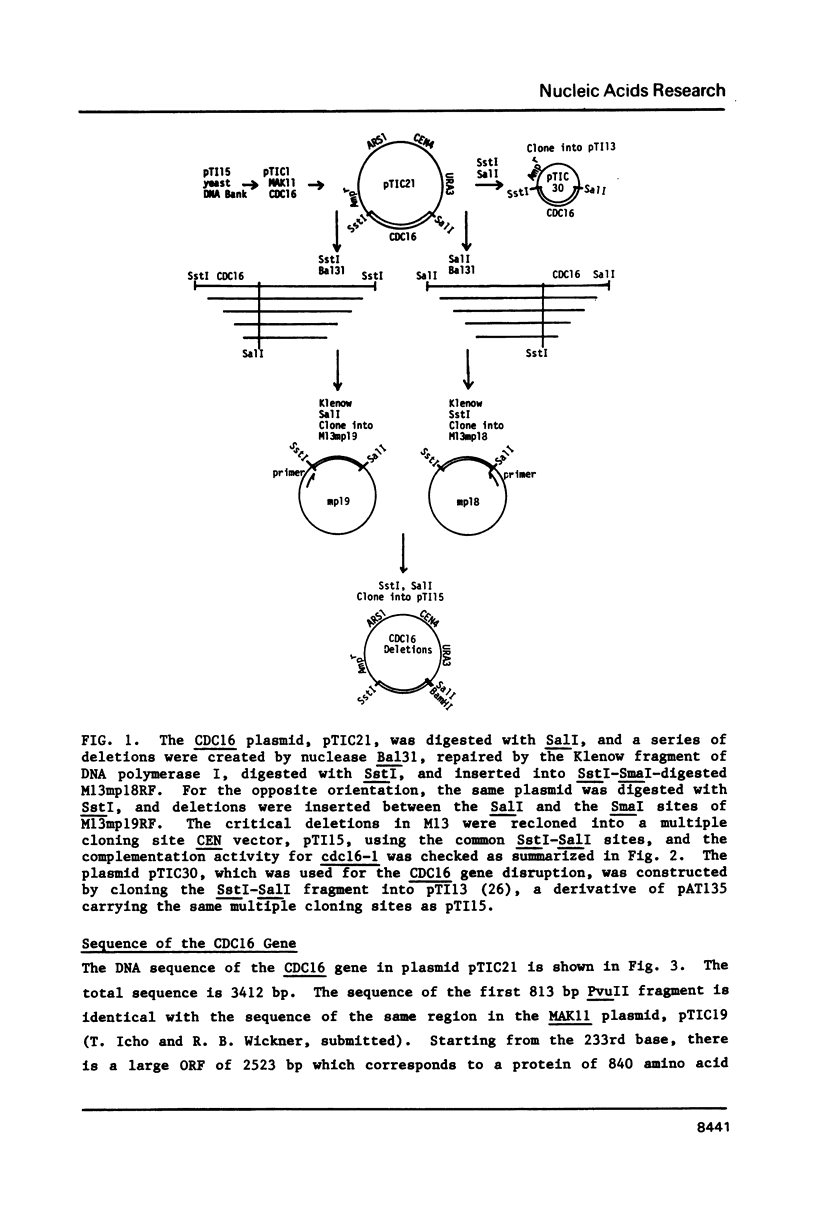
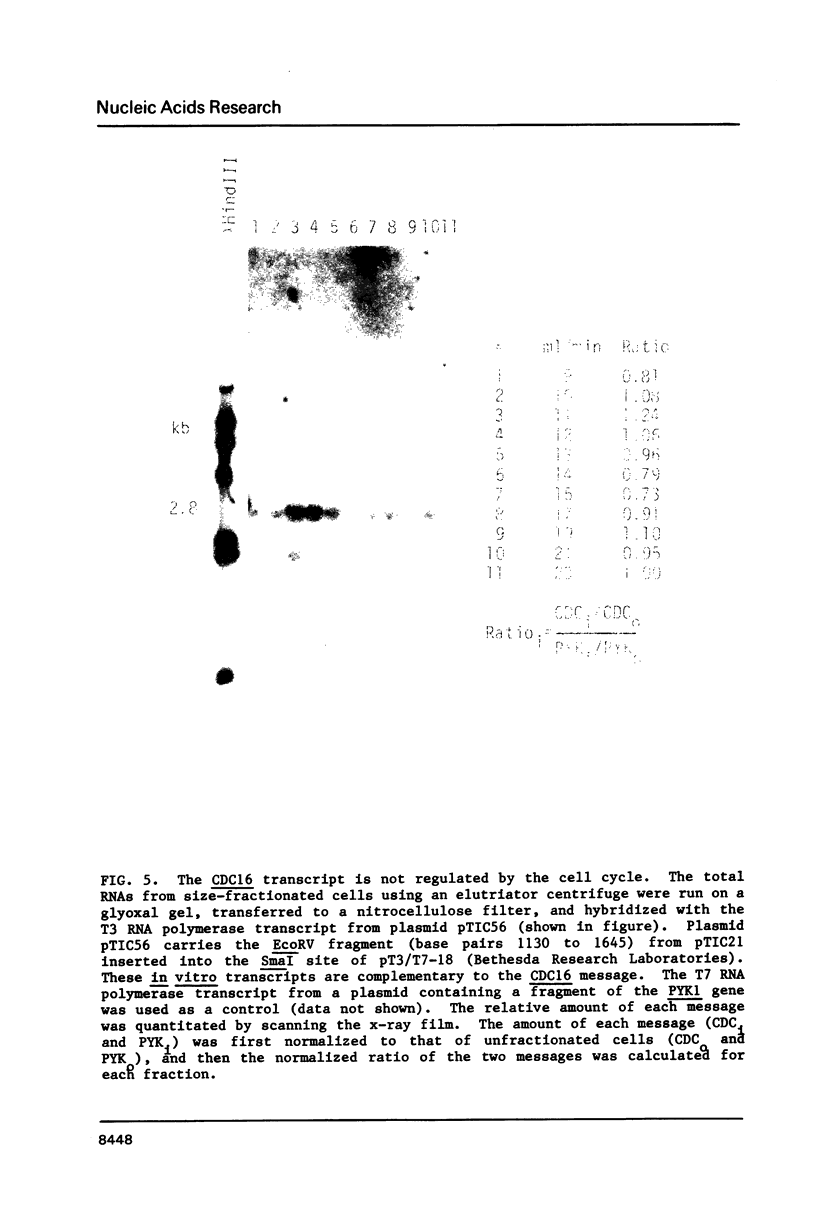
Abstract
The CDC16 gene is involved in the process of chromosome segregation in mitosis and a cdc16ts mutant accumulates the predominant microtubule-associated protein at the nonpermissive temperature. We find that the CDC16 gene open reading frame (ORF) is capable of encoding a protein whose calculated molecular weight and pI are 94,967 and 6.60, respectively. This hypothetical protein contains 16 cysteine residues; five are clustered at the N-terminal, 4 are placed about 3 residues apart in the middle of the peptide, and 3 are located close to the C-terminal. Each of these could form a metal-binding, nucleic acid-binding domain, suggesting this protein acts either as a repressor of the microtubule-associated protein gene or as a component necessary for spindle elongation, possibly interacting with the DNA. The start of the CDC16 ORF is only 95 bp downstream from the end of the MAK11 ORF. In this region there are two TATA boxes in tandem, but there is no room for a UAS or other regulatory sequences. An ATG is present 5 bp upstream of the start of the large ORF. Its frame terminates after only two amino acids.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Goetsch L. Duplication of spindle plaques and integration of the yeast cell cycle. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:123–131. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson M. J., Tuite M. F., Roberts N. A., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M., Perkins R. E., Conroy S. C., Fothergill L. A. Conservation of high efficiency promoter sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2625–2637. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon C. N., Elliott S. C. Fractionation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell populations by centrifugal elutriation. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):97–100. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.97-100.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Hereford L., Herskowitz I. Targeting of E. coli beta-galactosidase to the nucleus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1057–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R., Watanabe C. K., de Boer H. A. Compilation and comparison of the sequence context around the AUG startcodons in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3581–3593. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne T. A., Blumberg H., Young E. T. Sequence homology of the yeast regulatory protein ADR1 with Xenopus transcription factor TFIIIA. Nature. 1986 Mar 20;320(6059):283–287. doi: 10.1038/320283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Jun;38(2):164–198. doi: 10.1128/br.38.2.164-198.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Smith D. Altered fidelity of mitotic chromosome transmission in cell cycle mutants of S. cerevisiae. Genetics. 1985 Jul;110(3):381–395. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icho T., Bulawa C. E., Raetz C. R. Molecular cloning and sequencing of the gene for CDP-diglyceride hydrolase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12092–12098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of yeast transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in protein genes. Differences in synonymous codon choice patterns of yeast and Escherichia coli with reference to the abundance of isoaccepting transfer RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 15;158(4):573–597. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R. J., Hodnett J. L., Gray H. B., Jr Extracellular nucleases of pseudomonas BAL 31. III. Use of the double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activity as the basis of a convenient method for the mapping of fragments of DNA produced by cleavage with restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 May;5(5):1445–1464. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.5.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messenguy F., Dubois E., Descamps F. Nucleotide sequence of the ARGRII regulatory gene and amino acid sequence homologies between ARGRII PPRI and GAL4 regulatory proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 15;157(1):77–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchen G. Are mitotic functions required in meiosis? Genetics. 1974 Apr;76(4):745–753. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.4.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Naturally occurring poly(dA-dT) sequences are upstream promoter elements for constitutive transcription in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8419–8423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura H., Shiba T., Machida M., Matsui I., Jigami Y., Tanaka H. A positive regulatory sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ENO1 gene. J Biochem. 1987 Jul;102(1):181–189. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]