Abstract
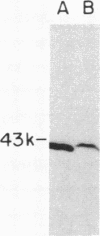
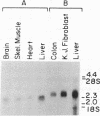
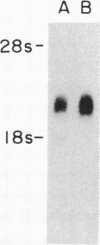
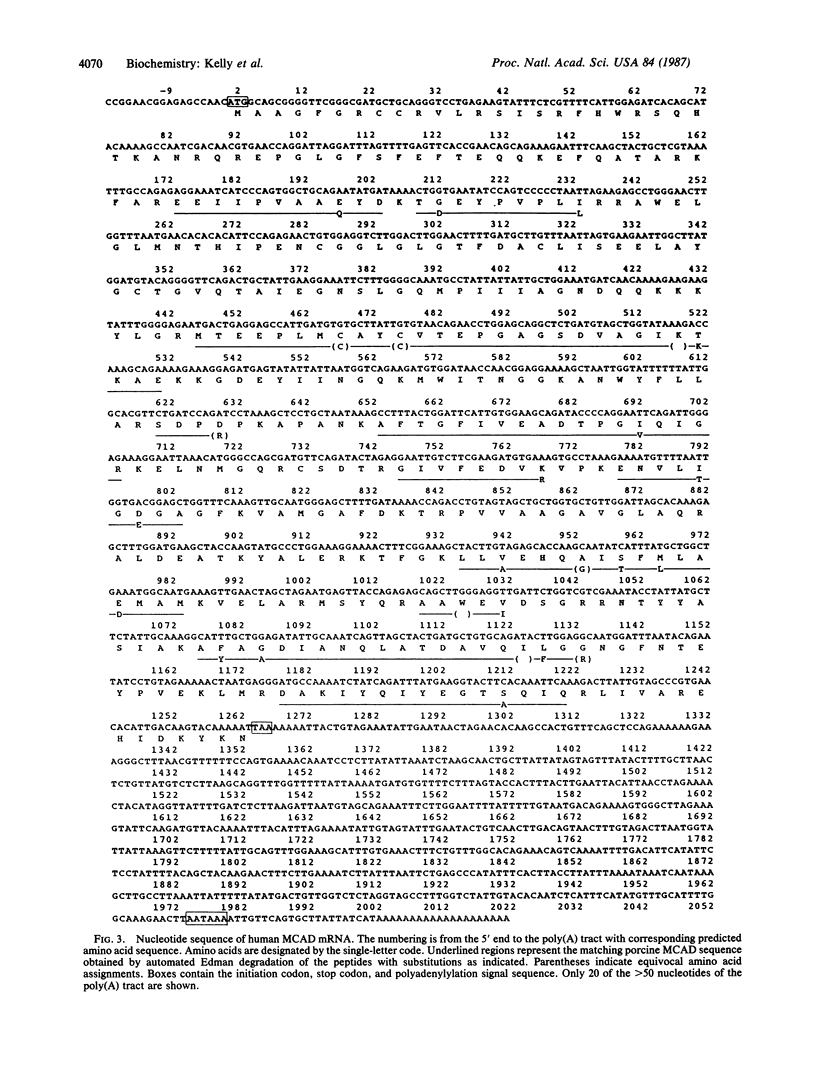
Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD; acyl-CoA: (acceptor) 2,3-oxidoreductase, EC 1.3.99.3) is one of three similar enzymes that catalyze the initial step of fatty acid beta-oxidation. Definition of the primary structure of MCAD and the tissue distribution of its mRNA is of biochemical and clinical importance because of the recent recognition of inherited MCAD deficiency in humans. The MCAD mRNA nucleotide sequence was determined from two overlapping cDNA clones isolated from human liver and placental cDNA libraries, respectively. The MCAD mRNA includes a 1263-base-pair coding region and a 738-base-pair 3'-nontranslated region. A partial amino acid sequence (137 residues) determined on peptides derived from MCAD purified from porcine liver confirmed the identity of the cDNA clone. Comparison of the amino acid sequence predicted from the human MCAD cDNA with the partial protein sequence of the porcine MCAD revealed a high degree (88%) of interspecies sequence identity. RNA blot analysis shows that MCAD mRNA is expressed in a variety of rat (2.2 kilobases) and human (2.4 kilobases) tissues. Blot hybridization of RNA prepared from cultured skin fibroblasts from a patient with MCAD deficiency disclosed that mRNA was present and of similar size to MCAD mRNA derived from control fibroblasts. The isolation and characterization of MCAD cDNA is an important step in the definition of the defect underlying MCAD deficiency and in understanding its metabolic consequences.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Billadello J. J., Roman D. G., Grace A. M., Sobel B. E., Strauss A. W. The nature of post-translational formation of MM creatine kinase isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):14988–14992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bougnères P. F., Rocchiccioli F., Kølvraa S., Hadchouel M., Lalau-Keraly J., Chaussain J. L., Wadman S. K., Gregersen N. Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency in two siblings with a Reye-like syndrome. J Pediatr. 1985 Jun;106(6):918–921. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates P. M., Hale D. E., Stanley C. A., Corkey B. E., Cortner J. A. Genetic deficiency of medium-chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase: studies in cultured skin fibroblasts and peripheral mononuclear leukocytes. Pediatr Res. 1985 Jul;19(7):671–676. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198507000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., WATTIAUX R., BAUDHUIN P. Distribution of enzymes between subcellular fractions in animal tissues. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1962;24:291–358. doi: 10.1002/9780470124888.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B., Schulz H. Separation, properties, and regulation of acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenases from bovine heat and liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Jan;213(1):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90450-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillmann W. H., Barrieux A., Neeley W. E., Contreras P. Influence of thyroid hormone on the in vitro translational activity of specific mRNAs in the rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7738–7745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divry P., David M., Gregersen N., Kølvraa S., Christensen E., Collet J. P., Dellamonica C., Cotte J. Dicarboxylic aciduria due to medium chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase defect. A cause of hypoglycemia in childhood. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1983 Nov;72(6):943–949. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1983.tb09849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D. Three-dimensional structure of membrane and surface proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:595–623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frerman F. E., Goodman S. I. Fluorometric assay of acyl-CoA dehydrogenases in normal and mutant human fibroblasts. Biochem Med. 1985 Feb;33(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(85)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta S., Miyazawa S., Hashimoto T. Purification and properties of rat liver acyl-CoA dehydrogenases and electron transfer flavoprotein. J Biochem. 1981 Dec;90(6):1739–1750. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Smith D. P., Andy R., Alpers D. H., Schonfeld G., Strauss A. W. The primary translation product of rat intestinal apolipoprotein A-I mRNA is an unusual preproprotein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):971–978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale D. E., Batshaw M. L., Coates P. M., Frerman F. E., Goodman S. I., Singh I., Stanley C. A. Long-chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency: an inherited cause of nonketotic hypoglycemia. Pediatr Res. 1985 Jul;19(7):666–671. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198507000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. L., Heijkenskjöld L., Bártfai T., Ernster L., Kamin H. Acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenases and electron-transferring flavoprotein from beef hart mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Dec;177(2):402–414. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90453-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. L., Kamin H. The purification and some properties of electron transfer flavoprotein and general fatty acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase from pig liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3476–3486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda Y., Hale D. E., Keese S. M., Coates P. M., Tanaka K. Biosynthesis of variant medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase in cultured fibroblasts from patients with medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Pediatr Res. 1986 Sep;20(9):843–847. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198609000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda Y., Okamura-Ikeda K., Tanaka K. Purification and characterization of short-chain, medium-chain, and long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenases from rat liver mitochondria. Isolation of the holo- and apoenzymes and conversion of the apoenzyme to the holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1311–1325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara Y., Kraus J. P., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Rosenberg L. E., Tanaka K. Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding rat and human medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase and assignment of the gene to human chromosome 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6543–6547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhead W. J., Amendt B. A., Fritchman K. S., Felts S. J. Dicarboxylic aciduria: deficient [1-14C]octanoate oxidation and medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase in fibroblasts. Science. 1983 Jul 1;221(4605):73–75. doi: 10.1126/science.6857268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice D. W., Schulz G. E., Guest J. R. Structural relationship between glutathione reductase and lipoamide dehydrogenase. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 15;174(3):483–496. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90332-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Edmundson A. B. Use of helical wheels to represent the structures of proteins and to identify segments with helical potential. Biophys J. 1967 Mar;7(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86579-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley C. A., Hale D. E., Coates P. M., Hall C. L., Corkey B. E., Yang W., Kelley R. I., Gonzales E. L., Williamson J. R., Baker L. Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency in children with non-ketotic hypoglycemia and low carnitine levels. Pediatr Res. 1983 Nov;17(11):877–884. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198311000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe C., Matthews R. G., Williams C. H., Jr Acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase from pig kidney. Purification and properties. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 23;18(2):331–337. doi: 10.1021/bi00569a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull D. M., Bartlett K., Stevens D. L., Alberti K. G., Gibson G. J., Johnson M. A., McCulloch A. J., Sherratt H. S. Short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency associated with a lipid-storage myopathy and secondary carnitine deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 8;311(19):1232–1236. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411083111906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Mitochondrial targeting sequences may form amphiphilic helices. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1335–1342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]