Abstract
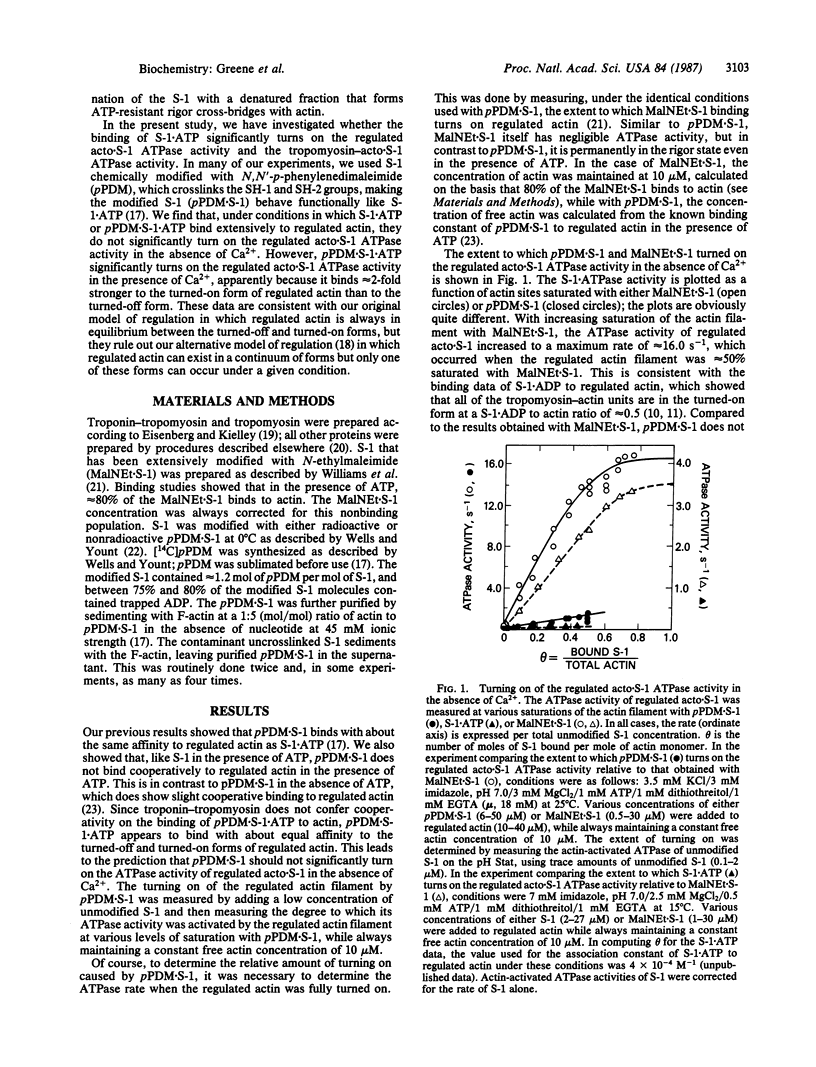
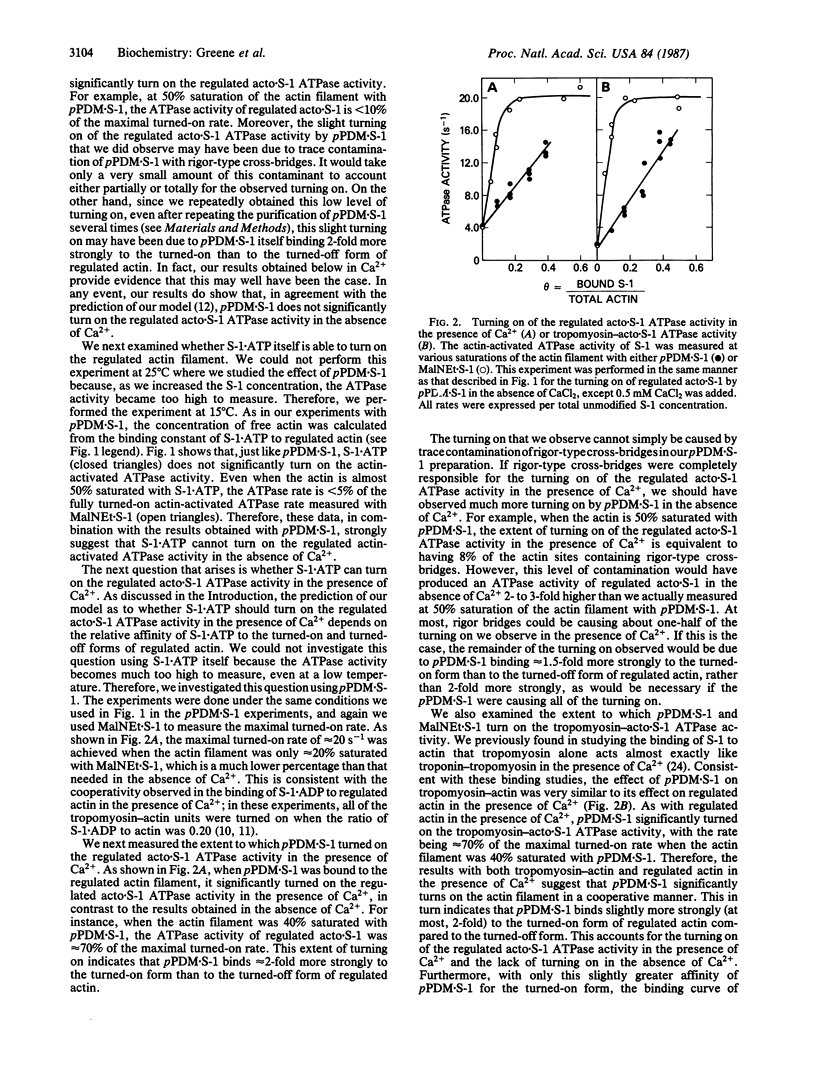
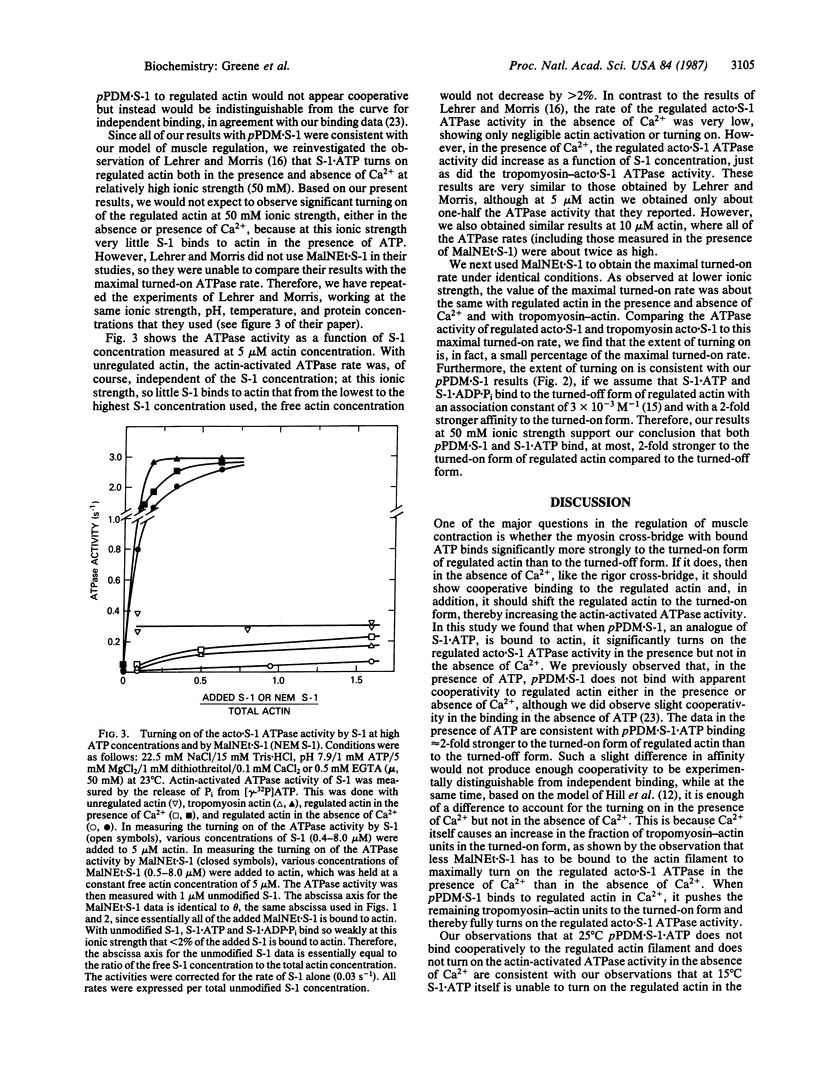
In our model of regulation, the observed lack of cooperativity in the binding of myosin subfragment 1 (S-1) with bound ATP to the troponin-tropomyosin-actin complex (regulated actin) is explained by S-1.ATP having about the same affinity for the conformation of the regulated actin that activates the myosin ATPase activity (turned-on form) and the conformation that does not activate the myosin ATPase activity (turned-off form). This predicts that, in the absence of Ca2+, S-1.ATP should not turn on the regulated actin filament. In the present study, we tested this prediction by using either unmodified S-1 or S-1 chemically modified with N,N'-p-phenylenedimaleimide (pPDM X S-1) so that functionally it acts like S-1.ATP, although it does not hydrolyze ATP. We found that, in the absence of Ca2+, neither S-1.ATP nor pPDM X S-1.ATP significantly turns on the ATPase activity of the regulated complex of actin and S-1 (acto X S-1). In contrast, in the presence of Ca2+, pPDM X S-1.ATP binding almost completely turns on the regulated acto.S-1 ATPase activity. These results can be explained by our original cooperativity model, with pPDM X S-1.ATP binding only approximately equal to 2-fold more strongly to the turned-on form than to the turned-off form of regulated actin. However, our results are not consistent with our alternative model, which predicts that if pPDM X S-1.ATP binds to actin in the absence of Ca2+ but does not turn on the ATPase activity, then it should also not turn on the ATPase activity in the presence of Ca2+.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bremel R. D., Weber A. Cooperation within actin filament in vertebrate skeletal muscle. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):97–101. doi: 10.1038/newbio238097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Schoenberg M., Chalovich J. M., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Evidence for cross-bridge attachment in relaxed muscle at low ionic strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7288–7291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalovich J. M., Chock P. B., Eisenberg E. Mechanism of action of troponin . tropomyosin. Inhibition of actomyosin ATPase activity without inhibition of myosin binding to actin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):575–578. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalovich J. M., Eisenberg E. Inhibition of actomyosin ATPase activity by troponin-tropomyosin without blocking the binding of myosin to actin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2432–2437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalovich J. M., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Crosslinked myosin subfragment 1: a stable analogue of the subfragment-1.ATP complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4909–4913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S. The Croonian lecture, 1979: Regulation of muscle contraction. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Mar 21;207(1168):259–286. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Kielley W. W. Troponin-tropomyosin complex. Column chromatographic separation and activity of the three, active troponin components with and without tropomyosin present. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4742–4748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. E., Chalovich J. M., Eisenberg E. Effect of nucleotide on the binding of N,N'-p-phenylenedimaleimide-modified S-1 to unregulated and regulated actin. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 11;25(3):704–709. doi: 10.1021/bi00351a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Cooperative binding of myosin subfragment-1 to the actin-troponin-tropomyosin complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. The effect of nucleotide on the binding of myosin subfragment 1 to regulated actin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13993–13999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Eisenberg E., Greene L. E. Alternate model for the cooperative equilibrium binding of myosin subfragment-1-nucleotide complex to actin-troponin-tropomyosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):60–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Eisenberg E., Greene L. Theoretical model for the cooperative equilibrium binding of myosin subfragment 1 to the actin-troponin-tropomyosin complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3186–3190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer S. S., Morris E. P. Dual effects of tropomyosin and troponin-tropomyosin on actomyosin subfragment 1 ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8073–8080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. M., Knox M. K., Trueblood C. E., Weber A. Do tropomyosin and myosin compete for actin sites in the presence of calcium? FEBS Lett. 1980 May 19;114(1):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80886-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. M., Knox M. K., Trueblood C. E., Weber A. Potentiated state of the tropomyosin actin filament and nucleotide-containing myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 2;21(5):906–915. doi: 10.1021/bi00534a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. M., Weber A., Knox M. K. Myosin subfragment 1 binding to relaxed actin filaments and steric model of relaxation. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 3;20(3):641–649. doi: 10.1021/bi00506a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuben J. P., Brandt P. W., Berman M., Grundfest H. Regulation of tension in the skinned crayfish muscle fiber. I. Contraction and relaxation in the absence of Ca (pCa is greater than 9). J Gen Physiol. 1971 Apr;57(4):385–407. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.4.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein L. A., Schwarz R. P., Jr, Chock P. B., Eisenberg E. Mechanism of actomyosin adenosine triphosphatase. Evidence that adenosine 5'-triphosphate hydrolysis can occur without dissociation of the actomyosin complex. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 4;18(18):3895–3909. doi: 10.1021/bi00585a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner P. D., Giniger E. Calcium-sensitive binding of heavy meromyosin to regulated actin in the presence of ATP. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12647–12650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Murray J. M. Molecular control mechanisms in muscle contraction. Physiol Rev. 1973 Jul;53(3):612–673. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.3.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Yount R. G. Active site trapping of nucleotides by crosslinking two sulfhydryls in myosin subfragment 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4966–4970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C. Rigor contraction and the effect of various phosphate compounds on glycerinated insect flight and vertebrate muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):583–605. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L., Jr, Greene L. E. Comparison of the effects of tropomyosin and troponin-tropomyosin on the binding of myosin subfragment 1 to actin. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2770–2774. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L., Jr, Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Comparison of effects of smooth and skeletal muscle tropomyosins on interactions of actin and myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4150–4155. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


