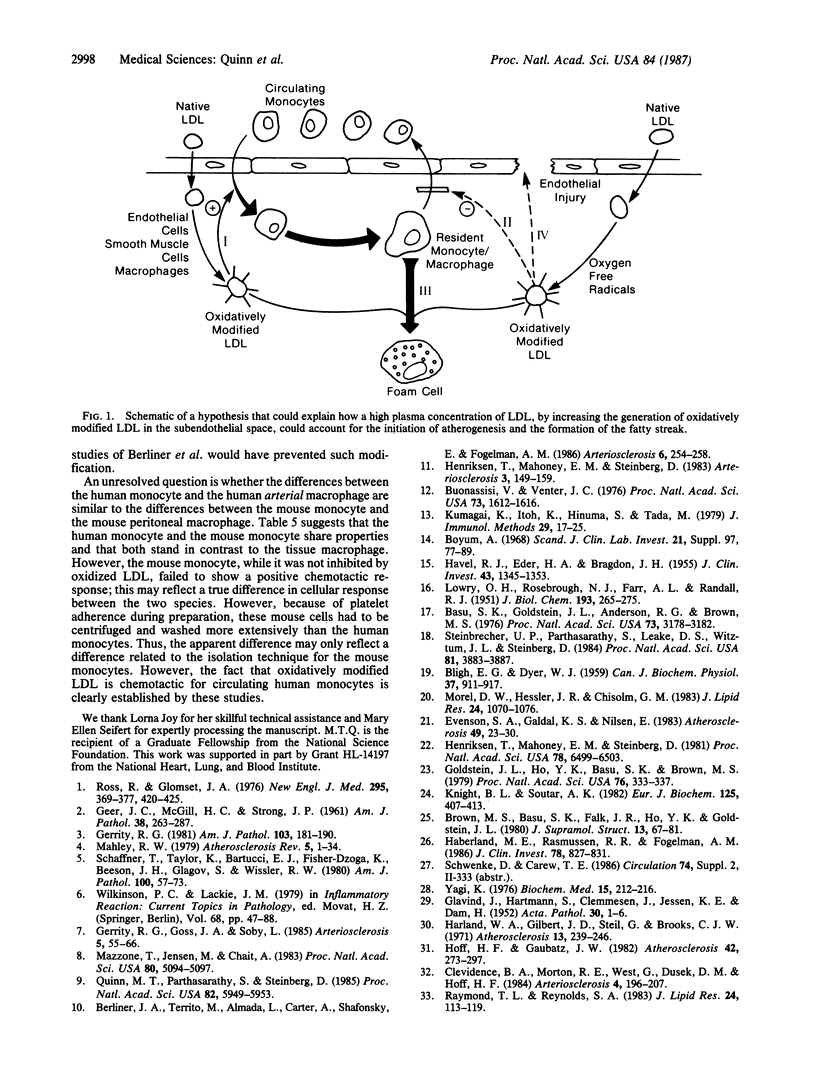
Previous studies in this laboratory established that low density lipoprotein (LDL) incubated with cultured endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, or macrophages undergoes free radical-catalyzed oxidative modification that generates lipid peroxides and extensive structural changes in the LDL molecule. The oxidatively modified LDL strongly inhibited chemotactic responses of the mouse resident peritoneal macrophage. The present studies show that this oxidized LDL does not inhibit the motility of mouse monocytes and actually exhibits a chemotactic activity for human monocytes; the chemotactic activity of the oxidized LDL resides in the lipid fraction. These findings allow us to propose a pathogenetic sequence by which elevated plasma LDL levels, followed by oxidative modification in the arterial wall, could sufficiently account for the generation of the lipid-laden foam cells and the initiation of the fatty streak, the earliest well-defined lesion in atherogenesis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Anderson G. W., Brown M. S. Degradation of cationized low density lipoprotein and regulation of cholesterol metabolism in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3178–3182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner J. A., Territo M., Almada L., Carter A., Shafonsky E., Fogelman A. M. Monocyte chemotactic factor produced by large vessel endothelial cells in vitro. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):254–258. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.3.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Basu S. K., Falck J. R., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. The scavenger cell pathway for lipoprotein degradation: specificity of the binding site that mediates the uptake of negatively-charged LDL by macrophages. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(1):67–81. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonassisi V., Venter J. C. Hormone and neurotransmitter receptors in an established vascular endothelial cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1612–1616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevidence B. A., Morton R. E., West G., Dusek D. M., Hoff H. F. Cholesterol esterification in macrophages. Stimulation by lipoproteins containing apo B isolated from human aortas. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 May-Jun;4(3):196–207. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.3.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evensen S. A., Galdal K. S., Nilsen E. LDL-induced cytotoxicity and its inhibition by anti-oxidant treatment in cultured human endothelial cells and fibroblasts. Atherosclerosis. 1983 Oct;49(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(83)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEER J. C., McGILL H. C., Jr, STRONG J. P. The fine structure of human atherosclerotic lesions. Am J Pathol. 1961 Mar;38:263–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLAVIND J., HARTMANN S., CLEMMESEN J., JESSEN K. E., DAM H. Studies on the role of lipoperoxides in human pathology. II. The presence of peroxidized lipids in the atherosclerotic aorta. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1952;30(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1952.tb00157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity R. G., Goss J. A., Soby L. Control of monocyte recruitment by chemotactic factor(s) in lesion-prone areas of swine aorta. Arteriosclerosis. 1985 Jan-Feb;5(1):55–66. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.5.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrity R. G. The role of the monocyte in atherogenesis: I. Transition of blood-borne monocytes into foam cells in fatty lesions. Am J Pathol. 1981 May;103(2):181–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Ho Y. K., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Binding site on macrophages that mediates uptake and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein, producing massive cholesterol deposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberland M. E., Rasmussen R. R., Fogelman A. M. Receptor recognition of maleyl-albumin induces chemotaxis in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):827–831. doi: 10.1172/JCI112647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland W. A., Gilbert J. D., Steel G., Brooks C. J. Lipids of human atheroma. 5. The occurrence of a new group of polar sterol esters in various stages of human atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1971 Mar-Apr;13(2):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(71)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen T., Mahoney E. M., Steinberg D. Enhanced macrophage degradation of biologically modified low density lipoprotein. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Mar-Apr;3(2):149–159. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen T., Mahoney E. M., Steinberg D. Enhanced macrophage degradation of low density lipoprotein previously incubated with cultured endothelial cells: recognition by receptors for acetylated low density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6499–6503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff H. F., Gaubatz J. W. Isolation, purification, and characterization of a lipoprotein containing Apo B from the human aorta. Atherosclerosis. 1982 Apr;42(2-3):273–297. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(82)90157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight B. L., Soutar A. K. Changes in the metabolism of modified and unmodified low-density lipoproteins during the maturation of cultured blood monocyte-macrophages from normal and homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemic subjects. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jul;125(2):407–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai K., Itoh K., Hinuma S., Tada M. Pretreatment of plastic Petri dishes with fetal calf serum. A simple method for macrophage isolation. J Immunol Methods. 1979;29(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzone T., Jensen M., Chait A. Human arterial wall cells secrete factors that are chemotactic for monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5094–5097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel D. W., Hessler J. R., Chisolm G. M. Low density lipoprotein cytotoxicity induced by free radical peroxidation of lipid. J Lipid Res. 1983 Aug;24(8):1070–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn M. T., Parthasarathy S., Steinberg D. Endothelial cell-derived chemotactic activity for mouse peritoneal macrophages and the effects of modified forms of low density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5949–5953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond T. L., Reynolds S. A. Lipoproteins of the extravascular space: alterations in low density lipoproteins of interstitial inflammatory fluid. J Lipid Res. 1983 Feb;24(2):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J. A. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 19;295(8):420–425. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608192950805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner T., Taylor K., Bartucci E. J., Fischer-Dzoga K., Beeson J. H., Glagov S., Wissler R. W. Arterial foam cells with distinctive immunomorphologic and histochemical features of macrophages. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jul;100(1):57–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrecher U. P., Parthasarathy S., Leake D. S., Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Modification of low density lipoprotein by endothelial cells involves lipid peroxidation and degradation of low density lipoprotein phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3883–3887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K. A simple fluorometric assay for lipoperoxide in blood plasma. Biochem Med. 1976 Apr;15(2):212–216. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(76)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


