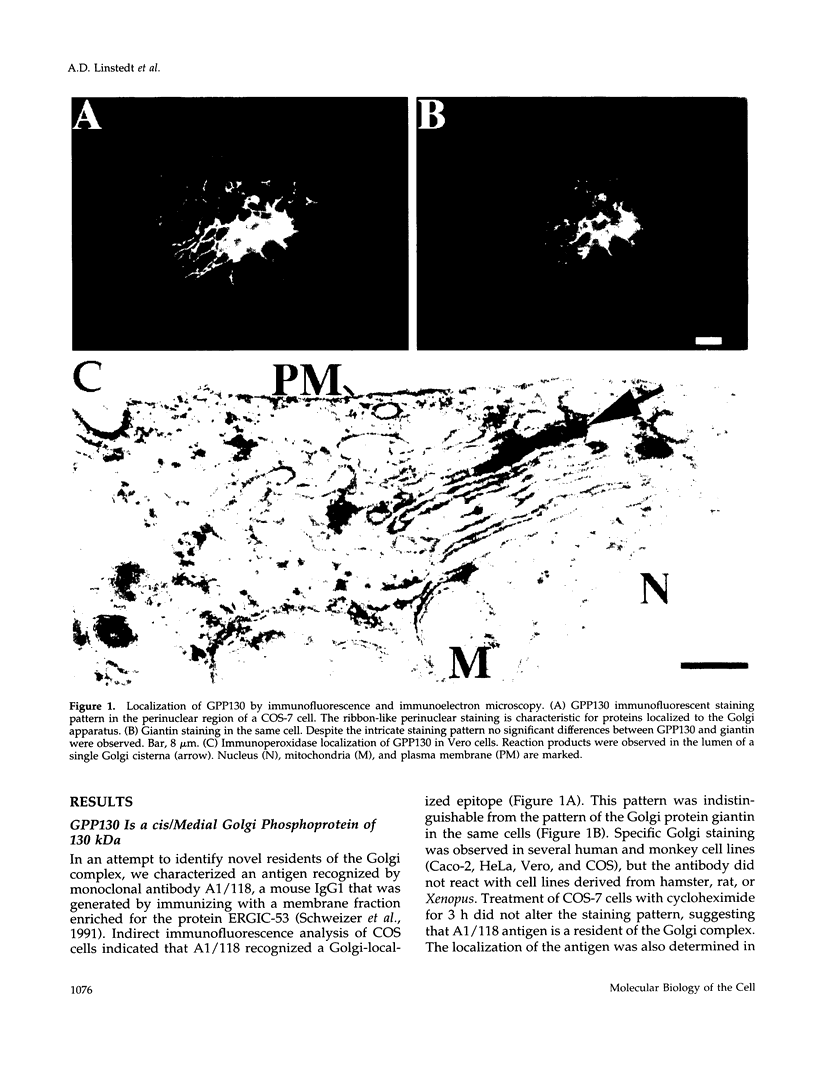
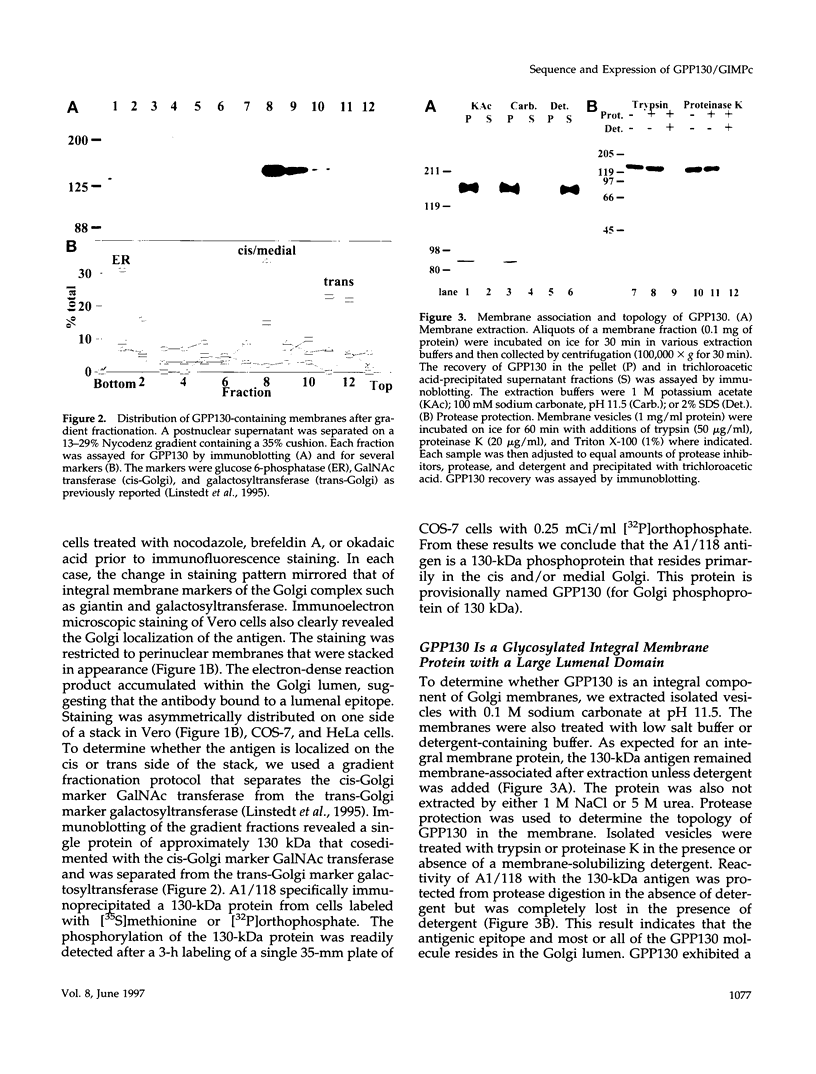
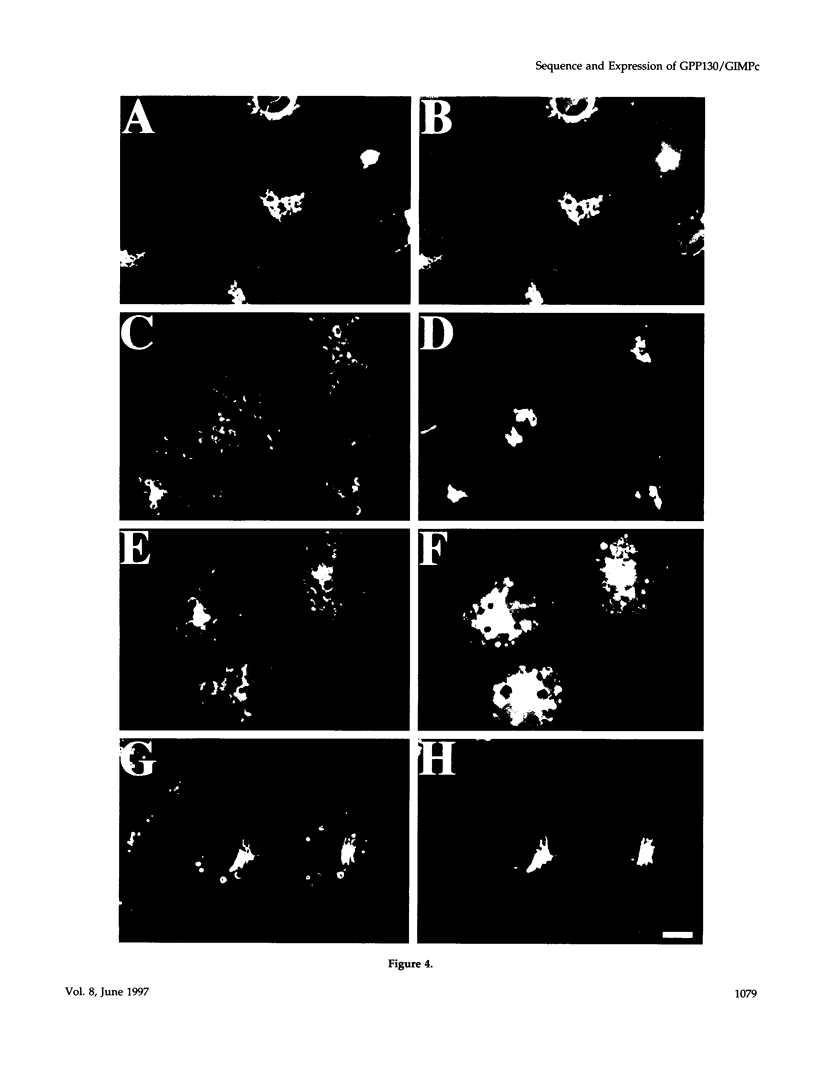
Abstract
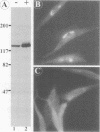
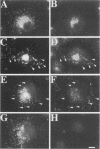
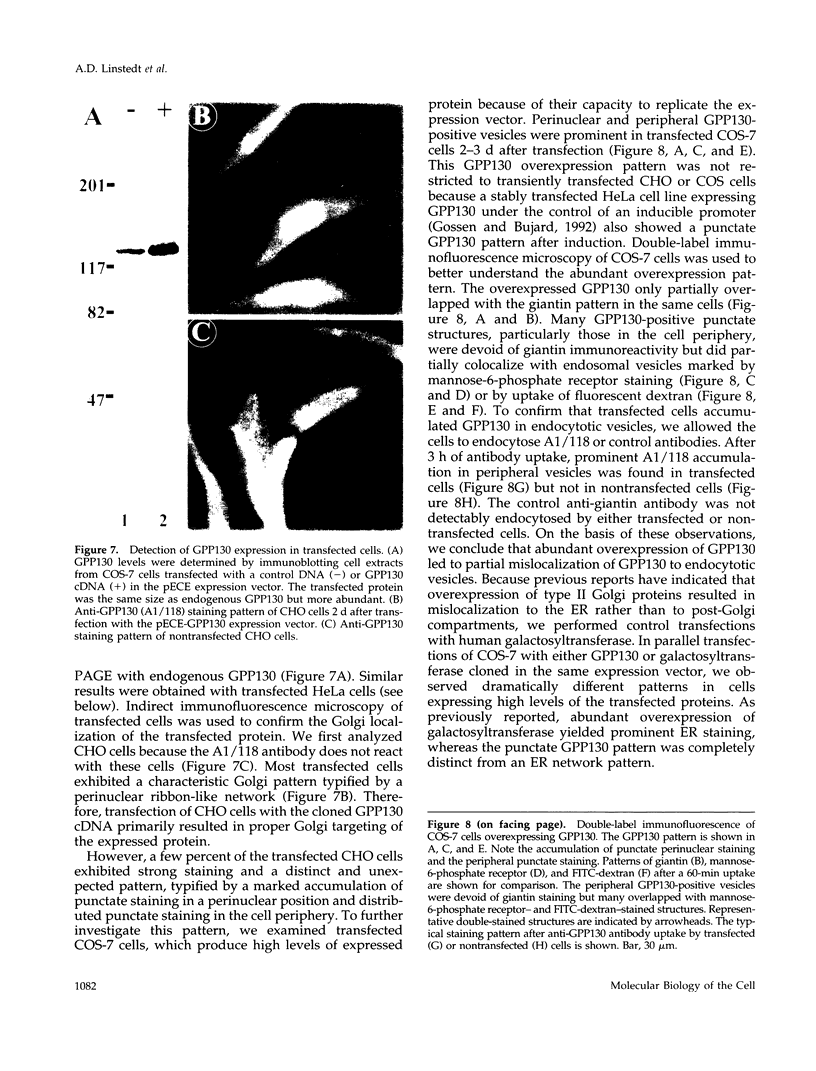
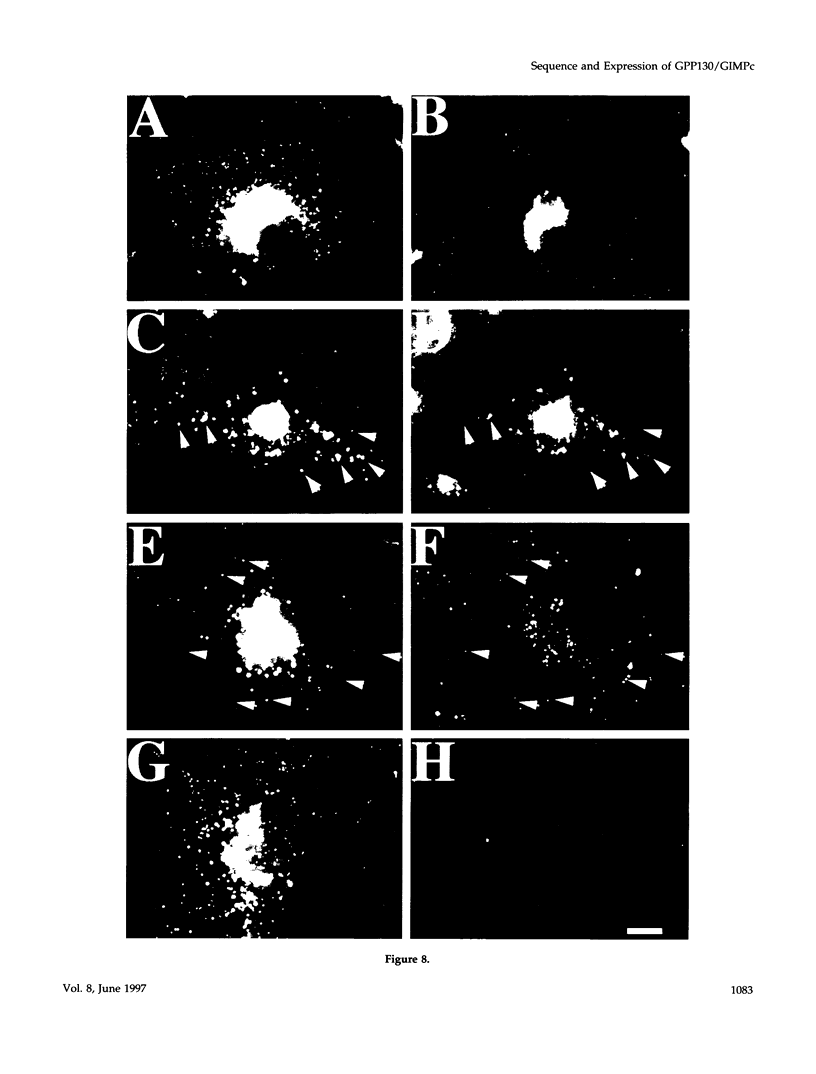
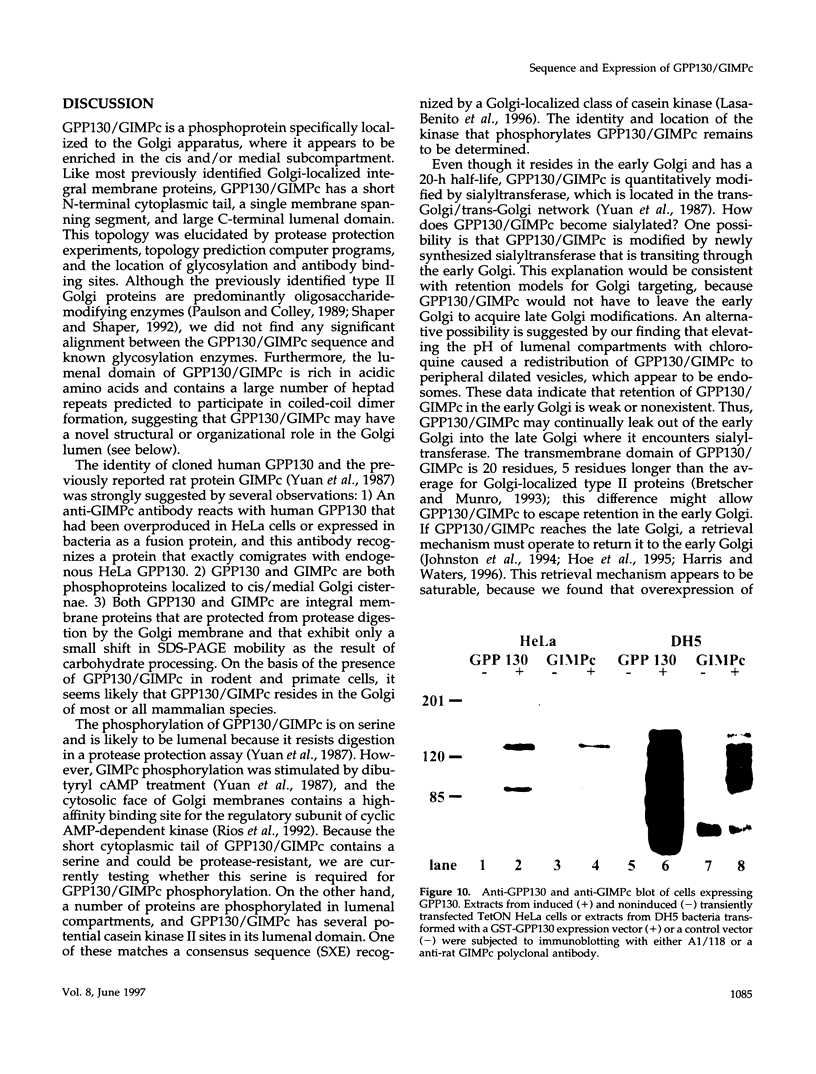
It is thought that residents of the Golgi stack are localized by a retention mechanism that prevents their forward progress. Nevertheless, some early Golgi proteins acquire late Golgi modifications. Herein, we describe GPP130 (Golgi phosphoprotein of 130 kDa), a 130-kDa phosphorylated and glycosylated integral membrane protein localized to the cis/medial Golgi. GPP130 appears to be the human counterpart of rat Golgi integral membrane protein, cis (GIMPc), a previously identified early Golgi antigen that acquires late Golgi carbohydrate modifications. The sequence of cDNAs encoding GPP130 indicate that it is a type II membrane protein with a predicted molecular weight of 81,880 and an unusually acidic lumenal domain. On the basis of the alignment with several rod-shaped proteins and the presence of multiple predicted coiled-coil regions, GPP130 may form a flexible rod in the Golgi lumen. In contrast to the behavior of previously studied type II Golgi proteins, overexpression of GPP130 led to a pronounced accumulation in endocytotic vesicles, and endogenous GPP130 reversibly redistributed to endocytotic vesicles after chloroquine treatment. Thus, localization of GPP130 to the early Golgi involves steps that are saturable and sensitive to lumenal pH, and GPP130 contains targeting information that specifies its return to the Golgi after chloroquine washout. Given that GIMPc acquires late Golgi modifications in untreated cells, it seems likely that GPP130/GIMPc continuously cycles between the early Golgi and distal compartments and that an unidentified retrieval mechanism is important for its targeting.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antebi A., Fink G. R. The yeast Ca(2+)-ATPase homologue, PMR1, is required for normal Golgi function and localizes in a novel Golgi-like distribution. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jun;3(6):633–654. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.6.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appel R. D., Bairoch A., Hochstrasser D. F. A new generation of information retrieval tools for biologists: the example of the ExPASy WWW server. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jun;19(6):258–260. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. G., Aegerter E., Mandel T., Hauri H. P. Monoclonal antibodies to soluble, human milk galactosyltransferase (lactose synthase A protein). Carbohydr Res. 1986 Jun 1;149(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90366-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. G., Grimm K., Bächi T., Bosshart H., Kleene R., Watzele M. Double immunofluorescent staining of alpha 2,6 sialyltransferase and beta 1,4 galactosyltransferase in monensin-treated cells: evidence for different Golgi compartments? J Cell Biochem. 1993 Jul;52(3):275–288. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240520304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos K., Wraight C., Stanley K. K. TGN38 is maintained in the trans-Golgi network by a tyrosine-containing motif in the cytoplasmic domain. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2219–2228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05870.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Bucher P., Nourbakhsh I. R., Blaisdell B. E., Karlin S. Methods and algorithms for statistical analysis of protein sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2002–2006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S., Munro S. Cholesterol and the Golgi apparatus. Science. 1993 Sep 3;261(5126):1280–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.8362242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J., Goodhouse J., Farquhar M. G. Mannose-6-phosphate receptors for lysosomal enzymes cycle between the Golgi complex and endosomes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1235–1247. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. E., Munro S. Retrieval of TGN proteins from the cell surface requires endosomal acidification. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2305–2312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06514.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole N. B., Smith C. L., Sciaky N., Terasaki M., Edidin M., Lippincott-Schwartz J. Diffusional mobility of Golgi proteins in membranes of living cells. Science. 1996 Aug 9;273(5276):797–801. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5276.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G., Palade G. E. The Golgi apparatus (complex)-(1954-1981)-from artifact to center stage. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):77s–103s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.77s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossen M., Bujard H. Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Hoflack B., Simons K., Mellman I., Kornfeld S. The mannose 6-phosphate receptor and the biogenesis of lysosomes. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):329–341. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. E., Lund O., Engelbrecht J., Bohr H., Nielsen J. O., Hansen J. E. Prediction of O-glycosylation of mammalian proteins: specificity patterns of UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. Biochem J. 1995 Jun 15;308(Pt 3):801–813. doi: 10.1042/bj3080801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris S. L., Waters M. G. Localization of a yeast early Golgi mannosyltransferase, Och1p, involves retrograde transport. J Cell Biol. 1996 Mar;132(6):985–998. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.6.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Sterchi E. E., Bienz D., Fransen J. A., Marxer A. Expression and intracellular transport of microvillus membrane hydrolases in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):838–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobohm U., Sander C. A sequence property approach to searching protein databases. J Mol Biol. 1995 Aug 18;251(3):390–399. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoe M. H., Slusarewicz P., Misteli T., Watson R., Warren G. Evidence for recycling of the resident medial/trans Golgi enzyme, N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I, in ldlD cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 20;270(42):25057–25063. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.42.25057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. S., Peters P. J., Yuan L. C., Bonifacino J. S. Localization of TGN38 to the trans-Golgi network: involvement of a cytoplasmic tyrosine-containing sequence. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1123–1135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Stieber A., Gonatas N. K. A hypothesis on the traffic of MG160, a medial Golgi sialoglycoprotein, from the trans-Golgi network to the Golgi cisternae. J Cell Sci. 1994 Mar;107(Pt 3):529–537. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Interpreting cDNA sequences: some insights from studies on translation. Mamm Genome. 1996 Aug;7(8):563–574. doi: 10.1007/s003359900171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasa-Benito M., Marin O., Meggio F., Pinna L. A. Golgi apparatus mammary gland casein kinase: monitoring by a specific peptide substrate and definition of specificity determinants. FEBS Lett. 1996 Mar 11;382(1-2):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Kim I. G., Marekov L. N., O'Keefe E. J., Parry D. A., Steinert P. M. The structure of human trichohyalin. Potential multiple roles as a functional EF-hand-like calcium-binding protein, a cornified cell envelope precursor, and an intermediate filament-associated (cross-linking) protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):12164–12176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linstedt A. D., Foguet M., Renz M., Seelig H. P., Glick B. S., Hauri H. P. A C-terminally-anchored Golgi protein is inserted into the endoplasmic reticulum and then transported to the Golgi apparatus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):5102–5105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.5102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linstedt A. D., Hauri H. P. Giantin, a novel conserved Golgi membrane protein containing a cytoplasmic domain of at least 350 kDa. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jul;4(7):679–693. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.7.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupas A., Van Dyke M., Stock J. Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1162–1164. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E. Targeting and retention of Golgi membrane proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;5(4):606–612. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90129-E. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Mikawa T., Ebashi S. Detection of calcium binding proteins by 45Ca autoradiography on nitrocellulose membrane after sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):511–519. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masibay A. S., Balaji P. V., Boeggeman E. E., Qasba P. K. Mutational analysis of the Golgi retention signal of bovine beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9908–9916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Simons K. The Golgi complex: in vitro veritas? Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):829–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90027-A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy S. S., Thomas L., VanSlyke J. K., Stenberg P. E., Thomas G. Intracellular trafficking and activation of the furin proprotein convertase: localization to the TGN and recycling from the cell surface. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):18–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06231.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S. Sequences within and adjacent to the transmembrane segment of alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase specify Golgi retention. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3577–3588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04924.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Hoe M. H., Slusarewicz P., Rabouille C., Watson R., Hunte F., Watzele G., Berger E. G., Warren G. Kin recognition between medial Golgi enzymes in HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):562–574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06294.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Lucocq J. M., Mackay D., Warren G. The membrane spanning domain of beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase specifies trans Golgi localization. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3567–3575. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Slusarewicz P., Hoe M. H., Warren G. Kin recognition. A model for the retention of Golgi enzymes. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 6;330(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80906-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Warren G. Retention and retrieval in the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;6(4):517–521. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90070-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nothwehr S. F., Roberts C. J., Stevens T. H. Membrane protein retention in the yeast Golgi apparatus: dipeptidyl aminopeptidase A is retained by a cytoplasmic signal containing aromatic residues. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(6):1197–1209. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.6.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. C., Colley K. J. Glycosyltransferases. Structure, localization, and control of cell type-specific glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17615–17618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambourg A., Clermont Y. Three-dimensional electron microscopy: structure of the Golgi apparatus. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;51(2):189–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaves B., Banting G. Overexpression of TGN38/41 leads to mislocalisation of gamma-adaptin. FEBS Lett. 1994 Sep 12;351(3):448–456. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00813-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaves B., Horn M., Banting G. TGN38/41 recycles between the cell surface and the TGN: brefeldin A affects its rate of return to the TGN. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):93–105. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reggio H., Webster P., Louvard D. Use of immunocytochemical techniques in studying the biogenesis of cell surfaces in polarized epithelia. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:379–395. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rios R. M., Celati C., Lohmann S. M., Bornens M., Keryer G. Identification of a high affinity binding protein for the regulatory subunit RII beta of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in Golgi enriched membranes of human lymphoblasts. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1723–1731. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Molecular dissection of the secretory pathway. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):409–415. doi: 10.1038/355409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer P. E., Lederkremer G. Z., Williams S., Fogliano M., Baldini G., Lodish H. F. Cab45, a novel (Ca2+)-binding protein localized to the Golgi lumen. J Cell Biol. 1996 Apr;133(2):257–268. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer A., Matter K., Ketcham C. M., Hauri H. P. The isolated ER-Golgi intermediate compartment exhibits properties that are different from ER and cis-Golgi. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):45–54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift A. M., Machamer C. E. A Golgi retention signal in a membrane-spanning domain of coronavirus E1 protein. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):19–30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sönnichsen B., Watson R., Clausen H., Misteli T., Warren G. Sorting by COP I-coated vesicles under interphase and mitotic conditions. J Cell Biol. 1996 Sep;134(6):1411–1425. doi: 10.1083/jcb.134.6.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorhees P., Deignan E., van Donselaar E., Humphrey J., Marks M. S., Peters P. J., Bonifacino J. S. An acidic sequence within the cytoplasmic domain of furin functions as a determinant of trans-Golgi network localization and internalization from the cell surface. EMBO J. 1995 Oct 16;14(20):4961–4975. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisz O. A., Swift A. M., Machamer C. E. Oligomerization of a membrane protein correlates with its retention in the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(6):1185–1196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.6.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. H., Hong W. The SXYQRL sequence in the cytoplasmic domain of TGN38 plays a major role in trans-Golgi network localization. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22853–22862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L., Barriocanal J. G., Bonifacino J. S., Sandoval I. V. Two integral membrane proteins located in the cis-middle and trans-part of the Golgi system acquire sialylated N-linked carbohydrates and display different turnovers and sensitivity to cAMP-dependent phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):215–227. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]