Abstract
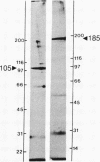
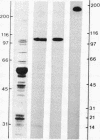
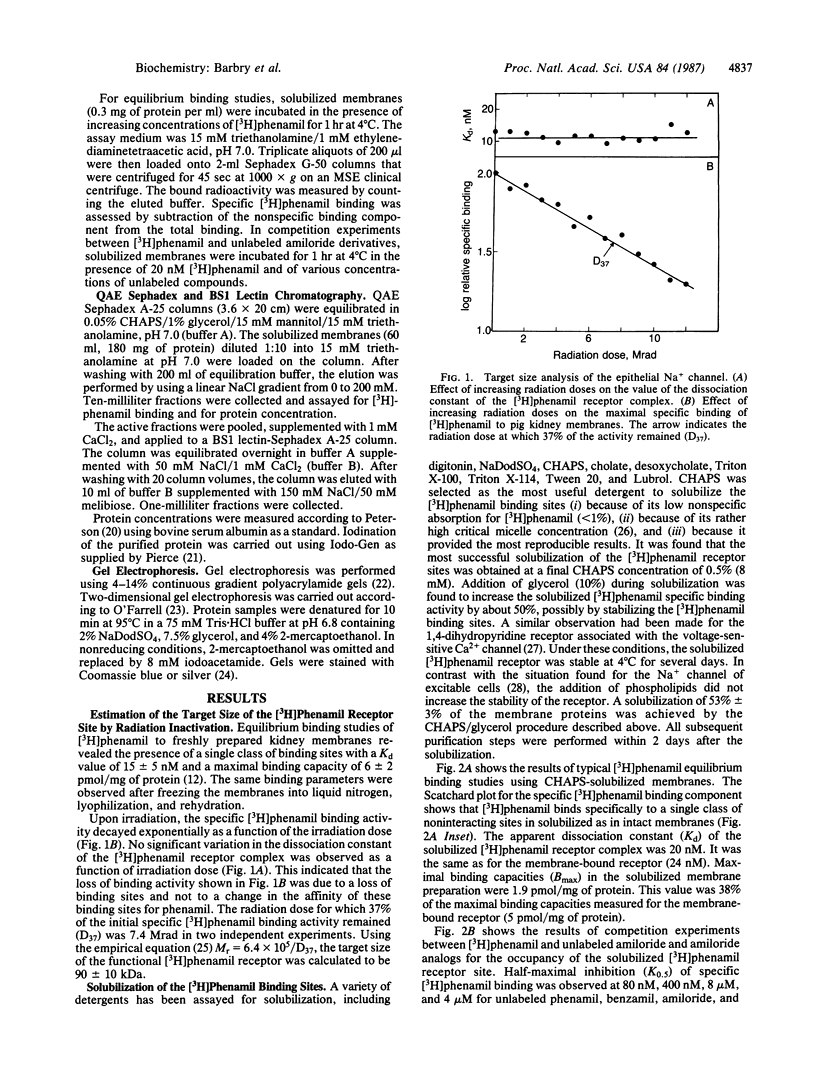
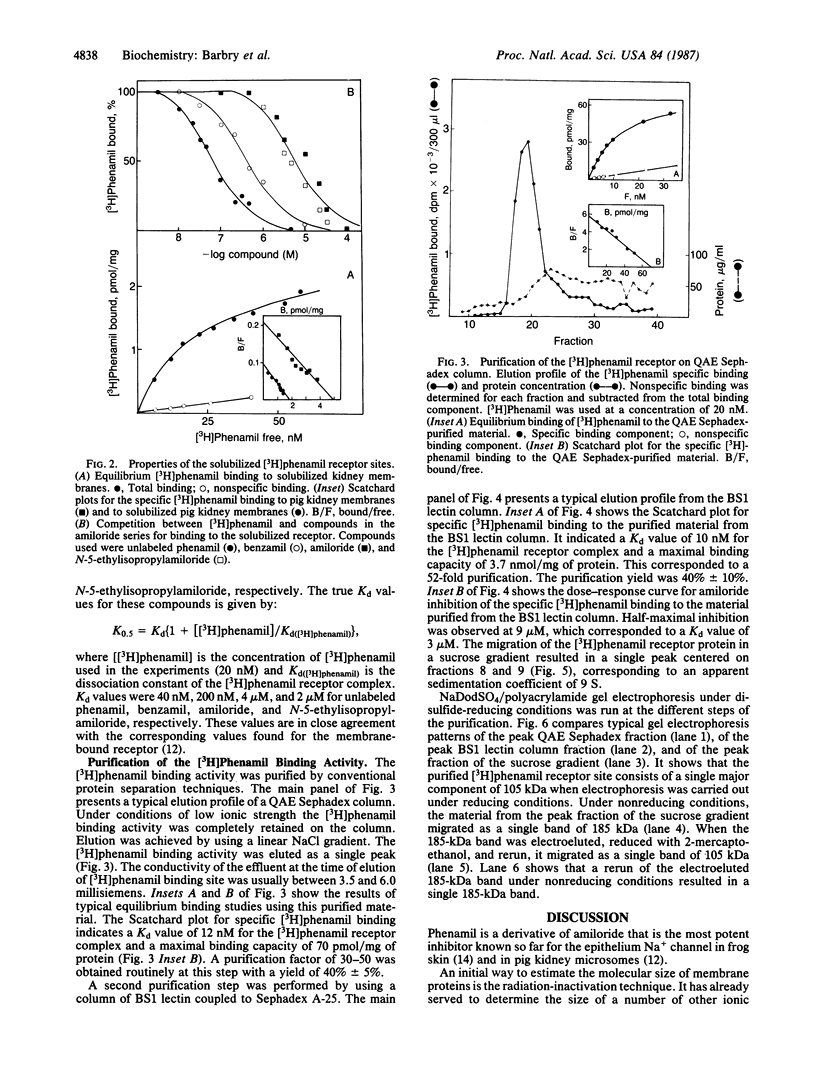
Sodium crosses the apical membrane of tight epithelia through a sodium channel, which is inhibited by the diuretic amiloride and by analogs such as phenamil. Target size analysis indicated that the functional size of the [3H]phenamil binding sites associated with the epithelial Na+ channel from pig kidney is 92 +/- 10 kDa. The [3H]phenamil receptor was solubilized by using 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate. The solubilized material displayed the same properties of interaction with amiloride and its derivatives as the membrane-bound receptor. A two-step purification of the epithelial Na+ channel was achieved by using QAE Sephadex chromatography and affinity chromatography on a Bandeiraea simplicifolia lectin column. It results in an 1100-fold purification of the Na+ channel as compared to pig kidney microsomes with a yield of 15% +/- 5%. The maximal specific activity was 3.7 nmol/mg of protein. NaDodSO4/poly-acrylamide gel electrophoresis of the purified Na+ channel under nonreducing conditions showed the presence of a single major polypeptide chain of apparent molecular mass 185 kDa. Under disulfide-reducing conditions, the purified epithelial Na+ channel migrated as a single band of apparent molecular mass 105 kDa. It is suggested that the epithelial Na+ channel from pig kidney has a total molecular mass of 185 kDa and consists of two nearly identical 90- to 105-kDa polypeptide chains crosslinked by disulfide bridges.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aceves J., Cuthbert A. W., Edwardson J. M. Estimation of the density of sodium entry sites in frog skin epithelium from the uptake of [3H]benzamil. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:477–490. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agnew W. S., Levinson S. R., Brabson J. S., Raftery M. A. Purification of the tetrodotoxin-binding component associated with the voltage-sensitive sodium channel from Electrophorus electricus electroplax membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2606–2610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agnew W. S., Raftery M. A. Solubilized tetrodotoxin binding component from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Stability as a function of mixed lipid-detergent micelle composition. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1912–1919. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbry P., Frelin C., Vigne P., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Lazdunski M. [3H]phenamil, a radiolabelled diuretic for the analysis of the amiloride-sensitive Na+ channels in kidney membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 26;135(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90937-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barhanin J., Schmid A., Lombet A., Wheeler K. P., Lazdunski M., Ellory J. C. Molecular size of different neurotoxin receptors on the voltage-sensitive Na+ channel. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):700–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J. Amiloride: a molecular probe of sodium transport in tissues and cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Mar;242(3):C131–C145. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.3.C131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J., Saccomani G., Brenner B. M., Sariban-Sohraby S. Purification and characterization of the amiloride-sensitive sodium channel from A6 cultured cells and bovine renal papilla. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8525–8529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley P. J. Amiloride: a potent inhibitor of sodium transport across the toad bladder. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):317–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsotto M., Barhanin J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. The 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor associated with the skeletal muscle voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel. Purification and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14255–14263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsotto M., Norman R. I., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Solubilization of the nitrendipine receptor from skeletal muscle transverse tubule membranes. Interactions with specific inhibitors of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;142(3):449–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Brunel C. Bovine kidney alkaline phosphatase. Purification, subunit structure, and metalloenzyme properties. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6040–6045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P. The acetylcholine receptor: an "allosteric" membrane protein. Harvey Lect. 1979 1980;75:85–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cragoe E. J., Jr, Woltersdorf O. W., Jr, Bicking J. B., Kwong S. F., Jones J. H. Pyrazine diuretics. II. N-amidino-3-amino-5-substituted 6-halopyrazinecarboxamides. J Med Chem. 1967 Jan;10(1):66–75. doi: 10.1021/jm00313a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Edwardson J. M. Benzamil binding to kidney cell membranes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Jun 1;30(11):1175–1183. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Borsotto M., Barhanin J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Characterization and photoaffinity labeling of receptor sites for the Ca2+ channel inhibitors d-cis-diltiazem, (+/-)-bepridil, desmethoxyverapamil, and (+)-PN 200-110 in skeletal muscle transverse tubule membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H. Mechanisms of aldosterone action in tight epithelia. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(3):193–205. doi: 10.1007/BF01870126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvin J. L., Simon S. A., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Mandel L. J. Phenamil: an irreversible inhibitor of sodium channels in the toad urinary bladder. J Membr Biol. 1985;87(1):45–54. doi: 10.1007/BF01870698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvin J. L., Simon S. A., Cragoe E. J., Mandel L. J. Binding of 3H-phenamil, an irreversible amiloride analog, to toad urinary bladder: effects of aldosterone and vasopressin. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(2):107–113. doi: 10.1007/BF01869928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelmeland L. M. A nondenaturing zwitterionic detergent for membrane biochemistry: design and synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6368–6370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kepner G. R., Macey R. I. Membrane enzyme systems. Molecular size determinations by radiation inactivation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 17;163(2):188–203. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleyman T. R., Yulo T., Ashbaugh C., Landry D., Cragoe E., Jr, Karlin A., Al-Awqati Q. Photoaffinity labeling of the epithelial sodium channel. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2839–2843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindemann B. Fluctuation analysis of sodium channels in epithelia. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:497–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F., Doucet A. Hormonal control of kidney functions at the cell level. Physiol Rev. 1986 Apr;66(2):377–468. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1986.66.2.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Shimizu S., Tanabe T., Takai T., Kayano T., Ikeda T., Takahashi H., Nakayama H., Kanaoka Y., Minamino N. Primary structure of Electrophorus electricus sodium channel deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):121–127. doi: 10.1038/312121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman R. I., Borsotto M., Fosset M., Lazdunski M., Ellory J. C. Determination of the molecular size of the nitrendipine-sensitive Ca2+ channel by radiation inactivation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 29;111(3):878–883. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91381-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman R. I., Schmid A., Lombet A., Barhanin J., Lazdunski M. Purification of binding protein for Tityus gamma toxin identified with the gating component of the voltage-sensitive Na+ channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4164–4168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Frindt G. Amiloride-sensitive Na channels from the apical membrane of the rat cortical collecting tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2767–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariban-Sohraby S., Benos D. J. Detergent solubilization, functional reconstitution, and partial purification of epithelial amiloride-binding protein. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4639–4646. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariban-Sohraby S., Benos D. J. The amiloride-sensitive sodium channel. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 1):C175–C190. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.2.C175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]