Abstract
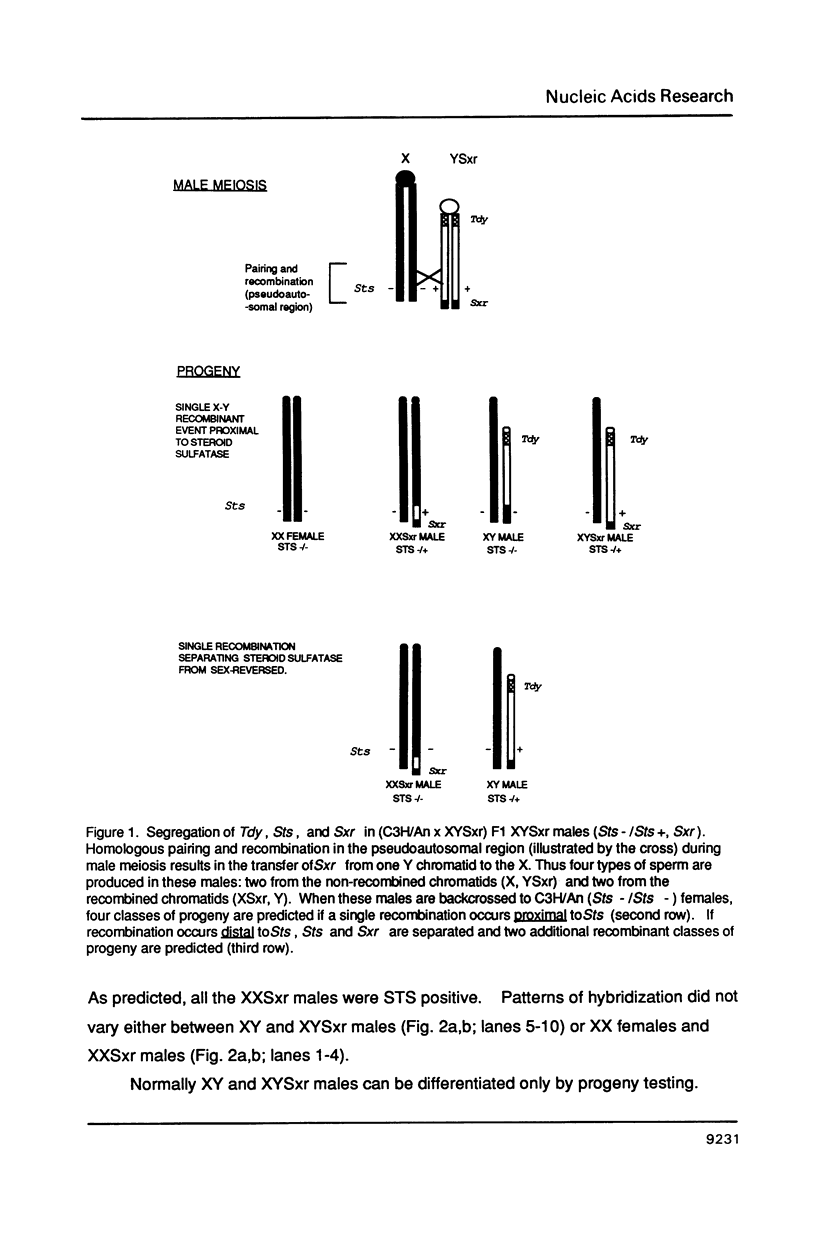
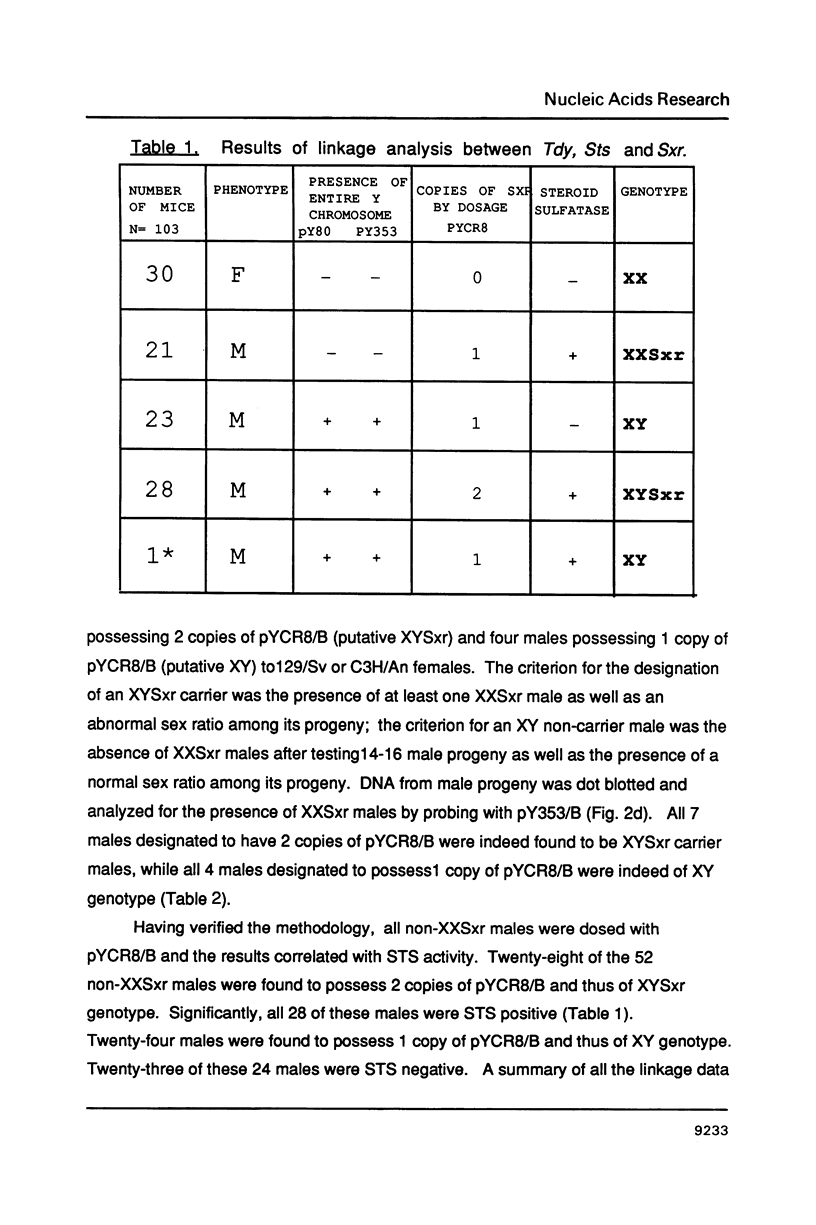
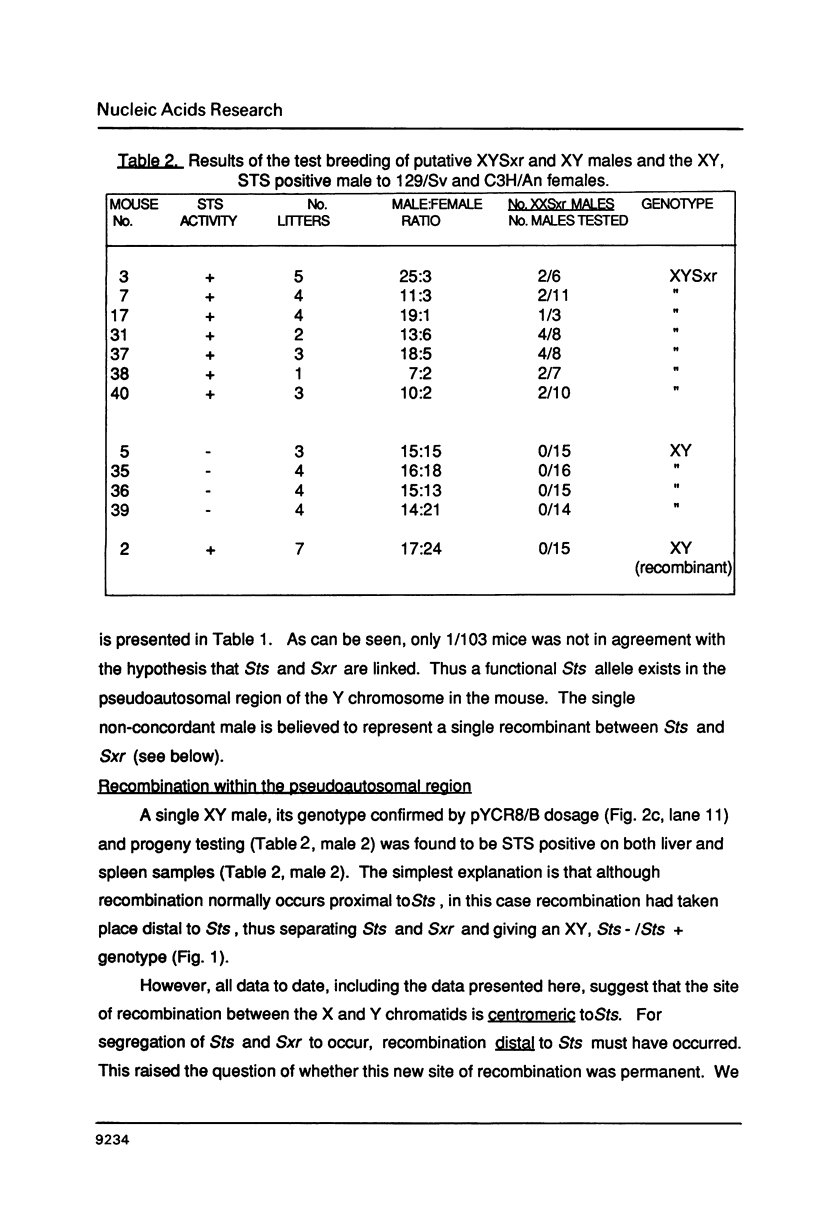
We present genetic and molecular data demonstrating linkage of the gene for steroid sulfatase (Sts) to the mutation sex reversed (Sxr) definitively showing the existance of a functional allele for Sts mapping to the pseudoautosomal region of the mouse Y chromosome. Thus, in mouse, functional Sts genes are present in the pseudoautosomal region of both the X and Y chromosomes. This is in contrast to man where Sts has been mapped to the short arm of the X just centromeric to the pseudoautosomal region. Only a single recombinant separating Sts and Sxr was found out of 103 male meioses analyzed; double recombinants were not found between sex (Tdy), Sts and Sxr. If the rate of recombination in the pseudoautosomal region in male mice is equivalent to that in man and thus 7-10X higher than normal, then our data suggest that the distance between Sts and Sxr (or the telomere of the Y) is approximately 100-200 kb in length. Our data is in contrast to a recent report of a recombination frequency separating Sts and Sxr of as high as 6.2-9.8%.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amar L. C., Arnaud D., Cambrou J., Guenet J. L., Avner P. R. Mapping of the mouse X chromosome using random genomic probes and an interspecific mouse cross. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3695–3700. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amor M., Tosi M., Duponchel C., Steinmetz M., Meo T. Liver mRNA probes disclose two cytochrome P-450 genes duplicated in tandem with the complement C4 loci of the mouse H-2S region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4453–4457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURSTEIN S., DORFMAN R. I. Determination of mammalian steroid sulfatase with 7 alpha-H3-3beta-hydroxyandrost-5-en-17-one sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1963 May;238:1656–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A., Parenti G., Carrozzo R., Sebastio G., Andria G., Buckle V., Fraser N., Craig I., Rocchi M., Romeo G. Isolation and characterization of a steroid sulfatase cDNA clone: genomic deletions in patients with X-chromosome-linked ichthyosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4519–4523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop C. E., Boursot P., Baron B., Bonhomme F., Hatat D. Most classical Mus musculus domesticus laboratory mouse strains carry a Mus musculus musculus Y chromosome. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):70–72. doi: 10.1038/315070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop C. E., Hatat D. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of a mouse Y chromosome RNA transcript expressed in the testis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):2959–2969. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns G. R. Purification and partial characterization of arylsulphatase C from human placental microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 13;759(3):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90313-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattanach B. M., Pollard C. E., Hawker S. G. Sex-reversed mice: XX and XO males. Cytogenetics. 1971;10(5):318–337. doi: 10.1159/000130151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher E. M., Washburn L. L. Genetic control of primary sex determination in mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:327–360. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson R. P., Harper K., Kramer J. M. Identification of an autosomal locus affecting steroid sulfatase activity among inbred strains of mice. Genetics. 1983 Sep;105(1):181–189. doi: 10.1093/genetics/105.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. P., Burtenshaw M. D., Cattanach B. M. Meitoic crossing-over between the X and Y chromosomes of male mice carrying the sex-reversing (Sxr) factor. Nature. 1982 Dec 2;300(5891):443–445. doi: 10.1038/300443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartler S. M., Rivest M. Evidence for X-linkage of steroid sulfatase in the mouse: steroid sulfatase levels in oocytes of XX and XO mice. Genetics. 1983 Jan;103(1):137–141. doi: 10.1093/genetics/103.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard E. F., Affara N. A., Yates J. R., Goudie D. R., Lambert J., Aitken D. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Deletion of a DNA sequence in eight of nine families with X-linked ichthyosis (steroid sulphatase deficiency). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):3977–3985. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.3977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Soriano P., Müller U., Jaenisch R. High frequency of unequal recombination in pseudoautosomal region shown by proviral insertion in transgenic mouse. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):682–685. doi: 10.1038/324682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. W., Singh L. Conserved repeated DNA sequences in vertebrate sex chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1981;58(1):46–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00284148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keinanen B. M., Nelson K., Daniel W. L., Roque J. M. Genetic analysis of murine arylsulfatase C and steroid sulfatase. Genetics. 1983 Sep;105(1):191–206. doi: 10.1093/genetics/105.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keitges E. A., Schorderet D. F., Gartler S. M. Linkage of the steroid sulfatase gene to the sex-reversed mutation in the mouse. Genetics. 1987 Jul;116(3):465–468. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keitges E., Gartler S. M. Dosage of the Sts gene in the mouse. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;39(4):470–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keitges E., Rivest M., Siniscalco M., Gartler S. M. X-linkage of steroid sulphatase in the mouse is evidence for a functional Y-linked allele. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):226–227. doi: 10.1038/315226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren A., Simpson E., Tomonari K., Chandler P., Hogg H. Male sexual differentiation in mice lacking H-Y antigen. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):552–555. doi: 10.1038/312552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNaught R. W., France J. T. Studies of the biochemical basis of steroid sulphatase deficiency: preliminary evidence suggesting a defect in membrane-enzyme structure. J Steroid Biochem. 1980 Mar;13(3):363–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(80)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R., Shapiro L. J., Norum R. A., Mohandas T., Axelman J., Dabora R. L. Differential expression of steroid sulphatase locus on active and inactive human X chromosome. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):838–840. doi: 10.1038/299838a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J., Sparkes R. S., Sparkes M. C. Regional assignment of the steroid sulfatase-X-linked ichthyosis locus: implications for a noninactivated region on the short arm of human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5779–5783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K., Daniel W. L. Interstrain variation of murine arylsulfatase C. Experientia. 1979 Mar 15;35(3):309–310. doi: 10.1007/BF01964317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renwick J. H. Progress in mapping human autosomes. Br Med Bull. 1969 Jan;25(1):65–73. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouyer F., Simmler M. C., Johnsson C., Vergnaud G., Cooke H. J., Weissenbach J. A gradient of sex linkage in the pseudoautosomal region of the human sex chromosomes. Nature. 1986 Jan 23;319(6051):291–295. doi: 10.1038/319291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh L., Purdom I. F., Jones K. W. Conserved sex-chromosome-associated nucleotide sequences in eukaryotes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):805–814. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster D., France J. T., Shapiro L. J., Weiss R. X-linked ichthyosis due to steroid-sulphatase deficiency. Lancet. 1978 Jan 14;1(8055):70–72. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. H., Allen E., Marsh B., Mohandas T., Wang N., Taggart R. T., Shapiro L. J. Cloning and expression of steroid sulfatase cDNA and the frequent occurrence of deletions in STS deficiency: implications for X-Y interchange. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):443–454. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90447-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



