Abstract
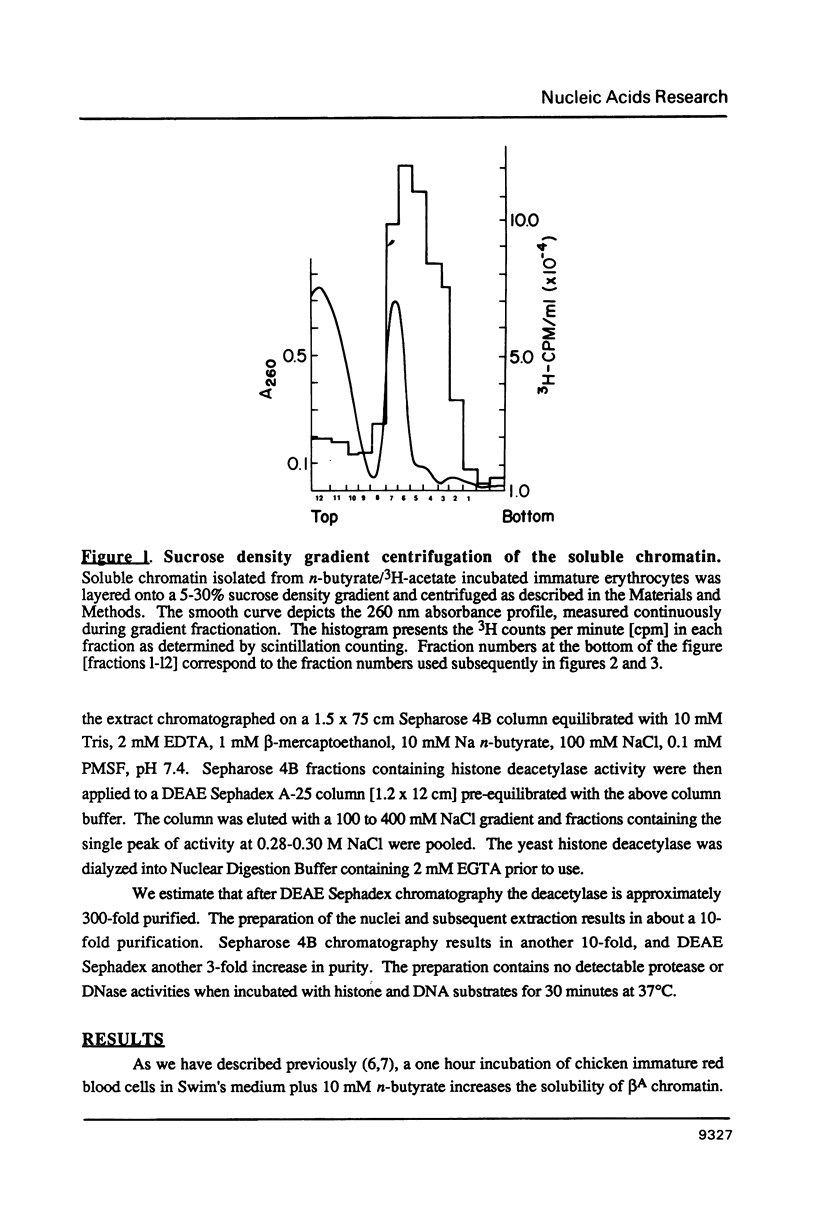
Chicken immature red blood cells were incubated for 1 hour in Swim's medium containing 3H-acetate and 10 mM n-butyrate. During the incubation period, the small percentage of dynamically acetylated and deacetylated histone is radiolabeled and hyperacetylated. A second effect of the n-butyrate incubation is to shift a small subset of nucleohistone into a soluble form. This chromatin is predominantly polynucleosome size (approximately dimer to pentamer) and can be separated from soluble mononucleosomes by 5-30% sucrose gradient centrifugation. The soluble polynucleosomes are 25-30 fold enriched for adult beta-globin (beta A) DNA and contain the hyperacetylated histones. We have tested whether histone hyperacetylation is responsible for the enhanced beta-globin chromatin solubility by in vitro deacetylation of the soluble chromatin histones. This procedure converts the beta-globin polynucleosomes to an insoluble form, demonstrating that histone hyperacetylation is in fact directly responsible for the increased solubility of the beta A chromatin.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso W. R., Nelson D. A. A novel yeast histone deacetylase: partial characterization and development of an activity assay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 26;866(2-3):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(86)90113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annunziato A. T., Seale R. L. Histone deacetylation is required for the maturation of newly replicated chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12675–12684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boffa L. C., Gruss R. J., Allfrey V. G. Manifold effects of sodium butyrate on nuclear function. Selective and reversible inhibition of phosphorylation of histones H1 and H2A and impaired methylation of lysine and arginine residues in nuclear protein fractions. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9612–9621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brotherton T. W., Covault J., Shires A., Chalkley R. Only a small fraction of avian erythrocyte histone is involved in ongoing acetylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):5061–5073. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.5061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A., Kimura T., Gould H., Allan J. Perturbation of chromatin structure in the region of the adult beta-globin gene in chicken erythrocyte chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90626-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Anna J. A., Tobey R. A., Gurley L. R. Concentration-dependent effects of sodium butyrate in Chinese hamster cells: cell-cycle progression, inner-histone acetylation, histone H1 dephosphorylation, and induction of an H1-like protein. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2656–2671. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenz C. R., Nelson D. A. N-Butyrate incubation of immature chicken erythrocytes preferentially enhances the solubility of beta A chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):1977–1995. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McReynolds L., O'Malley B. W., Nisbet A. D., Fothergill J. E., Givol D., Fields S., Robertson M., Brownlee G. G. Sequence of chicken ovalbumin mRNA. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):723–728. doi: 10.1038/273723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. A., Ferris R. C., Zhang D. E., Ferenz C. R. The beta-globin domain in immature chicken erythrocytes: enhanced solubility is coincident with histone hyperacetylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1667–1682. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. A., Perry M., Sealy L., Chalkley R. DNAse I preferentially digests chromatin containing hyperacetylated histones. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jun 29;82(4):1346–1353. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90337-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M., Chalkley R. Histone acetylation increases the solubility of chromatin and occurs sequentially over most of the chromatin. A novel model for the biological role of histone acetylation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7336–7347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M., Chalkley R. The effect of histone hyperacetylation on the nuclease sensitivity and the solubility of chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3313–3318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridsdale J. A., Davie J. R. Chicken erythrocyte polynucleosomes which are soluble at physiological ionic strength and contain linker histones are highly enriched in beta-globin gene sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1081–1096. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridsdale J. A., Davie J. R. Selective solubilization of beta-globin oligonucleosomes at low ionic strength. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):290–295. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs M. G., Whittaker R. G., Neumann J. R., Ingram V. M. n-Butyrate causes histone modification in HeLa and Friend erythroleukaemia cells. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):462–464. doi: 10.1038/268462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Groudine M. Chromosomal subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):848–856. doi: 10.1126/science.948749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D., Nelson D. A. Histone acetylation in chicken erythrocytes. Estimation of the percentage of sites actively modified. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):857–862. doi: 10.1042/bj2400857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]