Abstract
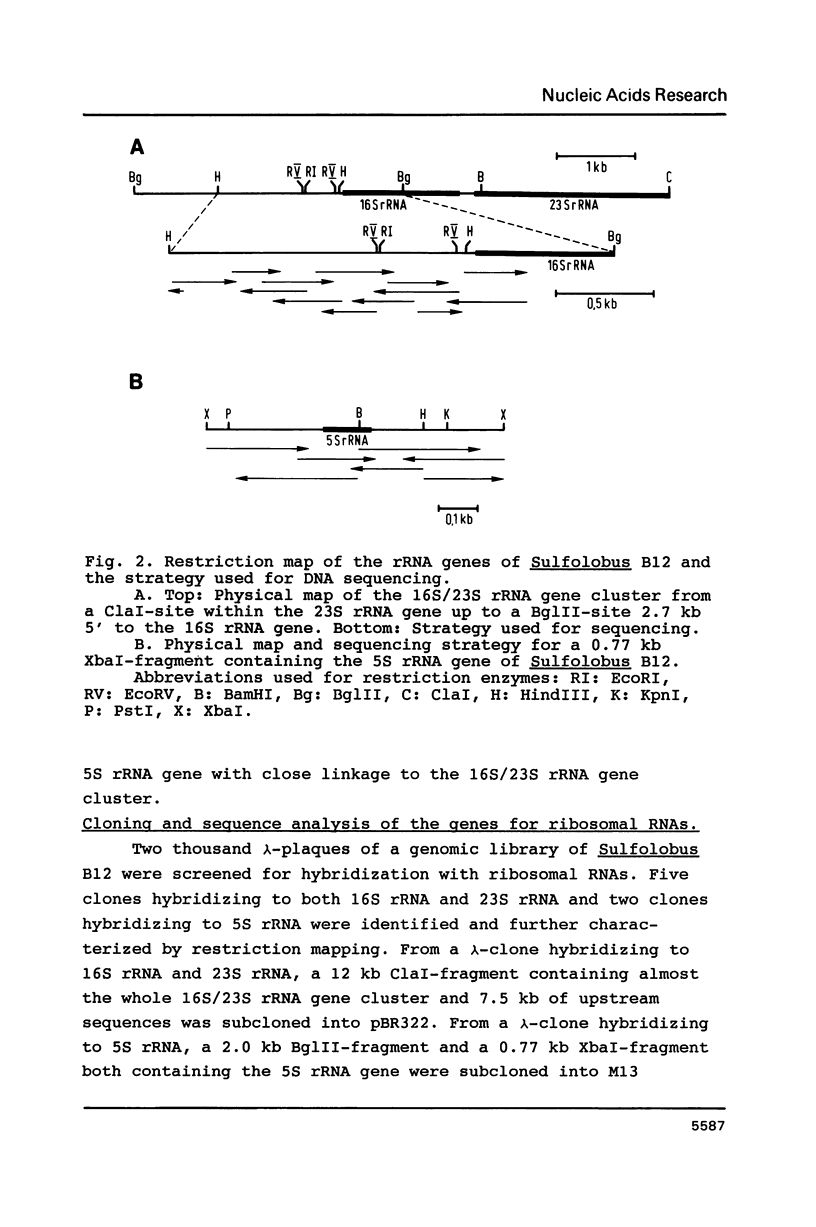
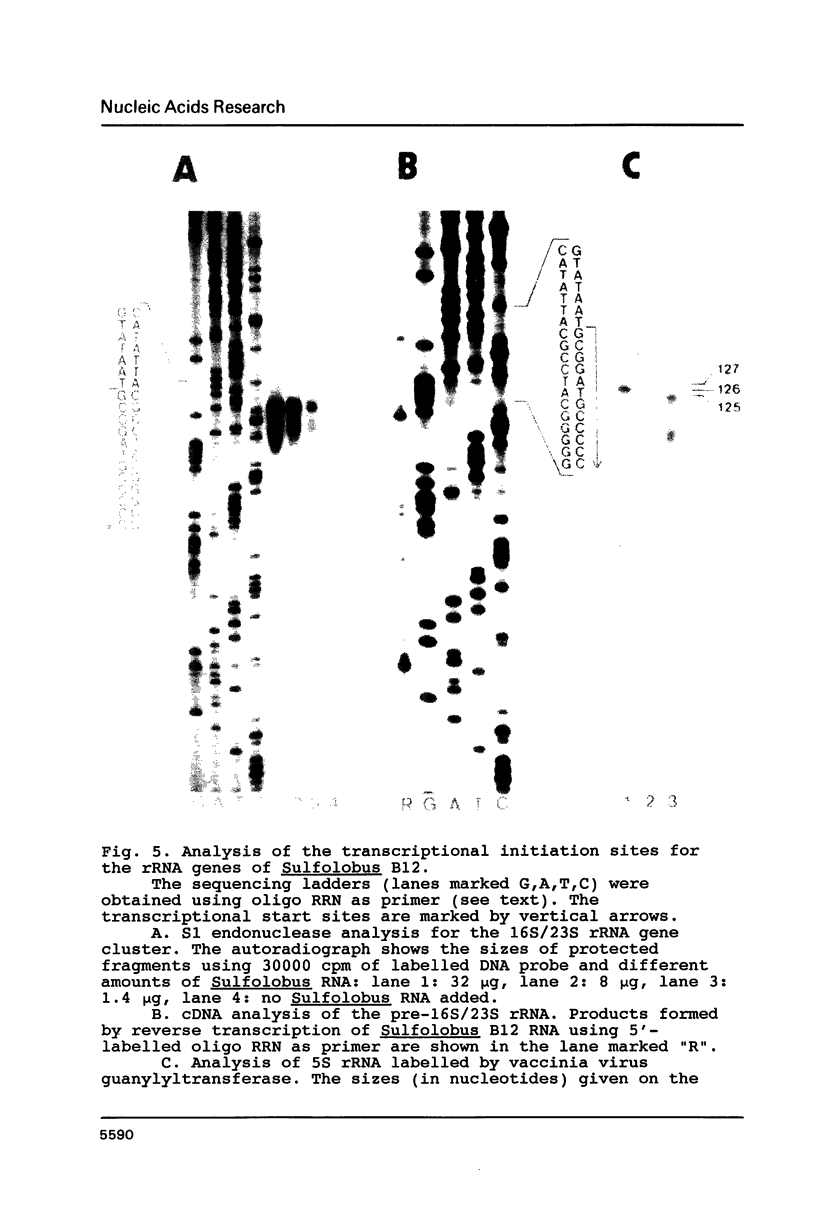
In Sulfolobus sp. strain B12, single-copy genes encode the three ribosomal RNAs. The genes for the 16S rRNA and for the 23S rRNA are closely linked but separated from the 5S rRNA gene. Transcription of the 16S/23S rRNA gene cluster starts 139 nucleotides upstream of the 5'-end of mature 16S rRNA. For the 5S rRNA gene the point of transcription initiation coincides with the 5'-end of mature 5S rRNA. The comparison of the upstream regions for these transcriptional start sites shows the presence of a completely conserved trinucleotide sequence around the point of transcription initiation and a completely conserved octanucleotide sequence about 22 nucleotides upstream of it. These sequences are only moderately homologous to putative promoter elements for stable RNA genes in the closely related archaebacterium Thermoproteus tenax (1), but they are very similar to corresponding sequences in the distantly related archaebacterium Methanococcus vannielii (2). The consensus sequence found for Sulfolobus and Methanococcus could therefore constitute the archetype of an archaebacterial promoter for stable RNA genes.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dams E., Londei P., Cammarano P., Vandenberghe A., De Wachter R. Sequences of the 5S rRNAs of the thermo-acidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus (Caldariella acidophila) and the thermophilic eubacteria Bacillus acidocaldarius and Thermus aquaticus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4667–4676. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dassarma S., Rajbhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. Bacterio-opsin mRNA in wild-type and bacterio-opsin-deficient Halobacterium halobium strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):125–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis P. P. Multiple promoters for the transcription of the ribosomal RNA gene cluster in Halobacterium cutirubrum. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):457–461. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doel M. T., Houghton M., Cook E. A., Carey N. H. The presence of ovalbumin mRNA coding sequences in multiple restriction fragments of chicken DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Nov;4(11):3701–3713. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.11.3701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman J. D., Lau R. H., Doolittle W. F. The number, physical organization and transcription of ribosomal RNA cistrons in an archaebacterium: Halobacterium halobium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1321–1333. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Pace N. R., Nuell M., Kaine B. P., Gupta R., Woese C. R. Sequence of the 16S rRNA gene from the thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus and its evolutionary implications. J Mol Evol. 1985;22(4):301–307. doi: 10.1007/BF02115685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. A., Luehrsen K. R., Woese C. R., Pace N. R. An unusual 5S rRNA, from Sulfolobus acidocaldarius, and its implications for a general 5S rRNA structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6129–6137. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wich G., Hummel H., Jarsch M., Bär U., Böck A. Transcription signals for stable RNA genes in Methanococcus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2459–2479. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wich G., Jarsch M., Böck A. Apparent operon for a 5S ribosomal RNA gene and for tRNA genes in the archaebacterium Methanococcus vannielii. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(1):146–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00334107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wich G., Leinfelder W., Böck A. Genes for stable RNA in the extreme thermophile Thermoproteus tenax: introns and transcription signals. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):523–528. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04784.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Olsen G. J. Archaebacterial phylogeny: perspectives on the urkingdoms. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1986;7:161–177. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(86)80001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeats S., McWilliam P., Zillig W. A plasmid in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1035–1038. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01292.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]