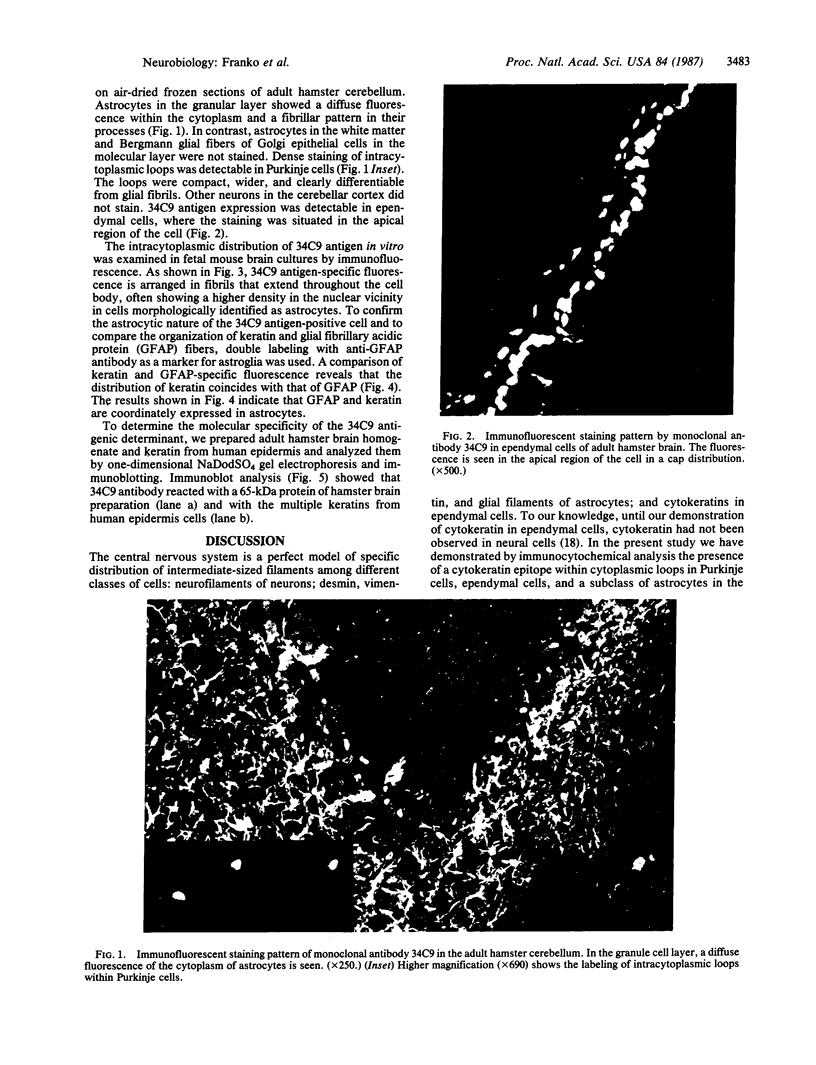
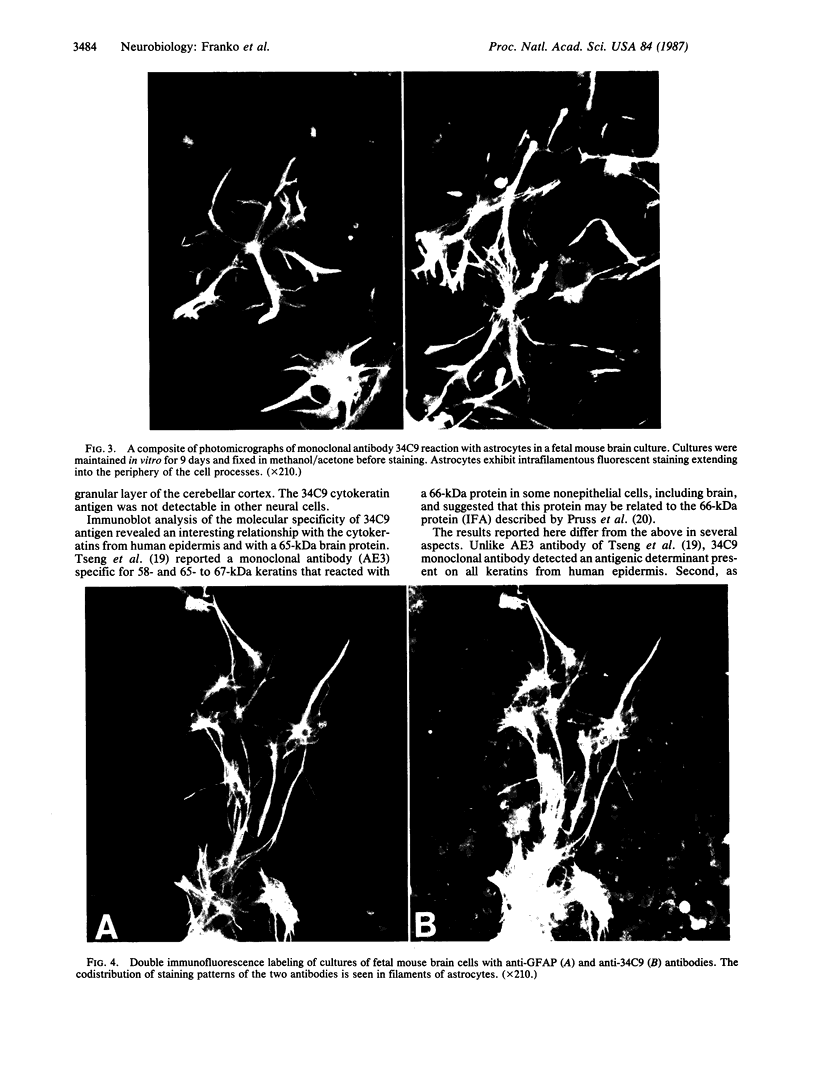
Abstract
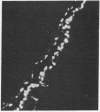
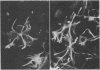
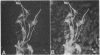
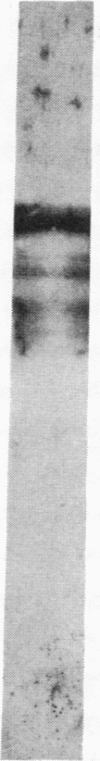
A monoclonal antibody directed against a 65-kDa brain protein demonstrates an epitope found in keratin from human epidermis. By indirect immunofluorescence, the antibody decorates intracytoplasmic filaments in a subclass of astrocytes and Purkinje cells of adult hamster brain. Double-label immunofluorescence study using antibody to glial fibrillary acidic protein and this antibody reveals the 65-kDa protein to be closely associated with glial filaments in astrocytes of fetal mouse brain cultures. Immunoblot analysis of purified human epidermal keratin and hamster brain homogenate confirms the reactivity of this antibody to epidermal keratin polypeptides. All the major epidermal keratins were recognized by this antibody. It did not bind to the remaining major intermediate filament proteins. These findings suggest that monoclonal antibody 34C9 recognizes a cytoskeletal structure connected with intermediate filaments. In addition, the monoclonal antibody demonstrates that epidermal keratins share an epitope not only among themselves but also with a "neural keratin."
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes L. D., Roberson G. M. Tubulin and microtubules from bovine kidney: purification, properties, and characterization of ligand binding. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Sep;196(2):511–524. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90303-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale B. A., Resing K. A., Lonsdale-Eccles J. D. Filaggrin: a keratin filament associated protein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:330–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50420.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert B. S., Daley R. A., Parysek L. M. Assembly of keratin onto PtK1 cytoskeletons: evidence for an intermediate filament organizing center. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):575–578. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Moll R., Winter S., Schmid E., Engelbrecht I., Denk H., Krepler R., Platzer B. Diversity of cytokeratins. Differentiation specific expression of cytokeratin polypeptides in epithelial cells and tissues. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 25;153(4):933–959. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franko M. C., Koski C. L., Gibbs C. J., Jr, McFarlin D. E., Gajdusek D. C. Monoclonal antibody specific for myelin glycoprotein P0: derivation and characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3618–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franko M. C., Masters C. L., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Monoclonal antibodies to central nervous system antigens. J Neuroimmunol. 1981 Dec;1(4):391–411. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(81)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R., Goldman A., Green K., Jones J., Lieska N., Yang H. Y. Intermediate filaments: possible functions as cytoskeletal connecting links between the nucleus and the cell surface. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:1–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennett R. H., Denis K. A., Tung A. S., Klinman N. R. Hybrid plasmacytoma production: fusions with adult spleen cells, monoclonal spleen fragments, neonatal spleen cells and human spleen cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:77–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D. Biochemistry of actomyosin-dependent cell motility (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):588–599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Howe S. C., Milstein C. Fusion between immunoglobulin-secreting and nonsecreting myeloma cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Apr;6(4):292–295. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., McDonald B. L., Lagenauer C., Schachner M., Franko M. C. Loop arrays in mouse brain demonstrated with antisera to cytokeratins and monoclonal antibodies to several classes of intermediate filaments: strain differences and developmental expression. Brain Res. 1985 May 20;334(2):267–279. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Krepler R., Franke W. W. Complex cytokeratin polypeptide patterns observed in certain human carcinomas. Differentiation. 1983;23(3):256–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1982.tb01291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napolitano E. W., Pachter J. S., Chin S. S., Liem R. K. beta-Internexin, a ubiquitous intermediate filament-associated protein. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1323–1331. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachter J. S., Liem R. K. alpha-Internexin, a 66-kD intermediate filament-binding protein from mammalian central nervous tissues. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1316–1322. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Mirsky R., Raff M. C., Thorpe R., Dowding A. J., Anderton B. H. All classes of intermediate filaments share a common antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo J., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C., Toh B. H., Wurth M. Method for preparing cultures of central neurons: cytochemical and immunochemical studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng S. C., Jarvinen M. J., Nelson W. G., Huang J. W., Woodcock-Mitchell J., Sun T. T. Correlation of specific keratins with different types of epithelial differentiation: monoclonal antibody studies. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90234-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Cairncross J. G., Yung W. K., Garber E. A., Liem R. K. An intermediate filament-associated protein, p50, recognized by monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1507–1514. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]