Abstract
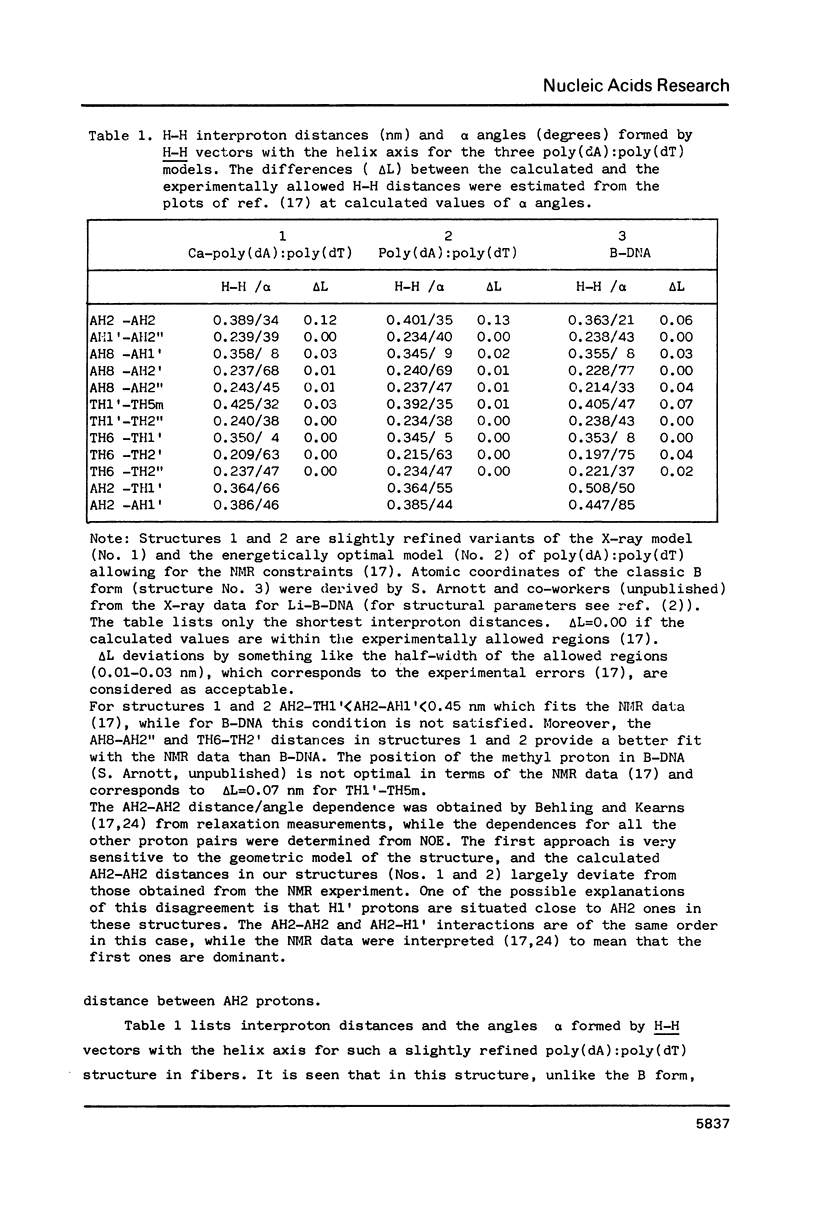
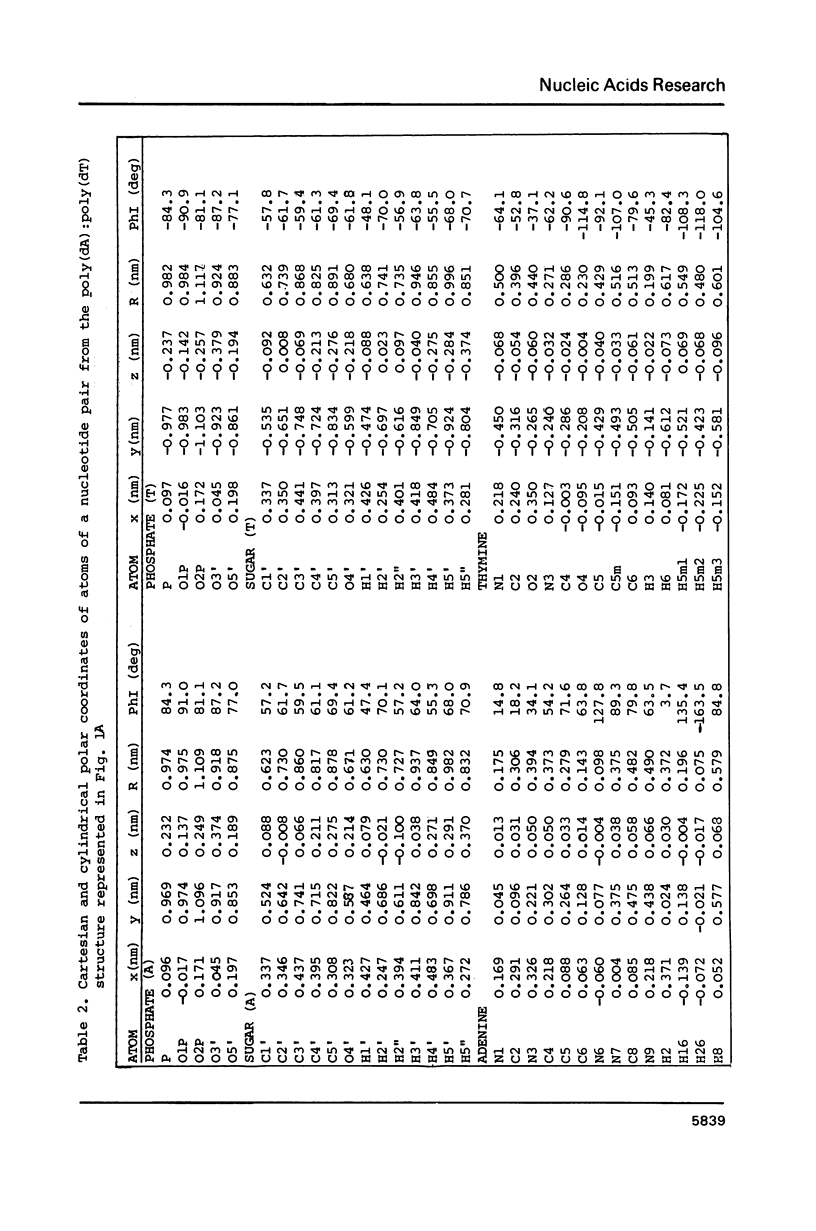
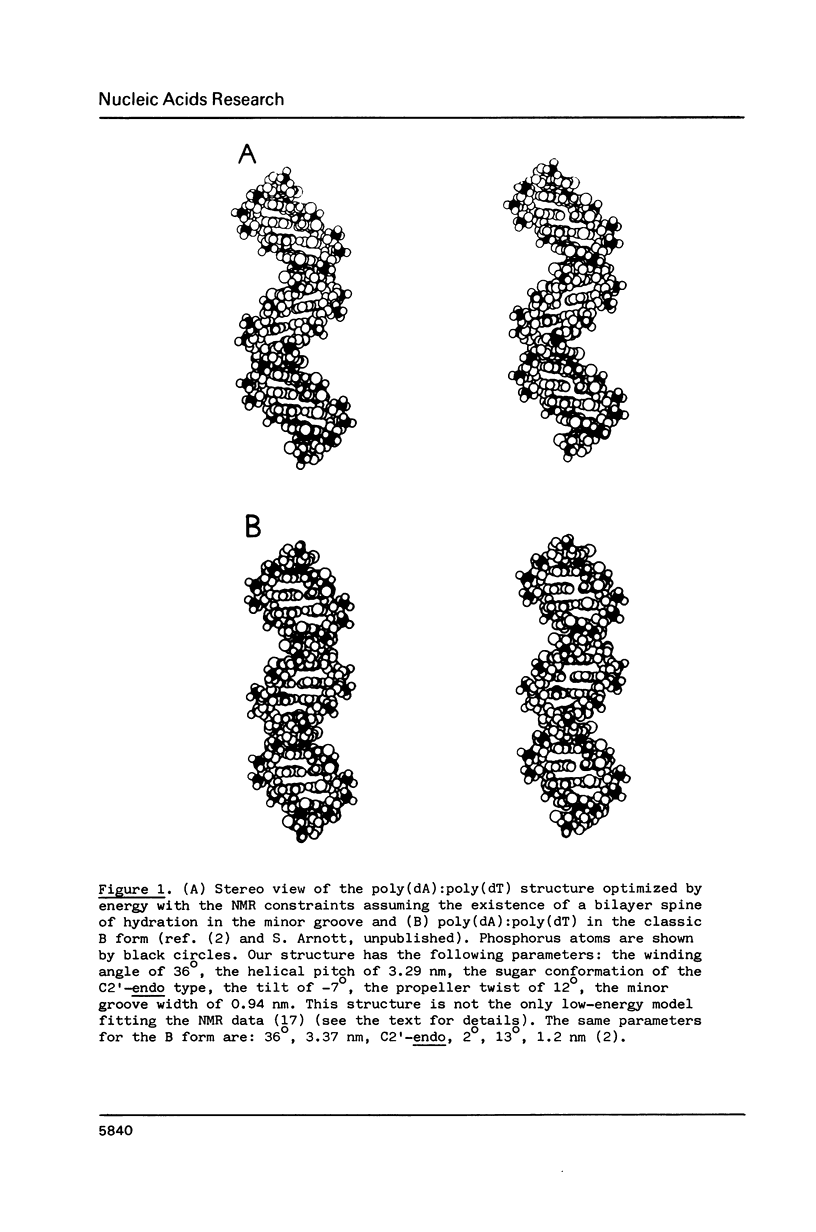
New X-ray and energetically optimal models of poly(dA):poly(dT) with the hydration spine in the minor groove have been compared with the NMR data in solution (Behling, R.W. and Kearns, D.R. (1986) Biochemistry 25, 3335-3346). These models have been refined to achieve a better fit with the NMR data. The obtained results suggest that the poly(dA):poly(dT) structure in a condensed state is similar to that in solution. The proposed conformations of poly(dA):poly(dT), unlike the classic B form, satisfy virtually all geometrical requirements which follow from the NMR data. Thus, the X-ray and energetically optimal poly(dA):poly(dT) structures (or those with slight modifications) can be considered as credible models of the poly(dA):poly(dT) double helix in solution. One of the features distinguishing these models from the classic B form is a narrowed minor groove.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexeev D. G., Lipanov A. A., Skuratovskii IYa Poly(dA).poly(dT) is a B-type double helix with a distinctively narrow minor groove. 1987 Feb 26-Mar 4Nature. 325(6107):821–823. doi: 10.1038/325821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Hall I. H., Puigjaner L. C. Heteronomous DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4141–4155. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Selsing E. Structures for the polynucleotide complexes poly(dA) with poly (dT) and poly(dT) with poly(dA) with poly (dT). J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):509–521. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90498-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behling R. W., Kearns D. R. 1H two-dimensional nuclear Overhauser effect and relaxation studies of poly(dA).poly(dT) Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3335–3346. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behling R. W., Kearns D. R. Determination of NOE "silent" dipolar interactions between magnetically equivalent nuclei: application to poly(dA).poly(dT). Biopolymers. 1985 Jul;24(7):1157–1167. doi: 10.1002/bip.360240705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuprina V. P. Anomalous structure and properties of poly (dA).poly(dT). Computer simulation of the polynucleotide structure with the spine of hydration in the minor groove. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):293–311. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuprina V. P. Regularities in formation of the spine of hydration in the DNA minor groove and its influence on the DNA structure. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 1;186(1):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81347-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. III. Geometry of hydration. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):535–556. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA structural variations in the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratini A. V., Kopka M. L., Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Reversible bending and helix geometry in a B-DNA dodecamer: CGCGAATTBrCGCG. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14686–14707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz D. S., Wang J. C. Torsional rigidity of DNA and length dependence of the free energy of DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 15;173(1):75–91. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Fratini A. V., Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Ordered water structure around a B-DNA dodecamer. A quantitative study. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 5;163(1):129–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Sequence dependence of the helical repeat of DNA in solution. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):375–378. doi: 10.1038/292375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poltev V. I., Grokhlina T. I., Malenkov G. G. Hydration of nucleic acid bases studied using novel atom-atom potential functions. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1984 Oct;2(2):413–429. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1984.10507576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Sequence-dependent helical periodicity of DNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):378–380. doi: 10.1038/292378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma M. H., Gupta G., Sarma R. H. Untenability of the heteronomous DNA model for poly(dA).poly(dT) in solution. This DNA adopts a right-handed B-DNA duplex in which the two strands are conformationally equivalent. A 500 MHz NMR study using one dimensional NOE. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Jun;2(6):1057–1084. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10507624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Gaillard C., Prunell A. Helical periodicity of DNA, Poly(dA) . poly(dT) and poly(dA-dT). poly(dA-dT) in solution. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(2):215–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06389.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ul'ianov N. B., Zhurkin V. B. Izuchenie gibkosti komplementarnykh dinukleozidfosfatov metodom Monte-Karlo. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1982 Sep-Oct;16(5):1075–1085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhurkin V. B., Poltev V. I., Florent'ev V. L. Atom-atomnye potentsial'nye funktsii dlia konformatsionnykh raschetov nukleinovykh kislot. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1980 Sep-Oct;14(5):1116–1130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


