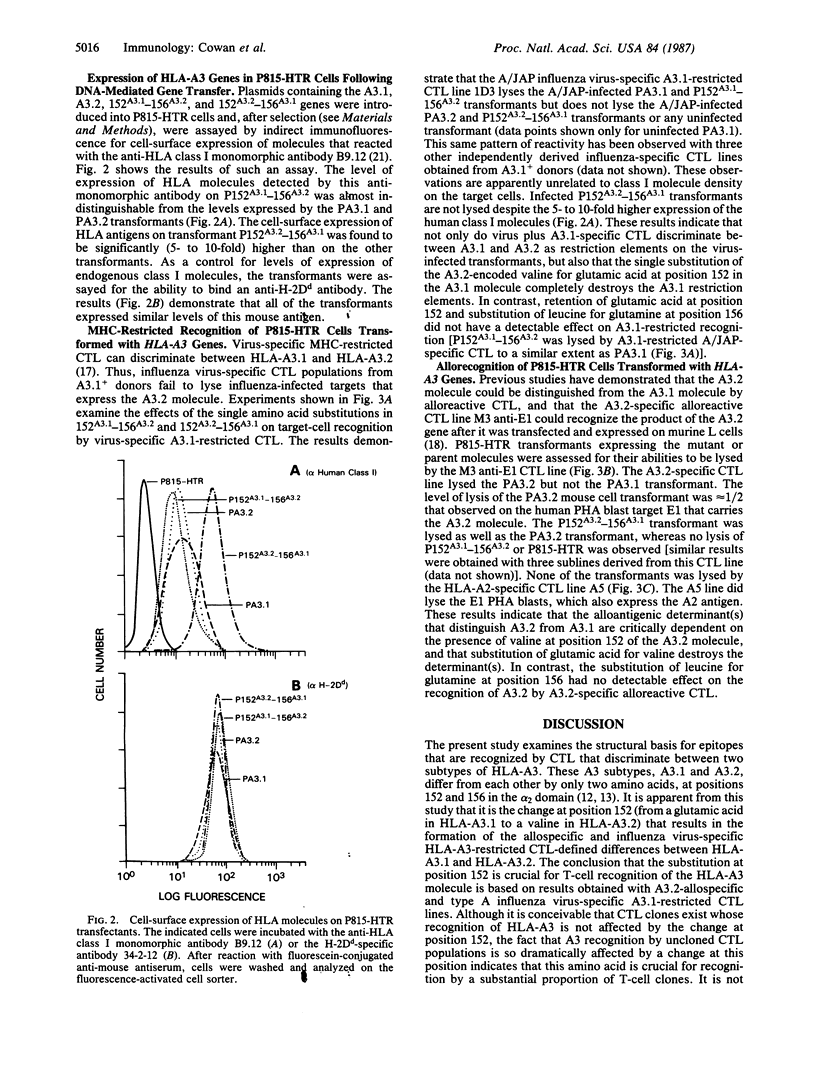
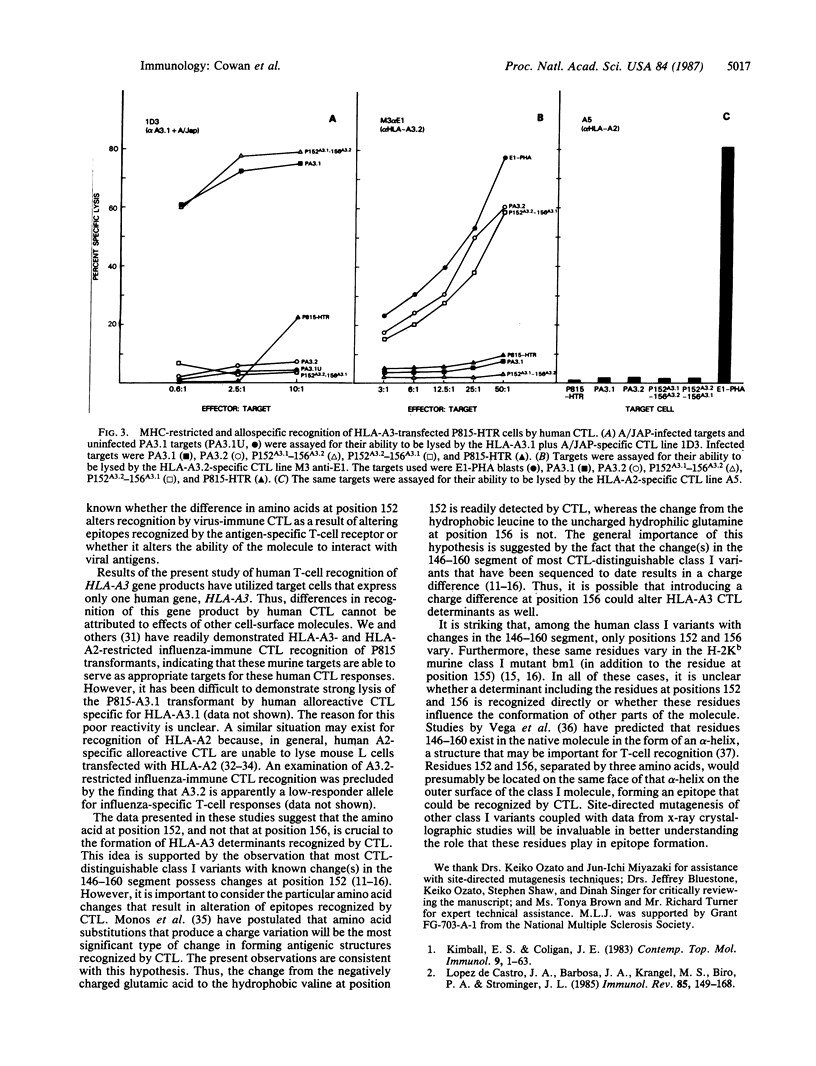
Abstract
Major histocompatibility complex-restricted and alloreactive cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) can discriminate between the HLA-A3.1 and HLA-A3.2 antigens. HLA-A3.1 and the rare variant HLA-A3.2 have been shown to differ by two amino acids in the alpha 2 domain at positions 152 (A3.1, glutamic acid; A3.2, valine) and 156 (A3.1, leucine; A3.2, glutamine). To determine the structural basis for the ability of CTL to differentiate A3.1 from A3.2, two site-directed mutants of the HLA-A3.2 gene were produced, 152A3.1-156A3.2 and 152A3.2-156A3.1, that have the indicated codons for positions 152 and 156. These mutated HLA-A3 genes, as well as the nonmutated HLA-A3.1 and HLA-A3.2 genes, were then transfected into the murine cell line P815-HTR and used as targets for human CTL. Influenza virus-specific HLA-A3.1-restricted CTL lysed virus-infected P815 cells transformed with the HLA-A3.1 and 152A3.1-156A3.2 genes, but not P815 cells transformed with the HLA-A3.2 and 152A3.2-156A3.1 genes. HLA-A3.2-allospecific CTL lysed the P815 cells transformed with the HLA-A3.2 and 152A3.2-156A3.1 genes but did not lyse P815 cells transformed with the HLA-A3.1 or 152A3.1-156A3.2 genes. Thus, a single amino acid change at position 152, substituting valine for glutamic acid and thereby introducing a charge difference, produces major structural changes in the epitopes recognized by major histocompatibility complex-restricted and alloreactive CTL.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold B., Burgert H. G., Hamann U., Hämmerling G., Kees U., Kvist S. Cytolytic T cells recognize the two amino-terminal domains of H-2 K antigens in tandem in influenza A infected cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90528-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold B., Horstmann U., Kuon W., Burgert H. G., Hämmerling G. J., Kvist S. Alloreactive cytolytic T-cell clones preferentially recognize conformational determinants on histocompatibility antigens: analysis with genetically engineered hybrid antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7030–7034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa J. A., Mentzer S. J., Minowada G., Strominger J. L., Burakoff S. J., Biro P. A. Recognition of HLA-A2 and -B7 antigens by cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes after gene transfer into human and monkey, but not mouse, cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7549–7553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger A. E., Davis J. E., Cresswell P. Monoclonal antibody to HLA-A3. Hybridoma. 1982;1(2):87–90. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1.1982.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddison W. E., Sharrow S. O., Shearer G. M. T cell subpopulations required for the human cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to influenza virus: evidence for T cell help. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):487–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddison W. E., Shearer G. M., Shaw S. Influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T cells are restricted by multiple HLA-A3-related self antigens: evidence for recognition of distinct self structures in conjunction with different foreign antigens. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2231–2235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan E. P., Coligan J. E., Biddison W. E. Human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte recognition of an HLA-A3 gene product expressed on murine L cells: the only human gene product required on the target cells for lysis is the class I heavy chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4490–4494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan E. P., Jordan B. R., Coligan J. E. Molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis of genes encoding cytotoxic T lymphocyte-defined HLA-A3 subtypes: the E1 subtype. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2835–2841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Berzofsky J. A. T-cell antigenic sites tend to be amphipathic structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7048–7052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomard E., Begue B., Sodoyer S., Maryanski J. L., Jordan B. R., Levy J. P. Murine cells expressing an HLA molecule are specifically lysed by HLA-restricted antiviral human T cells. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):153–154. doi: 10.1038/319153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball E. S., Coligan J. E. Structure of class I major histocompatibility antigens. Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1983;9:1–63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4517-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krangel M. S., Biddison W. E., Strominger J. L. Comparative structural analysis of HLA-A2 antigens distinguishable by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. II. Variant DK1: evidence for a discrete CTL recognition region. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1856–1862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krangel M. S., Taketani S., Biddison W. E., Strong D. M., Strominger J. L. Comparative structural analysis of HLA-A2 antigens distinguishable by cytotoxic T lymphocytes: variants M7 and DR1. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6313–6321. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez de Castro J. A., Barbosa J. A., Krangel M. S., Biro P. A., Strominger J. L. Structural analysis of the functional sites of class I HLA antigens. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;85:149–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryanski J. L., Moretta A., Jordan B., De Plaen E., Van Pel A., Boon T., Cerottini J. C. Human T cell recognition of cloned HLA class I gene products expressed on DNA transfectants of mouse mastocytoma P815. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Nov;15(11):1111–1117. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830151109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentzer S. J., Barbosa J. A., Strominger J. L., Biro P. A., Burakoff S. J. Species-restricted recognition of transfected HLA-A2 and HLA-B7 by human CTL clones. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):408–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki J., Appella E., Ozato K. Intracellular transport blockade caused by disruption of the disulfide bridge in the third external domain of major histocompatibility complex class I antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):757–761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monos D. S., Tekolf W. A., Shaw S., Cooper H. L. Comparison of structural and functional variation in class I HLA molecules: the role of charged amino acid substitutions. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1379–1385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., Choi E., Weis J., Seidman J. G., Ozato K., Liu L., Burakoff S. J., Reiss C. S. Dissection of serological and cytolytic T lymphocyte epitopes on murine major histocompatibility antigens by a recombinant H-2 gene separating the first two external domains. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):167–178. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathenson S. G., Geliebter J., Pfaffenbach G. M., Zeff R. A. Murine major histocompatibility complex class-I mutants: molecular analysis and structure-function implications. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:471–502. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Mayer N. M., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse major histocompatibility complex antigens. Transplantation. 1982 Sep;34(3):113–120. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198209000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebaï N., Malissen B. Structural and genetic analyses of HLA class I molecules using monoclonal xenoantibodies. Tissue Antigens. 1983 Aug;22(2):107–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1983.tb01176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss C. S., Greenstein J. L., Crimmins M. A., Liu L. L., Rao A., Maziaraz R. T., Murre C., Burakoff S. J. Recognition of the alpha-1 and alpha-2 domains of H-2 molecules by allospecific cloned T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2191–2194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze D. H., Pease L. R., Geier S. S., Reyes A. A., Sarmiento L. A., Wallace R. B., Nathenson S. G. Comparison of the cloned H-2Kbm1 variant gene with the H-2Kb gene shows a cluster of seven nucleotide differences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2007–2011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroishi T., Evans G. A., Appella E., Ozato K. In vitro mutagenesis of a mouse MHC class I gene for the examination of structure-function relationships. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):623–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroynowski I., Clark S., Henderson L. A., Hood L., McMillan M., Forman J. Interaction of alpha 1 with alpha 2 region in class I MHC proteins contributes determinants recognized by antibodies and cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2160–2166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroynowski I., Orn A., Goodenow R. S., McMillan M., Forman J., Brayton P. R., Frelinger J., Hood L. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize determinants on the BALB/c-H-2Ld molecule controlled by alpha 1 and alpha 2 but not alpha 3 external domains. Immunogenetics. 1984;20(2):141–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00364486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Pel A., De Plaen E., Boon T. Selection of highly transfectable variant from mouse mastocytoma P815. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Sep;11(5):467–475. doi: 10.1007/BF01534840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega M. A., Bragado R., Ezquerra A., López de Castro J. A. Variability and conformation of HLA class I antigens: a predictive approach to the spatial arrangement of polymorphic regions. Biochemistry. 1984 Feb 28;23(5):823–831. doi: 10.1021/bi00300a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega M. A., Wallace L., Rojo S., Bragado R., Aparicio P., López de Castro J. A. Delineation of functional sites in HLA-B27 antigens. Molecular analysis of HLA-B27 variant Wewak I defined by cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3323–3332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Mellor A., Golden L., Fahrner K., Simpson E., Hurst J., Flavell R. A. The structure of a mutant H-2 gene suggests that the generation of polymorphism in H-2 genes may occur by gene conversion-like events. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):671–674. doi: 10.1038/301671a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Schravendijk M. R., Biddison W. E., Berger A. E., Coligan J. E. Comparative structural analysis of HLA-A3 antigens distinguishable by cytotoxic T lymphocytes: variant E1. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):410–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn M., Bernabeu C., Royer-Pokora B., Weiss J., Seidman J. G., de Vries J., Spits H., Terhorst C. Recognition of HLA-A2 by cytotoxic T lymphocytes after DNA transfer into human and murine cells. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1083–1085. doi: 10.1126/science.6333726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


