Abstract
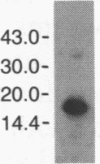
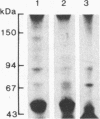
We compared the molecular structure of the receptor to human recombinant tumor necrosis factor (HurTNF) on cells of different tissue origin that differ in their response to one of the known activities of TNF. We studied tumor cell lines that respond to the cytotoxic action of TNF and resistant variants that bind TNF, normal cell lines that are stimulated to proliferate by TNF and those that are not affected by TNF, and peripheral blood granulocytes whose activation is also augmented by TNF. Using 125I-labeled HurTNF, we found that it bound mainly to four cellular polypeptides (138, 90, 75, and 54 kDa), three of which were found in every cell type examined and one (138 kDa) that was observed only in a human breast carcinoma cell line (MCF-7) that is highly responsive to the cytotoxic action of TNF. The 138-kDa polypeptide was not found in resistant variants of MCF-7 that bind TNF. In contrast to the other polypeptides, the 138-kDa protein was detected 30 min after incubation at 4 degrees C, as compared to 5 min. Scatchard analysis and cross-linking data suggest a model for the TNF receptor structure whereby the receptor is composed of noncovalently linked membrane-bound polypeptides that bind TNF with high affinity (Kd, 0.05-0.8 X 10(-9) M) with the 138-kDa protein being the least abundant and/or even absent in most cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiyer R. A. Structural characterization of insulin receptors. II. Subunit composition of receptors from turkey erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15000–15003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C., McCandless S., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Binding of human tumor necrosis factor to high affinity receptors on HeLa and lymphoblastoid cells sensitive to growth inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13395–13397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creasey A. A., Doyle L. V., Reynolds M. T., Jung T., Lin L. S., Vitt C. R. Biological effects of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor and its novel muteins on tumor and normal cell lines. Cancer Res. 1987 Jan 1;47(1):145–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creasey A. A., Reynolds M. T., Laird W. Cures and partial regression of murine and human tumors by recombinant human tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Res. 1986 Nov;46(11):5687–5690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Hollenberg M. D. Membrane receptors and hormone action. Adv Protein Chem. 1976;30:251–451. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60481-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower S. K., Call S. M., Gillis S., Urdal D. L. Similarity between the interleukin 1 receptors on a murine T-lymphoma cell line and on a murine fibroblast cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1060–1064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. R., Harlan J. M., Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A. Stimulation of the adherence of neutrophils to umbilical vein endothelium by human recombinant tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8667–8671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Dobrjansky A., Chiasson M. A., Carswell E., Schwartz M. K., Old L. J. Corynebacterium parvum as the priming agent in the production of tumor necrosis factor in the mouse. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Nov;59(5):1519–1522. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.5.1519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haranaka K., Satomi N. Cytotoxic activity of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) on human cancer cells in vitro. Jpn J Exp Med. 1981 Jun;51(3):191–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haranaka K., Satomi N., Sakurai A. Antitumor activity of murine tumor necrosis factor (TNF) against transplanted murine tumors and heterotransplanted human tumors in nude mice. Int J Cancer. 1984 Aug 15;34(2):263–267. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910340219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hass P. E., Hotchkiss A., Mohler M., Aggarwal B. B. Characterization of specific high affinity receptors for human tumor necrosis factor on mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12214–12218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel S., Hahn T., Holtmann H., Wallach D. Binding of human TNF-alpha to high-affinity cell surface receptors: effect of IFN. Immunol Lett. 1986 Apr;12(4):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(86)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Cellular receptor for 125I-labeled tumor necrosis factor: specific binding, affinity labeling, and relationship to sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5756–5760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Graham D., Toy K., Lin L. S., Senyk G., Fendly B. M. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor causes activation of human granulocytes. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):640–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Aggarwal B. B., Rinderknecht E., Assisi F., Chiu H. The synergistic anti-proliferative effect of gamma-interferon and human lymphotoxin. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1083–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann V., Dröge W. Demonstration of membrane receptors for human natural and recombinant 125I-labeled tumor necrosis factor on HeLa cell clones and their role in tumor cell sensitivity. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jul 1;158(1):1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09712.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A. A new solid-state reagent to iodinate proteins. I. Conditions for the efficient labeling of antiserum. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 15;125(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Subunit structure of a high-affinity receptor for type beta-transforming growth factor. Evidence for a disulfide-linked glycosylated receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7059–7066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N., Watkins J. F. Tumour-necrosis factor from the rabbit. I. Mode of action, specificity and physicochemical properties. Br J Cancer. 1978 Aug;38(2):302–309. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1978.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B. Y., Anderson S. L., Sullivan S. A., Williamson B. D., Carswell E. A., Old L. J. High affinity binding of 125I-labeled human tumor necrosis factor (LuKII) to specific cell surface receptors. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1099–1104. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheurich P., Ucer U., Krönke M., Pfizenmaier K. Quantification and characterization of high-affinity membrane receptors for tumor necrosis factor on human leukemic cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1986 Jul 15;38(1):127–133. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Aggarwal B. B., Rinderknecht E., Svedersky L. P., Finkle B. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2069–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon M., Klausner R. D., Cullen B. R., Chizzonite R., Leonard W. J. Novel interleukin-2 receptor subunit detected by cross-linking under high-affinity conditions. Science. 1986 Nov 14;234(4778):859–863. doi: 10.1126/science.3095922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Feinman R., Kohase M., Vilcek J. Characterization and affinity crosslinking of receptors for tumor necrosis factor on human cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Sep;249(2):563–568. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Feinman R., Vilcek J. Differential effects of type I IFN and IFN-gamma on the binding of tumor necrosis factor to receptors in two human cell lines. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2272–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor: specific binding and internalization in sensitive and resistant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7626–7630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandlen R. L., Arcuri K. E., Napier M. A. Identification of a receptor for atrial natriuretic factor in rabbit aorta membranes by affinity cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):10889–10892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Palombella V. J., Henriksen-DeStefano D., Swenson C., Feinman R., Hirai M., Tsujimoto M. Fibroblast growth enhancing activity of tumor necrosis factor and its relationship to other polypeptide growth factors. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):632–643. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Creasey A. A., Ladner M. B., Lin L. S., Strickler J., Van Arsdell J. N., Yamamoto R., Mark D. F. Molecular cloning of the complementary DNA for human tumor necrosis factor. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):149–154. doi: 10.1126/science.3856324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson B. D., Carswell E. A., Rubin B. Y., Prendergast J. S., Old L. J. Human tumor necrosis factor produced by human B-cell lines: synergistic cytotoxic interaction with human interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5397–5401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]