Abstract
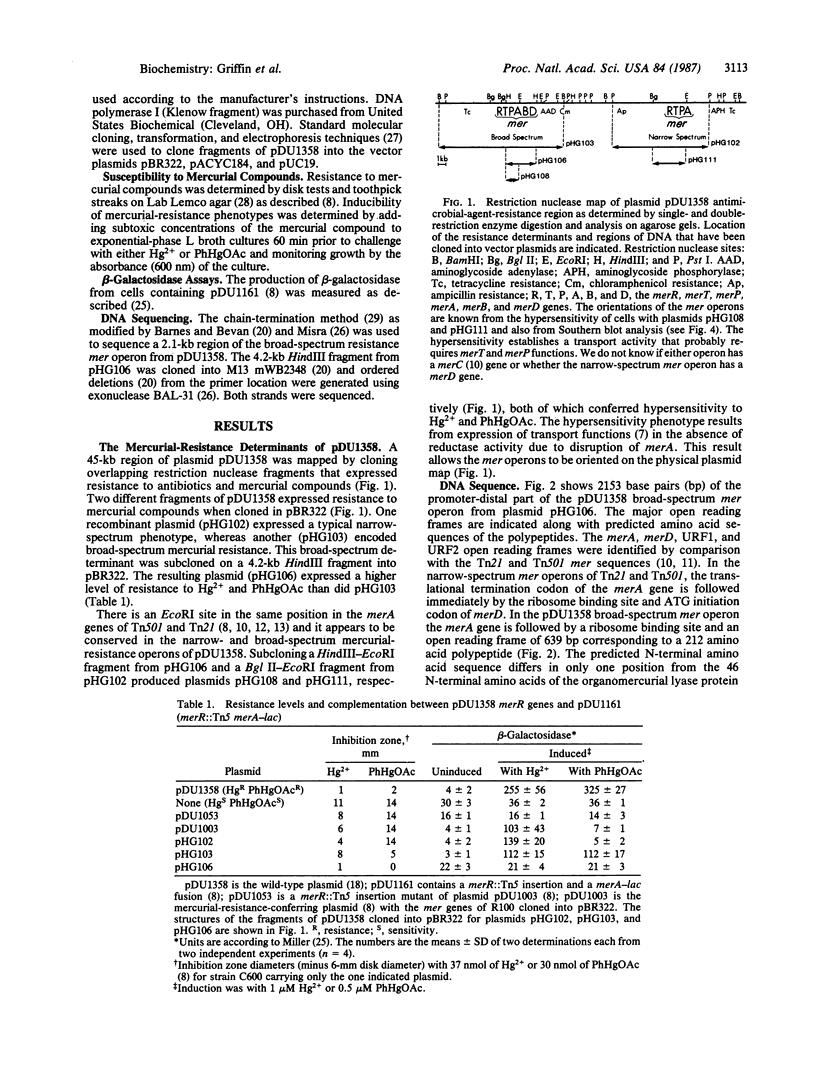
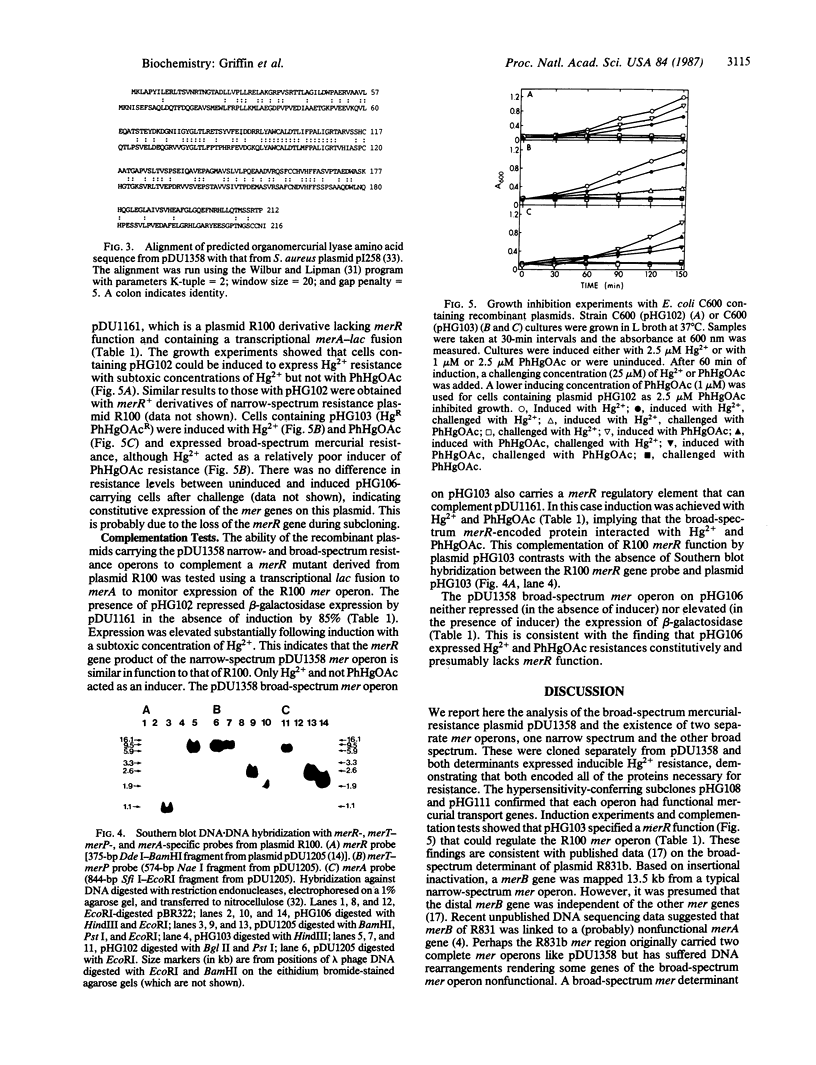
The broad-spectrum mercurial-resistance plasmid pDU1358 was analyzed by cloning the resistance determinants and preparing a physical and genetic map of a 45-kilobase (kb) region of the plasmid that contains two separate mercurial-resistance operons that mapped about 20 kb apart. One encoded narrow-spectrum mercurial resistance to Hg2+ and a few organomercurials; the other specified broad-spectrum resistance to phenylmercury and additional organomercurials. Each determinant governed mercurial transport functions. Southern DNA X DNA hybridization experiments using gene-specific probes from the plasmid R100 mer operon indicated close homology with the R100 determinant. The 2153 base pairs of the promoter-distal part of the broad-spectrum Hg2+-resistance operon of pDU1358 were sequenced. This region included the 3'-terminal part of the merA gene, merD, unidentified reading frame URF1, and a part of URF2 homologous to previously sequenced determinants of plasmid R100. Between the merA and merD genes, an open reading frame encoding a 212 amino acid polypeptide was identified as the merB gene that determines the enzyme organomercurial lyase that cleaves the C--Hg bond of phenylmercury.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes W. M., Bevan M. Kilo-sequencing: an ordered strategy for rapid DNA sequence data acquisition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):349–368. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrineau P., Gilbert P., Jackson W. J., Jones C. S., Summers A. O., Wisdom S. The DNA sequence of the mercury resistance operon of the IncFII plasmid NR1. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(6):601–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begley T. P., Walts A. E., Walsh C. T. Bacterial organomercurial lyase: overproduction, isolation, and characterization. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):7186–7192. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. L., Ford S. J., Pridmore R. D., Fritzinger D. C. Nucleotide sequence of a gene from the Pseudomonas transposon Tn501 encoding mercuric reductase. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 16;22(17):4089–4095. doi: 10.1021/bi00286a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. L., Misra T. K., Winnie J. N., Schmidt A., Seiff M., Silver S. The nucleotide sequence of the mercuric resistance operons of plasmid R100 and transposon Tn501: further evidence for mer genes which enhance the activity of the mercuric ion detoxification system. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jan;202(1):143–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00330531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J., Brown N. L. Identification of the merR gene of R100 by using mer-lac gene and operon fusions. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1153–1157. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1153-1157.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J., Ginnity F. Some mercurial resistance plasmids from different incompatibility groups specify merR regulatory functions that both repress and induce the mer operon of plasmid R100. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):773–776. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.773-776.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J. Plasmid-determined resistance to antimicrobial drugs and toxic metal ions in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):361–409. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.361-409.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J., Walsh A. Phenotypic characterization of R-factor tetracycline resistance determinants. Genet Res. 1974 Dec;24(3):333–343. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300015330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin H. G., Foster T. J., Falkiner F. R., Carr M. E., Coleman D. C. Molecular analysis of multiple-resistance plasmids transferred from gram-negative bacteria isolated in a urological unit. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):413–418. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lett M. C., Bennett P. M., Vidon D. J. Characterization of Tn3926, a new mercury-resistance transposon from Yersinia enterocolitica. Gene. 1985;40(1):79–91. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra T. K., Brown N. L., Fritzinger D. C., Pridmore R. D., Barnes W. M., Haberstroh L., Silver S. Mercuric ion-resistance operons of plasmid R100 and transposon Tn501: the beginning of the operon including the regulatory region and the first two structural genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5975–5979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra T. K., Brown N. L., Haberstroh L., Schmidt A., Goddette D., Silver S. Mercuric reductase structural genes from plasmid R100 and transposon Tn501: functional domains of the enzyme. Gene. 1985;34(2-3):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahara H., Silver S., Miki T., Rownd R. H. Hypersensitivity to Hg2+ and hyperbinding activity associated with cloned fragments of the mercurial resistance operon of plasmid NR1. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):161–166. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.161-166.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni'Bhriain N. N., Silver S., Foster T. J. Tn5 insertion mutations in the mercuric ion resistance genes derived from plasmid R100. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):690–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.690-703.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Murphy E., Gryczan T. J., Baron E., Edelman I. Penicillinase plasmids of Staphylococcus aureus: restriction-deletion maps. Plasmid. 1979 Jan;2(1):109–129. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa H. I., Tolle C. L., Summers A. O. Physical and genetic map of the organomercury resistance (Omr) and inorganic mercury resistance (Hgr) loci of the IncM plasmid R831b. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):311–320. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radford A. J., Oliver J., Kelly W. J., Reanney D. C. Translocatable resistance to mercuric and phenylmercuric ions in soil bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):1110–1112. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.1110-1112.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stüber D., Bujard H. Organization of transcriptional signals in plasmids pBR322 and pACYC184. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers A. O. Organization, expression, and evolution of genes for mercury resistance. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:607–634. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers A. O., Silver S. Microbial transformations of metals. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:637–672. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




