Abstract
Objective
To determine the effectiveness of exercise as an intervention in the management of depression.
Design
Systematic review and meta-regression analysis of randomised controlled trials obtained from five electronic databases (Medline, Embase, Sports Discus, PsycLIT, Cochrane Library) and through contact with experts in the field, bibliographic searches, and hand searches of recent copies of relevant journals.
Main outcome measures
Standardised mean difference in effect size and weighted mean difference in Beck depression inventory score between exercise and no treatment and between exercise and cognitive therapy.
Results
All of the 14 studies analysed had important methodological weaknesses; randomisation was adequately concealed in only three studies, intention to treat analysis was undertaken in only two, and assessment of outcome was blinded in only one. The participants in most studies were community volunteers, and diagnosis was determined by their score on the Beck depression inventory. When compared with no treatment, exercise reduced symptoms of depression (standardised mean difference in effect size –1.1 (95% confidence interval –1.5 to –0.6); weighted mean difference in Beck depression inventory –7.3 (–10.0 to –4.6)). The effect size was significantly greater in those trials with shorter follow up and in two trials reported only as conference abstracts. The effect of exercise was similar to that of cognitive therapy (standardised mean difference –0.3 (95% confidence interval –0.7 to 0.1)).
Conclusions
The effectiveness of exercise in reducing symptoms of depression cannot be determined because of a lack of good quality research on clinical populations with adequate follow up.
What is already known on this topic
Depression is common
Management is often inadequate and many patients do not comply with antidepressant medication
The effect of exercise on depression has been a subject of interest for many years
What this study adds
Most studies of the effect of exercise on depression are of poor quality, have brief follow up, and are undertaken on non-clinical volunteers
Exercise may be efficacious in reducing symptoms of depression in the short term but its effectiveness in clinical populations is unknown
A well designed, randomised controlled trial with long term follow up is needed
Introduction
Depression is a common and important cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Although effective pharmacological interventions are available, much depression remains inadequately treated. Compliance with antidepressant treatment is often poor: studies have shown that between 20% and 59% of patients in primary care stop taking antidepressants within three weeks of the drugs being prescribed.1,2 The effect of exercise on depression has been the subject of research for several decades, and the literature on the subject is growing.3 In the past decade “exercise on prescription” schemes have become popular in primary care in the United Kingdom,4 many of which include depression as a referral criterion.
Several plausible mechanisms for how exercise affects depression have been proposed. In the developed world taking regular exercise is seen as a virtue; the depressed patient who takes regular exercise may, as a result, get positive feedback from other people and an increased sense of self worth. Exercise may act as a diversion from negative thoughts, and the mastery of a new skill may be important.5,6 Social contact may be an important mechanism, and physical activity may have physiological effects such as changes in endorphin and monoamine concentrations.7,8
Three meta-analyses have looked at the effect of exercise on depression, and all found a benefit.9–11 However, these analyses pooled data from a range of study types that included uncontrolled studies and randomised as well as non-randomised controlled trials. They also pooled data from trials that compared exercise and no treatment with data from trials that compared exercise and other forms of treatment, and they did not explicitly assess the quality of the studies. Other studies have been completed since the most recent of these meta-analyses was published. This review summarises the evidence from randomised controlled trials of the effectiveness of exercise as a treatment for depression.
Methods
Identification of the studies
We searched Medline (1966-99), Embase (1980-99), Sports Discus (1975-99), PsycLIT (1981-99), the Cochrane Controlled Trials Register, and the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews using the terms “exercise,” “physical activity,” “physical fitness,” “walking,” “jogging,” “running,” “cycling,” “swimming,” “depression,” “depressive disorder,” and “dysthymia.” We also examined bibliographies, contacted experts, and hand searched copies published in the 12 months to December 1999 of the following journals: BMJ, JAMA, Archives of Internal Medicine, New England Journal of Medicine, Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, Comprehensive Psychiatry, British Journal of Psychiatry, Acta Psychiatrica Scandanavica, and British Journal of Sports Medicine. Three people independently reviewed titles and available abstracts to retrieve potentially relevant studies; studies needed to be identified by only one person to be retrieved.
Inclusion criteria
Studies were included in the review if the participants were diagnosed as having depression (by any method of diagnosis and with any severity of depression) and were aged 18 or above (with no upper age limit). Only randomised controlled trials were included. A trial was defined as a randomised controlled trial if the allocation of participants to treatment and comparison groups was described as randomised (including terms such as “randomly,” “random,” and “randomisation”). Studies had to include depression as an outcome measure and could be in any language. We excluded studies that compared different types of exercise, those that measured outcomes immediately before and after a single exercise session, and those that looked at the effect of exercise on anxiety or other neurotic disorders. We included studies that compared exercise and other, established treatments for depression.
Study quality
We assessed the quality of studies by noting whether allocation was concealed and intention to treat analysis was undertaken, and whether there was blinding.12,13 For concealment of allocation we distinguished between trials that were adequately concealed (central randomisation at a site remote from the study; computerised allocation in which records are in a locked, unreadable file that can be accessed only after entering patient details; the drawing of sealed and opaque sequentially numbered envelopes), inadequately concealed (open list or tables of random numbers; open computer systems; drawing of non-opaque envelopes), and unclear (no information in report, and the authors either did not respond to requests for information or were unable to provide information). We defined trials as using intention to treat analysis if all the patients were analysed in the groups to which they were randomly allocated. If only those who started treatment or only those who completed treatment were included in the analysis we defined the study as not using intention to treat analysis. For blinding we distinguished between trials in which the main outcome was measured by an assessor who was blind to treatment allocation and those in which the main outcome was measured either by the participants themselves or by a non-blinded assessor.
Data extraction
The two authors independently extracted data (the quality criteria, participant details, intervention details, outcome measures, baseline and post-intervention results, and main conclusions), using a structured form. We resolved discrepancies by referring to the original papers and discussion.
Contact with authors
We found current contact details of all authors through correspondence addresses on study reports and by searching websites. We contacted all authors by email or post (sending three reminders to non-responders), to establish missing details in the methods and results sections of the written reports and to determine authors' knowledge of or involvement in any current work in the area. On the envelopes we put return address details and a request to inform us if the addressee was no longer at that address.
Outcome measures
The studies used a number of psychometric instruments to assess depression, with several using more than one instrument. To include data from as many trials as possible we calculated effect sizes for each trial, using Cohen's method,14 and a standardised mean difference for the overall effect. To calculate a trial's effect size we defined the main outcome measure of depression as the one reported in the abstract or the first one reported in either the methods or results sections. As the main outcome measure in 10 of the 14 trials that were finally included was the Beck depression inventory, we also combined data from these trials to calculate the weighted mean difference in the Beck depression inventory score.
Statistical analysis
We undertook a narrative review of all studies and a meta-regression analysis of those studies with appropriate data. The effect of exercise compared with “no treatment” (controls on a waiting list; placebo intervention; or, where exercise was an adjunct, with both treatment and control groups receiving an identical established treatment) was considered separately from the effect of exercise compared with an established treatment for depression. Some studies were included in both analyses as they contained exercise, established treatment, and control groups.
We anticipated that systematic differences between studies (heterogeneity) would be likely. This was the case for the meta-analysis of studies comparing exercise with no treatment; for these we used a random effects model based on DerSimonian and Laird's method to calculate the pooled effect size.15 The results of studies comparing exercise with cognitive therapy were homogeneous; for meta-analysis of these we used the fixed effects inverse variance method.16 We also undertook a meta-regression analysis to assess the effects of allocation concealment, intention to treat analysis, blinding, the setting (whether participants were volunteers from the community or clinical patients), baseline severity of depression (using Beck depression inventory scores or, for the two studies that did not report baseline Beck depression inventory scores for the whole study sample, inputting the mean of these scores), type of exercise (aerobic or non-aerobic), type of publication (peer reviewed journal, conference abstract, or doctoral dissertation), and length of follow up. We used STATA (version 6) statistical software for all the analyses.
Results
Study inclusion and characteristics
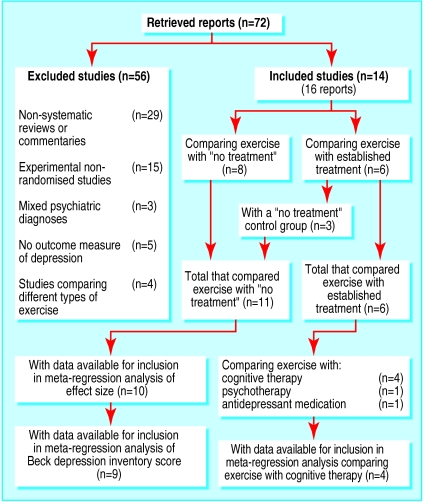
Figure 1 summarises the process of inclusion of the studies for review and analysis. Of 72 potentially relevant studies, we excluded 56: 29 were non-systematic reviews or commentaries,17–45 15 were experimental non-randomised controlled trials,46–60 three were of psychiatric patients with mixed diagnoses and had no separate analysis for depressed patients,61–63 five did not have an outcome measure of depression,64–68 and four compared different types of exercise but had no non-exercising group.69–72
Figure 1.
Process of inclusion of studies for review and analysis
Sixteen articles reporting 14 studies fulfilled the inclusion criteria.73–88 Of these 14 studies, 10 were in the United States,73,74,79–81,84–88 two were in the United Kingdom,75,78 and one each were in Canada77 and Norway.82 Eight of the 14 studies compared an exercise group with a no treatment group,74,75,77–79,82 and six compared exercise directly with an established form of therapy: four with cognitive therapy,80,81,84,87 one with psychotherapy,88 and one with antidepressant treatment.73 Three of these also had a no treatment group81,84,87; thus in total 11 studies compared exercise with no treatment and six compared it with an established treatment (fig 1).
Missing data and contact with authors
Authors of 11 of the 14 studies responded to our request to provide missing data,73–78,80,82–86,88 but three were unable to provide all the information.85,86,88 Only seven of the 14 written reports provided adequate data for statistical pooling and confirmation of study conclusions. Through contact with authors we were able to obtain adequate data for a further five.
Quality assessment
Most studies were of poor quality. In no study was treatment allocation described, and contact with authors established that allocation might have been adequately concealed in only three studies.74,75,82 Intention to treat analysis was undertaken in two studies.73,74 The main outcome was measured by the participants themselves, by means of a questionnaire, in all but two of the studies.73,75 The outcome assessor in one of these exceptions was not blinded,75 therefore assessment of outcome was blind in only one of the 14 studies.
Study populations
Nine of the studies involved non-clinical populations,73,74,77,79–81,84,85,87 and most participants were recruited through the media. The participants in the study by McCann and Holmes85 were a sample obtained from a screening of all female entrants in one year to an undergraduate psychology course at the University of Kansas; the report stated that students had to participate in research as part of their course. Two studies reported financial incentives for participants.79,80
Only four of the nine studies with non-clinical participants used clinical interview to confirm the presence of depression,73,74,79,84 the remainder using a cut-off point on the self reported Beck depression inventory score (each study using a different value). One of the studies in which depression was confirmed by clinical interview also included patients with dysthymia (depressed mood, without the full range of symptoms of clinical depression).74
Exercise compared with placebo intervention or as an adjunct to standard treatment
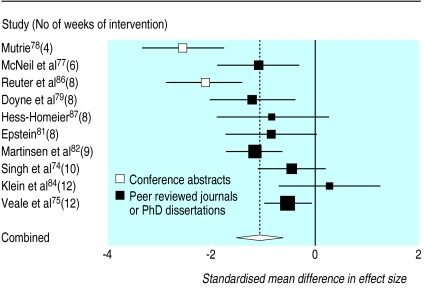
Table 1 summarises the 11 studies that compared exercise with no treatment, 10 of which had data available for analysis. The pooled standardised mean difference in effect size, calculated using the random effects model, was –1.1 (95% confidence interval –1.5 to –0.6). Significant heterogeneity between studies (Q=35.0, P<0.001) was not associated with allocation concealment, intention to treat analysis, blinding, setting, baseline severity of depression, or exercise type but was associated with type of publication and length of follow up. The reported effect of treatment was significantly higher in conference abstracts than in peer reviewed journals or doctoral dissertations (P<0.01). The estimated variance (τ2) between studies was reduced from 0.41 to 0.03 when “abstract” was added as a variable to the model. Length of follow up was significantly negatively associated with the size of effect: the addition of the variable “follow up” reduced τ2 from 0.41 to 0.08. When both these variables were combined in the model, τ2 was reduced to zero.
Table 1.
Summary of studies that compared effects of exercise with “no treatment”
| Study | Where published | Participants
|
Intervention
|
Main outcome results at end of study† (95% CI) | Study quality
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Type | Mean (range or SD) age | % female | Type* | Duration (No of weeks) | Conceal- ment | Intention to treat | Blinded | ||||
| Singh et al, 199774 | Peer reviewed journal, US | 32 | Volunteers from two community registers of people interested in research | 70 (61-88) | 63 | 1. Non-aerobic exercise: progressive resistance training 3 times a week. 2. Control: seminars on health of elderly people twice a week. Depression not discussed in either group. | 10 | Mean difference in BDI between exercise and control groups −4.0 (−10.1 to 2.1) | Yes | Yes | No | |
| McNeil et al, 199177 | Peer reviewed journal, Canada | 30 | Non-clinically depressed elderly people referred by religious and community organisations | 72.5 | N/A | 1. Exercise: walking near home (accompanied by experimenter) 3 times a week for 20-40 minutes. 2. Control: 1 home visit by psychology student, for “chat,” twice a week. 3. Waiting list control group. | 6 | Mean difference in BDI between exercise and waiting list control groups −3.6 (−6.6 to −0.6); no significant difference between exercise and social contact groups | No | No | No | |
| Mutrie, 198878 | Conference abstract, UK | 36 | Patients referred by general practitioners in Glasgow | 42.1 | 83 | 1. Supervised aerobic exercise: 3 sessions of 20 minutes per week. 2. Supervised non-aerobic exercise: 3 sessions of 20 minutes per week. 3. Waiting list control group. | 4 | Mean difference in BDI between aerobic exercise and control groups −11.9 (−16.7 to −7.1); no significant difference between non-aerobic exercise and control groups | No | No | No | |
| Doyne et al, 198779 | Peer reviewed journal, US | 57 | Volunteers from community, recruited through media | 28.5 (4.36) | 100 | 1. Aerobic exercise: supervised running or walking 4 times a week. 2. Supervised strength group: programme 4 times a week. 3. Waiting list control group. | 8 | Mean difference in BDI between aerobic exercise and waiting list control groups −7.1 (−12.3 to −1.9) | No | No | No | |
| Epstein, 198681 | Doctoral dissertation, US | 33 | Volunteers from community, recruited through media | 39.4 (24-60) | 92 | 1. Group running or walking for 30 minutes 3-5 times a week. 2. Cognitive therapy: 1 session of 1.5 hours per week. 3. Waiting list control group. | 8 | Mean difference in BDI between exercise and control groups −7.3 (−16.6 to 2.0). | No | No | No | |
| Martinsen et al, 198582 | Peer reviewed journal, Norway | 49 | Psychiatric inpatients | 40 (17-60) | N/A | 1. Aerobic exercise with instructor for 1 hour, 3 times a week. 2. Control group attended occupational therapy while intervention group exercised. | 9 | Mean difference in BDI between exercise and control groups −10.7 (−16.6 to −4.9) | Yes | No | No | |
| Veale et al, 199275 | Peer reviewed journal, UK | 83 | Psychiatric outpatients or patients at day hospital | 35.5 (19-58) | 64 | 1. Group running 3 times a week, plus routine care. 2. Control group: routine care only. | 12 | Mean difference in BDI between exercise and control group −3.9 (−7.5 to −0.2) | Yes | No | No | |
| Klein et al, 198584 | Peer reviewed journal, US | 74 | Volunteers from community, recruited through media | 30.1 (6.72) | 72 | 1. Supervised running twice weekly. 2. Control group: meditation for 1 hour twice weekly. 3. Group cognitive therapy for 2 hours once a week. | 12 | At 12 weeks: mean difference in symptom checklist score between exercise and control groups 0.2 (−2.3 to 2.7). At 9 months follow up: mean difference in symptom checklist between exercise and control groups 0.04 (−1.96 to 2.04) | No | No | No | |
| McCann and Holmes, 198485 | Peer reviewed journal, US | 47 | Female undergraduate psychology students with BDI ⩾11 (participation in research required as part of the course) | N/A | 100 | 1. Aerobic exercise: group running, jogging, or dancing for 1 hour twice weekly. 2. Placebo: progressive muscle relaxation for 15-20 minutes 4 times a week. 3. Waiting list control group. | 10 | Only graphical results presented in paper; these showed a benefit of exercise over both placebo and control groups (authors were unable to provide data) | No | No | No | |
| Reuter et al, 198486 | Conference abstract, US | 18 | University students presenting to mental health clinic with depression | N/A | N/A | 1. Counselling plus supervised running for at least 20 minutes, 3 times a week. 2. Control group: counselling only. | 10 | Mean difference in BDI at 8 weeks between exercise and control groups −13.46 (−19.4 to −7.5) | No | No | No | |
| Hess-Homeier, 198187 | Doctoral dissertation, US | 20 | Volunteers from community | N/A | N/A | 1. Running or walking with instructor for 30 minutes 4 times a week. 2. Cognitive therapy: 1 session of 1 hour and 2 of half an hour per week. 3. Waiting list control group. | 8 | Mean difference in BDI between exercise and control groups −6.4 (−15.5 to 2.7) | No | No | No | |
BDI=Beck depression inventory score. *Nos refer to groups. †Except where otherwise indicated.
Figure 2 shows the standardised mean differences in effect size of the 10 studies that provided these data, with the studies listed in order of length of intervention. Pooling studies according to type of publication gave standardised mean differences, calculated using the fixed effects model, of –0.7 (–1.0 to –0.5; n=8) for journal papers and dissertations and –2.3 (–2.9 to –1.8; n=2) for conference abstracts; pooling according to duration of intervention gave –1.8 (–2.3 to –1.3; n=2) for less than eight weeks, –1.3 (–1.8 to –0.9; n=4) for eight weeks, and –0.6 (–0.9 to –0.3; n=4) for more than eight weeks (there was no significant heterogeneity within these subgroups). Although the effect size remained significant when the two conference abstracts were excluded and when we analysed only those studies of more than eight weeks' duration, the effect was reduced.
Figure 2.
Standardised mean difference in size of effect of exercise compared with “no treatment” for depression
Pooling the nine studies that used the Beck depression inventory as a measure of depression gave a weighted mean difference in the score of –7.3 (–10.0 to –4.6). Again there was significant heterogeneity, associated with type of publication and length of follow up.
Exercise compared with standard treatments for depression
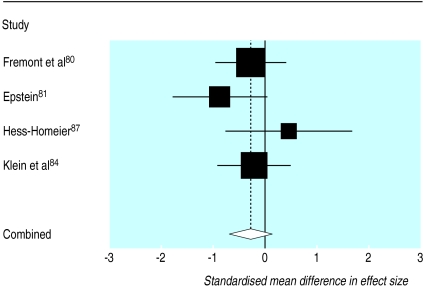
Table 2 summarises the six studies that compared exercise and standard interventions, four of which compared exercise and cognitive therapy. Figure 3, which shows the standardised mean differences of these four studies, shows that the difference in effect size between exercise and cognitive therapy was not significant (standardised mean difference –0.3 (95% confidence interval –0.7 to 0.1)). These studies were homogeneous (Q=2.9, P=0.4).
Table 2.
Summary of studies that compared effects of exercise with established treatments
| Study | Where published | Participants
|
Intervention
|
Main outcome results at end of study† (95% CI) | Study quality
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Type | Mean (range or SD) age | % female | Type* | Duration (No of weeks) | Conceal- ment | Intention to treat | Blinded | ||||
| Fremont et al, 198780 | Peer reviewed journal, US | 61 | Volunteers from community, recruited through media | N/A | N/A | 1. Group running with an instructor for 20 minutes 3 times a week. 2. Cognitive therapy: 1 session of 1 hour per week. 3. Combination of both interventions. | 10 | Mean difference in BDI between exercise and cognitive therapy group −1.9 (−6.7 to 2.9); no significant difference between combined treatment and individual treatments | No | No | No | |
| Epstein, 198681 | Doctoral dissertation, US | 33 | Volunteers from community, recruited through media | 39.4 (24-60) | 92 | 1. Group running or walking for 30 minutes 3-5 times a week. 2. Cognitive therapy: 1 session of 1.5 hours per week. 3. Waiting list control group. | 8 | Mean difference in BDI between exercise and cognitive therapy groups −8.2 (−18.0 to −1.6) | No | No | No | |
| Klein et al, 198584 | Peer reviewed journal, US | 74 | Volunteers from community, recruited through media | 30.1 (6.72) | 72 | 1. Supervised running for 45 minutes twice weekly. 2. Control group: 1 hour of meditation twice weekly. 3. Group cognitive therapy for 2 hours once a week. | 12 | At 12 weeks: mean difference in symptom checklist score between exercise and group therapy groups −0.2 (−2.6 to 2.2). At 9 months follow up: mean difference in symptom checklist score between exercise and cognitive therapy groups −0.5 (−2.6 to 1.65) | No | No | No | |
| Hess-Homeier, 198187 | Doctoral dissertation, US | 20 | Volunteers from community | N/A | N/A | 1. Running or walking with instructor for 30 minutes 4 times a week. 2. Cognitive therapy: 1 session of 1 hour and 2 of half an hour per week. 3. Waiting list control group. | 8 | Mean difference in BDI between exercise and cognitive therapy groups 2.6 (−4.7 to 9.9) | No | No | No | |
| Greist et al, 197988 | Peer reviewed journal, US | 28 | “Patients seeking treatment for neurotic or reactive depression aged 18-30” | N/A | 53.4 | 1. Running with experienced runner for 1 hour 3 times a week. 2. “Time limited” psychotherapy. 3. “Time unlimited” psychotherapy (2 and 3 not fully described). | 10 | “No significant difference between three groups on outcome Symptom Checklist scores” (no data available) | No | No | No | |
| Blumenthal, 199973 | Peer reviewed journal, US | 15 6 | Volunteers from community, recruited through media | N/A | N/A | 1. Group walking or jogging. 2. Standard dosage of sertraline, managed by psychiatrist. 3. Combination of both interventions. | 16 | Mean difference in Hamilton rating scale of depression between exercise and sertraline groups 0.74 (−1.8 to 3.7) | No | Yes | Yes | |
BDI=Beck depression inventory score. *Nos refer to groups. †Except where otherwise indicated.
Figure 3.
Standardised mean difference in size of effect of exercise compared with cognitive therapy
Only one study compared exercise and standard antidepressant treatment.73 Its main outcome measure—the Hamilton rating scale of depression—did not differ significantly between the groups of patients receiving the exercise intervention, medication, or both; and at the end of the intervention period the proportion of patients diagnosed as no longer depressed was similar in each group.
Discussion
Quality of the studies
Exercise may be efficacious in reducing depressive symptoms, but the poor quality of much of the evidence is of concern. The fact that none of the measures of study quality explained the variation among the studies is likely to be due to the low quality of most of the studies. The size of the effect is increased by results from two unpublished conference abstracts and studies with a shorter follow up period, suggesting that results may be sustained only in the short term. All the studies reported results at the end of the intervention, and only one study followed patients up beyond the completion of the intervention. This was the only study that found no effect of exercise, compared with the control group, at the end of the intervention period (12 weeks); at nine months' follow up the reduction in symptoms remained similar in the exercise intervention, control (meditation), and cognitive therapy groups.84 Thus this evidence does not support a sustained effect of exercise beyond the intervention period. Participants from one other study are being followed up for two years (N Singh, personal communication, 1999),74 and the results of this follow up will provide important information.
The size of the effect of exercise compared with no treatment in the studies we analysed is similar to those found by three previous meta-analyses.9–11 We aimed to provide a better quality analysis by including only trials that were described as randomised controlled trials. Our results did not differ from those of meta-analyses that also included non-randomised trials and observational data; this may be because the effect of randomisation was mitigated by the lack of adequate concealment, intention to treat analysis, and blinding, making the trials in our analysis no better than non-randomised trials.
Type of exercise
There was no association between type of exercise and the variation in results between studies, indicating that aerobic and non-aerobic exercise have a similar effect. Studies directly comparing different exercise types support such a finding.69–72 However, this may be because the effect is due to psychosocial factors, such as learning a new skill or socialising, rather than to the exercise itself. None of the participants in the studies we reviewed exercised alone: they were either with other participants or with a coach. McNeil et al included a social contact control group and found no significant difference in the effect on depressive symptoms between this group and the exercise group.77
Implications
Our aim was to assess clinical effectiveness—that is, the likely effect of exercise on clinical patients in everyday practice. Although no trial can exactly replicate everyday practice, the screening out of individuals who were not motivated to exercise, the use of non-clinical volunteers, and the lack of intention to treat analysis in most of the studies suggest that our results overestimate what would be likely in real life. In the United Kingdom rates of compliance with “exercise on prescription” schemes among patients with any referral criteria vary from 20% to 50%.4,89 It is reasonable to assume that compliance among patients with depression would be similar or worse. Salmon has pointed out that the allocation of depressed patients in these studies to activities such as running or aerobics “must puzzle clinicians, who in treating depressed people, often have to contend with an absence of motivation to tackle much less strenuous features of life's routine.”37 Baseline severity of depression, when added to the regression model, was not associated with any of the systematic differences between studies. This suggests that, although different criteria for determining inclusion were used, participants in each study had similar levels of depression. However, the fact that most studies used non-clinical participants means that the results may be less generalisable.
To use as much of the available data as possible we calculated the standardised mean difference using effect sizes. The result is therefore expressed as a standard deviation. That is to say, our results show that people who exercise are “1.1 standard deviations less depressed than non-exercisers”; in clinical terms such a result is difficult to understand. We also calculated pooled differences in the mean score on the Beck depression inventory (a common instrument in mental health research) for those studies in which this measure was used. We argue, however, that even such a well known instrument is difficult to interpret clinically. Our result shows that people who exercise score less on the Beck depression inventory scale (by 7.3 points) than those who do not exercise, a result that is likely to have little meaning for most doctors and patients. A more useful outcome measure would be the likelihood of being depressed after the intervention, but only two studies included a dichotomous outcome.73,81 Epstein, comparing exercise and no treatment, found no significant difference between the exercise and control groups in the numbers of participants who were still diagnosed as having depression.81 A dichotomous result is a more understandable and perhaps a more important outcome measure in clinical terms, and such measures should be included in future research in this area.
Many of the problems we identified in the studies we reviewed are also present in research into other interventions in the management of depression,90,91 highlighting the need for better quality research in the area of depression. We conclude that it is not possible to determine from the available evidence the effectiveness of exercise in the management of depression. However, exercise may be efficacious in reducing the symptoms of depression in some volunteers in the short term. Doctors could recommend more physical activity to their motivated patients, but this should not replace standard treatment, particularly for those with severe disease. Other health benefits could accrue to patients who do become more active.92,93 There is a need for well designed, randomised controlled trials on a clinical population that measure both continuous and dichotomous outcomes and that follow up participants for at least 12 months.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work began as part of a training course at the NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York, and we thank Jos Kleinan and other staff at the centre for their help. Alan Lui (audit nurse, Airedale General Hospital, West Yorkshire) helped with the protocol development and retrieval of articles. Domenico Scala (senior house officer, psychiatry, Lynfield Mount Hospital, Bradford) translated one Italian paper. Matthias Egger and David Gunnell (department of social medicine, University of Bristol) gave useful comments on an earlier draft.
Footnotes
Funding: None.
Competing interests: None declared.
References
- 1.Thompson J, Rankin H, Ashcroft GW, Yates CM, McQueen JK, Cummings SW. The treatment of depression in general practice: a comparison of L-tryptophan, amitriptyline and a combination of L-tryptophan and amitriptyline with placebo. Psychol Med. 1982;12:741–751. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700049047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Johnson DAW. Treatment of depression in general practice. BMJ. 1973;ii:18–20. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5857.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Scott MG. The contributions of physical activity to psychological development. Res Q. 1960;31:307–320. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Biddle S, Fox K, Edmund L. Physical activity in primary care in England. London: Health Education Authority; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lepore SJ. Expressive writing moderates the relation between intrusive thoughts and depressive symptoms. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1997;73:1030–1037. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.73.5.1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mynors-Wallis LM, Gath DH, Baker F. Randomised controlled trial of problem solving treatment, antidepressant medication, and combined treatment for major depression in primary care. BMJ. 2000;320:26–30. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7226.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Leith LM. Foundations of exercise and mental health. Morgantown, WV: Fitness Information Technology; 1994. pp. 17–44. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Thornen P, Floras JS, Hoffman P, Seals DR. Endorphins and exercise: physiological mechanisms and clinical implications. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1990;22:417–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.North TC, McCullagh P, Vu Tran Z. Effect of exercise on depression. Exerc Sports Sci Rev. 1990;80:379–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Carlson DL. Milwaukee: University of Wisconsin; 1991. The effects of exercise on depression: a review and meta-regression analysis [dissertation] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Craft LL, Landers DM. The effects of exercise on clinical depression and depression resulting from mental illness: a meta-regression analysis. J Sport Exerc Psychol. 1998;20:339–357. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, Stroup DF.for the QUOROM Group. Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement Lancet 19993541896–1900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA. 1995;273:408–412. doi: 10.1001/jama.273.5.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rosenthal R. Parametric measures of effect size. In: Cooper H, Hedges LV, editors. The handbook of research synthesis. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 15.DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-regression analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–188. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Berlin JA, Laird NM, Sacks HS, Chalmers TC. A comparison of statistical methods for combining events rates from clinical trials. Stat Med. 1989;8:141–151. doi: 10.1002/sim.4780080202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Antonelli F. Sport and depression therapy. Int J Sport Psychol. 1982;13:187–193. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Biddle S. Exercise and psychosocial health. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1995;66:292–297. doi: 10.1080/02701367.1995.10607914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Biddle S. Exercise and the treatment of depression. Br J Hosp Med. 1989;42:267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Burbach FR. The efficacy of physical activity interventions within mental health services: anxiety and depressive disorders. J Ment Health. 1997;6:543–566. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Broocks A, Meyer TF, George A, Pekrun G, Hillmer-Vogel U, Hajak G, et al. Value of sports in treatment of psychiatric illness. Psychotherapie, Psychosomatik, Medizinische Psychologie. 1997;47:379–393. . (In German.) [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Byrne A, Byrne DG. The effect of exercise on depression, anxiety and other mood states: a review. J Psychosom Res. 1993;37:565–574. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(93)90050-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.De Coverley Veale DMW. Exercise and mental health. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1987;76:113–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1987.tb02872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dishman RK. Physical activity and public health: mental health. Quest. 1995;47:362–385. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Glenister D. Exercise and mental health: a review. J R Soc Health. 1996;116:7–13. doi: 10.1177/146642409611600102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gleser J, Mendelberg H. Exercise and sport in mental health: a review of the literature. Isr J Psychiatry Related Sci. 1990;27:99–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hales RE, Travis TW. Exercise as a treatment option for anxiety and depressive disorders. Milit Med. 1987;152:299–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.LaFontaine TP, DiLorenzo TM, Frensch PA, Stucky-Ropp RC, Bargman EP, McDonald DG. Aerobic exercise and mood. Sports Med. 1992;13:160–170. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199213030-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Martinsen EW. Proceedings of sport, health psychology and exercise symposium. London: Sports Council and Health Education Authority; 1988. Exercise intervention studies in patients with anxiety and depressive disorders [abstract] pp. 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Martinsen EW. Therapeutic implications of exercise for clinically anxious and depressed patients. Int J Sport Psychol. 1993;24:185–199. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Martinsen EW. The role of aerobic exercise in the treatment of depression. Stress Med. 1987;3:93–100. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Martinsen EW. Physical activity and depression: clinical experience. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1994;377(suppl):23–7S. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1994.tb05797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Moore KA, Blumenthal JA. Exercise training as an alternative treatment for depression among older adults. Altern Ther Health Med. 1998;4:48–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pezzarossa B, Fortuna E. Physical activity and psychopathological variables. Analytic Psychother Psychopathology. 1991;10:163–168. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Plante TG. Getting physical: does exercise help in the treatment of psychiatric disorders? J Psychos Nurs Ment Health Serv. 1996;34:39–43. doi: 10.3928/0279-3695-19960301-18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Raglin JS. Exercise and mental health. Beneficial and detrimental effects. Sports Med. 1990;9:323–329. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199009060-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Salmon P. Psychiatric benefits of physical exercise. Br J Hosp Med. 1990;43:107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sachs ML. Running therapy for the depressed client. Top Clin Nurs. 1981;3:77–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sachs ML. Exercise and running: effects on anxiety, depression and psychology. Humanistic Education Dev. 1982;21:51–57. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Scully D, Kremer J, Meade MM, Graham R, Dudgeon K. Physical exercise and psychological well being: a critical review. Br J Sports Med. 1998;32:111–120. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.32.2.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Simons AD, McGowan CR, Epstein LH, Kupfer DJ. Exercise as a treatment for depression: an update. Clin Psychol Rev. 1985;5:553–568. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sonstroem RJ. The psychological benefits of exercise. Med Health R I. 1997;80:295–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Van Coppenolle H, Pieters G, Knapen J, Peuskens J. Psychomotor therapy in depressive patients. Issues Special Education Rehabil. 1993;8:29–34. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Weinstein WS, Meyers AW. Running as treatment for depression: is it worth it? J Sport Psych. 1983;5:288–301. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Weyerer S, Kupfer B. Physical exercise and psychological health. Sports Med. 1994;17:108–116. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199417020-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Auchus MP, Kaslow NJ. Weight lifting therapy: a preliminary report. Psychosoc Rehabil J. 1994;18:99–102. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Blue FR. Aerobic running as a treatment for moderate depression. Percept Motor Skills. 1979;48:228. doi: 10.2466/pms.1979.48.1.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Conroy RW, Smith K, Felthous AR. The value of exercise on a psychiatric hospital unit. Hosp Community. 1982;33:641–645. doi: 10.1176/ps.33.8.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.D'Amato G. Hempstead, NY: Hofstra University; 1990. The relative efficacy of structured reminiscence and physical exercise on clinically depressed geriatric inpatients [dissertation] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Doyne EJ, Chambless DL, Beutler LE. Aerobic exercise as a treatment for depression in women. Behav Ther. 1983;14:434–440. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Fetsch RJ, Sprinkle RL. Effects of running on depressed adults. Am Ment Health Counselors Assoc J. 1983;5:75–84. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Giardinelli L, Di Bernardo M, Aiazzi V, Basile V. Depression and psychomotor retardation: exercise intervention combined with a pharmacological treatment of inpatients. Minerva Psichiatr. 1996;37:179–188. . (In Italian.) [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hartz GW, Wallace WL, Cayton TG. Effect of aerobic conditioning upon mood in clinically depressed men and women: a preliminary investigation. Percept Motor Skills. 1982;55:1217–1218. doi: 10.2466/pms.1982.55.3f.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kaplan K, Mendelson LB, Dubroff MP. The effect of a jogging program on psychiatric inpatients with symptoms of depression. Occup Ther J Res. 1983;3:173–175. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Martinsen EW, Sandvik L, Klobjornsrud O-B. Aerobic exercise in the treatment of nonpsychotic mental disorders: an exploratory study. Nord Psykiatr Tidsskr. 1989;43:521–529. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Palleschi L, De Gennaro E, Sottosanti G, Vetta F, Ponzoni S, Lato PFA, et al. The role of exercise training in aged subjects with anxiety-depression syndrome. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 1998;6(suppl):381–34S. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Pappas G, Golin S, Meyer DL. Reducing symptoms of depression with exercise [letter] Psychosomatics. 1990;31:112–113. doi: 10.1016/S0033-3182(90)72232-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Rief W, Hermanutz M. Responses to activation and rest in patients with panic disorder and major depression. Br J Clin Psychol. 1996;35:605–616. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8260.1996.tb01216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Stewart NJ, McMullen LM, Rubin LD. Movement therapy with depressed inpatients: a randomised multiple single case design. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 1994;8:22–29. doi: 10.1016/0883-9417(94)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Williams JM, Getty D. Effect of levels of exercise on psychological mood states, physical fitness and plasma beta-endorphin. Percept Mot Skills. 1986;63:1099–1105. doi: 10.2466/pms.1986.63.3.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Hannaford CP, Harrell EH, Cox K. Psychophysiological effects of a running program on depression and anxiety in a psychiatric population. Psychological Record. 1988;38:37–48. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Netz Y, Yaretzki A, Salganik I, Jacob T, Finkeltov B, Argov E. The effect of supervised physical activity on cognitive and affective state of geriatric and psychogeriatric in-patients. Clin Gerontol. 1994;15:47–56. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Pelham TW, Compagna PD, Ritvo PG, Birnnie WA. The effects of exercise therapy on clients in a psychiatric rehabilitation program. Psychosoc Rehabil J. 1993;16:75–83. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Perri S, II, Temper DI. The effects of an aerobic exercise programme on psychological variables in older adults. Int J Aging Hum Dev. 1985;20:1984–1985. doi: 10.2190/a6ab-mbn1-g8hv-258h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Roth DL, Holmes DS. Influence of aerobic exercise training and relaxation training on physical and psychological health following stressful life events. Psychosom Med. 1987;49:355–365. doi: 10.1097/00006842-198707000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.DiLornzo TM, Bargman EP, Stucky-Ropp R, Brassington GS, Frensch PA, LaFontaine T. Long term effects of aerobic exercise on psychological outcomes. Prev Med. 1999;28:75–85. doi: 10.1006/pmed.1998.0385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Emery CF, Gatz A. Psychological and cognitive effects of an exercise program for community-residing older adults. Gerontologist. 1990;30:184–188. doi: 10.1093/geront/30.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Emery CF, Blumenthal JA. Perceived change among participants in an exercise program for older adults. Gerontologist. 1990;30:516–521. doi: 10.1093/geront/30.4.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Bosscher RJ. Running and mixed physical exercises with depressed psychiatric patients. Int J Sport Psychol. 1993;24:170–184. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Martinsen EW. Proceedings of sport, health psychology and exercise symposium. London: Sports Council and Health Education Authority; 1988. Comparing aerobic and non-aerobic forms of exercise in the treatment of clinical depression: a randomised trial [abstract] pp. 84–95. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Martinsen EW, Hoffart A, Solberg O. Comparing aerobic with nonaerobic forms of exercise in the treatment of clinical depression: a randomised trial. Compr Psychiatry. 1989;30:324–331. doi: 10.1016/0010-440x(89)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Sexton H, Maere A, Dahl NH. Exercise intensity and reduction in neurotic symptoms. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1989;80:231–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1989.tb01332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Blumenthal JA, Babyak MA, Moore KA, Craighead WE, Herman S, Khatri P, et al. Effects of exercise training on older patients with major depression. Arch Intern Med. 1999;159:2349–2356. doi: 10.1001/archinte.159.19.2349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Singh NA, Clements KM, Fiatarone MA. A randomized controlled trial of progressive resistance training in depressed elders. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1997;52(1):M27–M35. doi: 10.1093/gerona/52a.1.m27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Veale D, Le Fevre K, Pantelis C, de Souza V, Mann A. Aerobic exercise in the adjunctive treatment of depression: a randomised controlled trial. J R Soc Med. 1992;85:541–544. doi: 10.1177/014107689208500910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Veale D, Le Fevre K. Proceedings of sport, health psychology and exercise symposium. London: Sports Council and Health Education Authority; 1988. Aerobic exercise in the adjunctive treatment of depression: a randomised controlled trial [abstract] pp. 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- 77.McNeil JK, LeBlanc EM, Joyner M. The effect of exercise on depressive symptoms in the moderately depressed elderly. Psychol Aging. 1991;6:487–488. doi: 10.1037//0882-7974.6.3.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Mutrie N. Proceedings of sport, health psychology and exercise symposium. London: Sports Council and Health Education Authority; 1988. Exercise as a treatment for moderate depression in the UK National Health Service[abstract] pp. 96–105. [Google Scholar]
- 79.Doyne EJ, Ossip-Klein DJ, Bowman ED, Osborn KM, McDoughall-Wilson IB, Neimeyer RA. Running versus weight lifting in the treatment of depression. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1987;55:748–754. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.55.5.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Fremont J, Wilcoxon Craighead L. Aerobic exercise and cognitive therapy in the treatment of dysphoric moods. Cognitive Ther Res. 1987;11:241–251. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Epstein D. Reno: University of Nevada; 1986. Aerobic activity versus group cognitive therapy: an evaluative study of contrasting interventions for the alleviation of clinical depression [dissertation] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Martinsen EW, Medhus A, Sandvik L. Effects of aerobic exercise on depression: a controlled study. BMJ. 1985;291:109. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6488.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Martinsen EW, Medhus A. Adherence to exercise and patients' evaluation of physical exercise in a comprehensive treatment programme for depression. Nord Psykiatr Tidsskr. 1989;43:411–415. [Google Scholar]
- 84.Klein MH, Greist JH, Gurman RA, Neimeyer RA, Lesser DP, Bushnell NJ, et al. A comparative outcome study of group psychotherapy vs. exercise treatments for depression. Int J Ment Health. 1985;13:148–177. [Google Scholar]
- 85.McCann L, Holmes DS. Influence of aerobic exercise on depression. J Pers Social Psychol. 1984;46:1142–1147. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.46.5.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Reuter M, Mutrie N, Harris DV. Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania State University; 1984. Running as an adjunct to counseling in the treatment of depression [dissertation] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Hess-Homeier MJ. Missoula: University of Montana; 1981. A comparison of Beck's cognitive therapy and jogging as treatments for depression [dissertation] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Greist JH, Klein MH, Eischens RJ, Faris J, Gurman AS, Morgan WP. Running as treatment for depression. Compr Psychiatry. 1979;20:41–54. doi: 10.1016/0010-440x(79)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Fox K, Biddle S, Edmunds L, Bowler I, Killoran AL. Physical activity promotion through primary health care in England. Br J Gen Pract. 1997;47:367–369. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Hotopf M, Lewis G, Normand C. Putting trials on trial—the costs and consequences of small trials in depression: a systematic review of methodology. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1997;51:354–358. doi: 10.1136/jech.51.4.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Streiner DL, Joffe R. The adequacy of reporting randomized controlled trials in the evaluation of antidepressants. Can J Psychiatry. 1998;43:1026–1030. doi: 10.1177/070674379804301008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Fentem PH. Benefits of exercise in health and disease. BMJ. 1994;308:1291–1295. doi: 10.1136/bmj.308.6939.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Berlin JA, Colditz GA. A meta-regression analysis of physical activity in the prevention of coronary heart disease. Am J Epidemiol. 1990;132:612–628. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.