Abstract
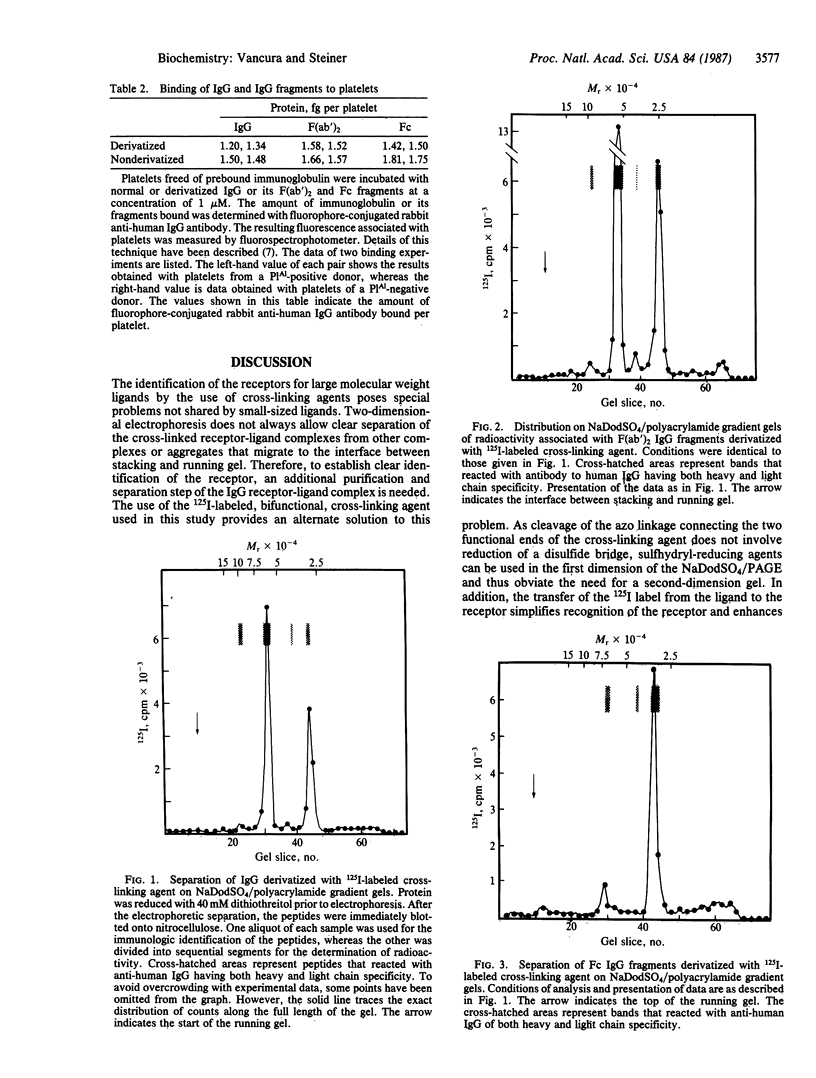
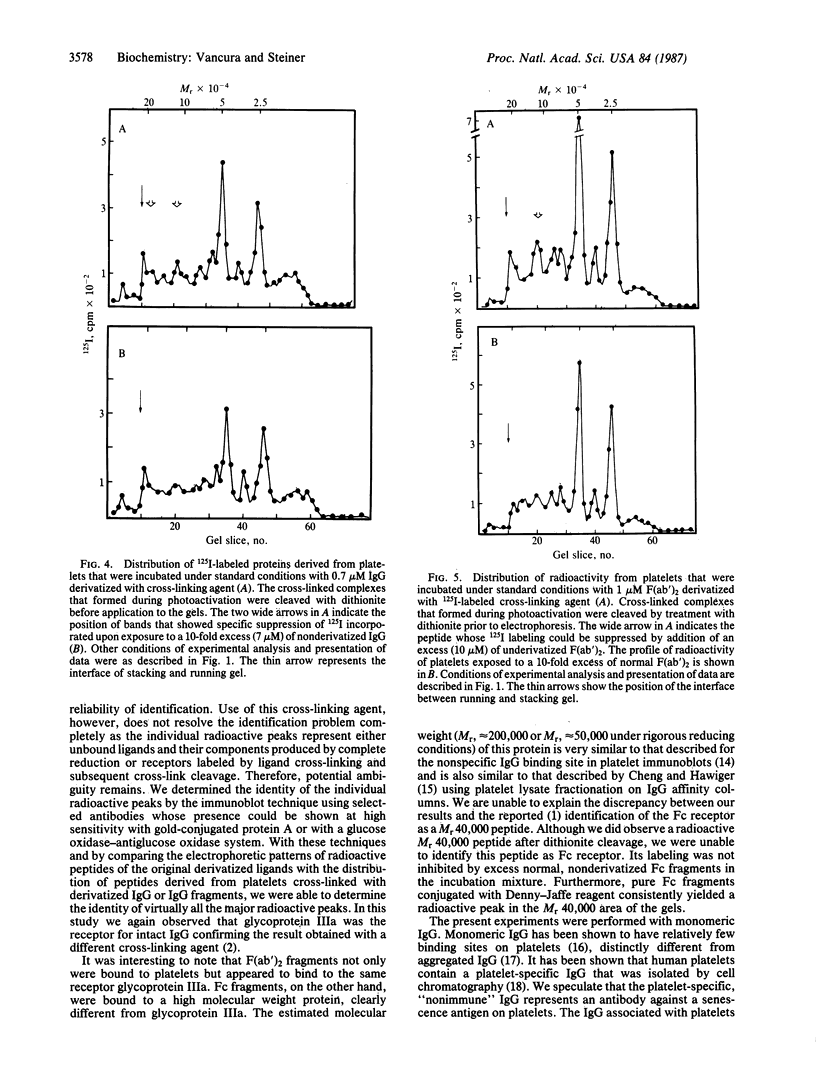
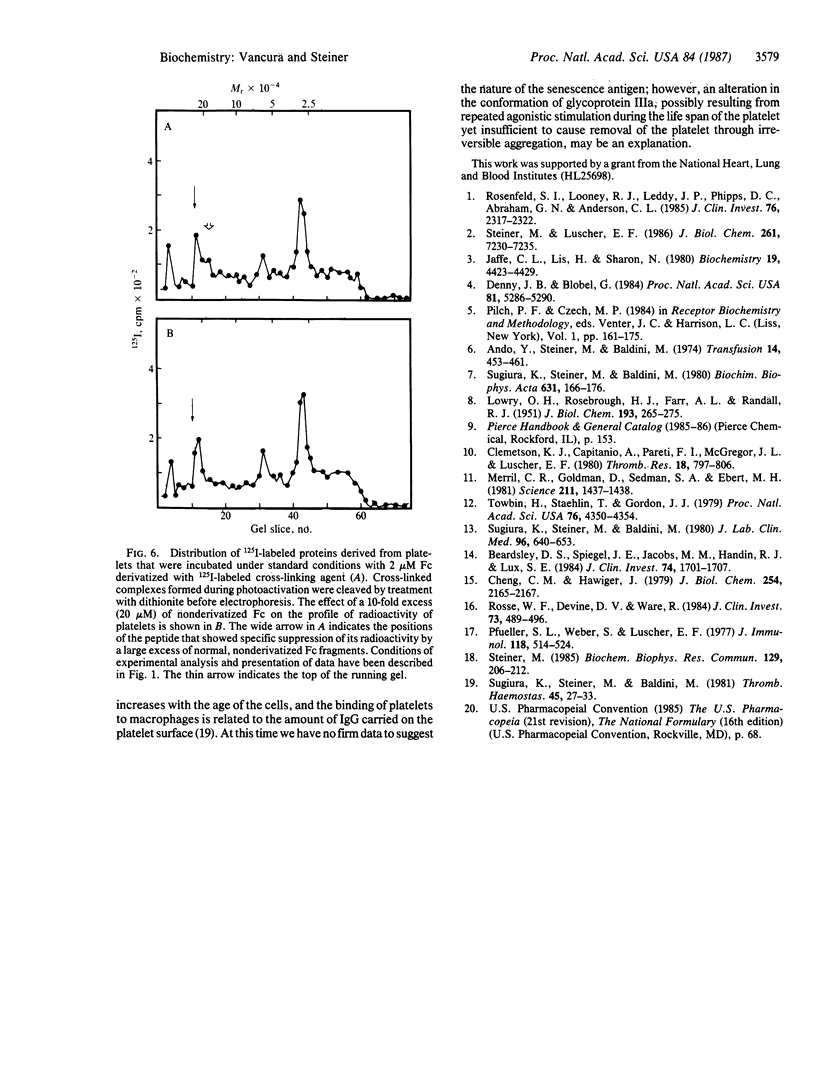
The human platelet receptors for normal, nonimmune IgG and its F(ab')2 and Fc fragments were studied by the use of a cleavable, bifunctional, photoactivable, 125I-labeled cross-linking agent. Derivatization of the ligands with N-[4-(p-azido-m-[125I]iodophenylazo) benzoyl]-3-aminopropyl-N'-oxysuccinimide ester (Denny-Jaffe reagent) reduced their binding to platelets by greater than or equal to 20%. Cleavage of the azo linkage of the Denny-Jaffe reagent, which splits the molecule so that its 125I-labeled portion becomes associated with the receptor half of the cross-linked ligand-receptor complex, was utilized to directly identify receptors for the various immunoglobulin ligands. Specificity of the binding reaction could be demonstrated by suppressing the iodination of the receptors with excess nonderivatized ligand. Two principal IgG-related receptors could be identified by high-resolution NaDodSO4/PAGE and subsequent analysis of the electrophoretically transferred peptides to nitrocellulose filters for localization of radioactivity and immunological characterization. Intact monomeric IgG and F(ab')2 fragments derived from it appeared to have the glycoprotein IIIa as the major receptor, whereas Fc fragments bound predominantly to a peptide of Mr approximately 200,000 (Mr, approximately 50,000 under rigorous reducing conditions).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando Y., Steiner M., Baldini M. Effect of chilling on membrane related functions of platelets. Transfusion. 1974 Sep-Oct;14(5):453–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1974.tb04560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beardsley D. S., Spiegel J. E., Jacobs M. M., Handin R. I., Lux S. E., 4th Platelet membrane glycoprotein IIIa contains target antigens that bind anti-platelet antibodies in immune thrombocytopenias. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1701–1707. doi: 10.1172/JCI111587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng C. M., Hawiger J. Affinity isolation and characterization of immunoglobulin G Fc fragment-binding glycoprotein from human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2165–2167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemetson K. J., Capitanio A., Pareti F. I., McGregor J. L., Lüscher E. F. Additional platelet membrane glycoprotein abnormalities in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia: A comparison with normals by high resolution two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Thromb Res. 1980 Jun 15;18(6):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny J. B., Blobel G. 125I-labeled crosslinking reagent that is hydrophilic, photoactivatable, and cleavable through an azo linkage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5286–5290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe C. L., Lis H., Sharon N. New clevable photoreactive heterobifunctional cross-linking reagents for studying membrane organization. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 16;19(19):4423–4429. doi: 10.1021/bi00560a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfueller S. L., Weber S., Lüscher E. F. Studies of the mechanism of the human platelet release reaction induced by immunologic stimuli. III. Relationship between the binding of soluble IgG aggregates to the Fc receptor and cell response in the presence and absence of plasma. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):514–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. I., Looney R. J., Leddy J. P., Phipps D. C., Abraham G. N., Anderson C. L. Human platelet Fc receptor for immunoglobulin G. Identification as a 40,000-molecular-weight membrane protein shared by monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2317–2322. doi: 10.1172/JCI112242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Devine D. V., Ware R. Reactions of immunoglobulin G-binding ligands with platelets and platelet-associated immunoglobulin G. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):489–496. doi: 10.1172/JCI111235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner M., Lüscher E. F. Identification of the immunoglobulin G receptor of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7230–7235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner M. Platelet-associated IgG is a specific protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 31;129(1):206–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura K., Steiner M., Baldini M. G. Platelet antibody in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and other thrombocytopenias. A quantitative, sensitive, and rapid assay. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Oct;96(4):640–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura K., Steiner M., Baldini M. Charcterization and measurement of normal platelet-associated immunoglobulin G by fluorospectrophotometry. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 1;631(1):166–176. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90064-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura K., Steiner M., Baldini M. Physiological effects of nonimmune platelet associated immunoglobulin G. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Feb 23;45(1):27–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


