Abstract
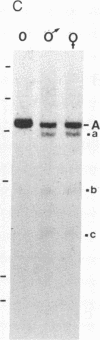
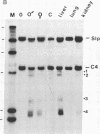
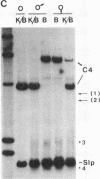
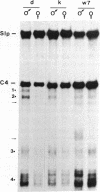
There are four major regions of DNase I hypersensitivity in the 5' regions of the genes for the murine fourth component of complement (C4) and its homologous neighbor, Slp (sex-limited protein). Hypersensitivity around the start site of transcription and approximately equal to 0.5 kilobases upstream correlates qualitatively with expression of these genes. Two hypersensitive sites, at -2.3 and -2.0 kilobases, map specifically to the Slp gene and correlate with its hormonal regulation. That is, these sites are more prominent in male liver chromatin and become more apparent in chromatin from females treated with testosterone. Further, these sites are established in males to a greater extent than in females prior to expression of Slp and may reflect gene-commitment events. Comparison of chromatin from mouse strains differing in C4 and Slp alleles indicates that the four regions of hypersensitivity may be necessary but are not sufficient for high levels of expression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babiss L. E., Bennett A., Friedman J. M., Darnell J. E., Jr DNase I-hypersensitive sites in the 5'-flanking region of the rat serum albumin gene: correlation between chromatin structure and transcriptional activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6504–6508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Weintraub H. Temporal order of chromatin structural changes associated with activation of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. D., Woods D. E., Whitehead A. S., Goldberger G., Colten H. R., Seidman J. G. Molecular map of the murine S region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6947–6951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danoff T. M., Goldman M. B., Goldman J. N. Murine sex-limited protein expression requires androgens and pituitary hormones. Immunogenetics. 1986;23(1):7–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00376515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg J. C., Cartwright I. L., Thomas G. H., Elgin S. C. Selected topics in chromatin structure. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:485–536. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of chromatin. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Lewis C. D., Felsenfeld G. Interaction of specific nuclear factors with the nuclease-hypersensitive region of the chicken adult beta-globin gene: nature of the binding domain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Eichinger D., Nussenzweig V. The murine sex-limited protein (Slp): reassessment of its sex limitation. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1506–1508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritton H. P., Sippel A. E., Igo-Kemenes T. Nuclease-hypersensitive sites in the chromatin domain of the chicken lysozyme gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3467–3485. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T. H., Shreffler D. C. Characterization of a constitutive variant of the murine serum protein allotype, Slp. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1507–1513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemenway C., Kalff M., Stavenhagen J., Walthall D., Robins D. Sequence comparison of alleles of the fourth component of complement (C4) and sex-limited protein (Slp). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2539–2554. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Strauss M., Tosi M., Steinmetz M., Klein J., Meo T. Multiple duplications of complement C4 gene correlate with H-2-controlled testosterone-independent expression of its sex-limited isoform, C4-Slp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1746–1750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Kimura H., Yeul Y. D., Yokoyama S., Nakayama K., Takahashi M. Identification of the 5'-flanking regulatory region responsible for the difference in transcriptional control between mouse complement C4 and Slp genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7883–7887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Takahashi M., Natsuume-Sakai S., Nonaka M., Tanaka S., Shimizu A., Honjo T. Isolation of cDNA clones specifying the fourth component of mouse complement and its isotype, sex-limited protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6822–6826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R. T., Sepich D. S. Genes for murine fourth complement component (C4) and sex-limited protein (Slp) identified by hybridization to C4- and Slp-specific cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4908–4911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R. T., Sepich D. S. Murine sex-limited protein: complete cDNA sequence and comparison with murine fourth complement component. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4239–4244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to the regulatory site of an hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore H. C., Shreffler D. C. A sex-limited serum protein variant in the mouse: hormonal control of phenotypic expression. Biochem Genet. 1971 Apr;5(2):201–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00485645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R., Schütz G., von der Ahe D., Beato M. Sequences in the promoter region of the chicken lysozyme gene required for steroid regulation and receptor binding. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins D. M., Malissen M., Hood L., Ferreira A., Walthall D., Mitchell M. Multiple C4/Slp genes distinguished by expression after transfection. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):134–141. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sepich D. S., Noonan D. J., Ogata R. T. Complete cDNA sequence of the fourth component of murine complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5895–5899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreffler D. C. The S region of the mouse major histocompatibility complex (H-2): genetic variation and functional role in complement system. Transplant Rev. 1976;32:140–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavenhagen J., Loreni F., Hemenway C., Kalff M., Robins D. M. Molecular genetics of androgen-dependent and -independent expression of mouse sex-limited protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1716–1724. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock R., Sweet R., Weiss M., Cedar H., Axel R. Intragenic DNA spacers interrupt the ovalbumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1299–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Activating protein factor binds in vitro to upstream control sequences in heat shock gene chromatin. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):81–84. doi: 10.1038/311081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Yamamoto K. R. Reversible and persistent changes in chromatin structure accompany activation of a glucocorticoid-dependent enhancer element. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90523-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]