Abstract
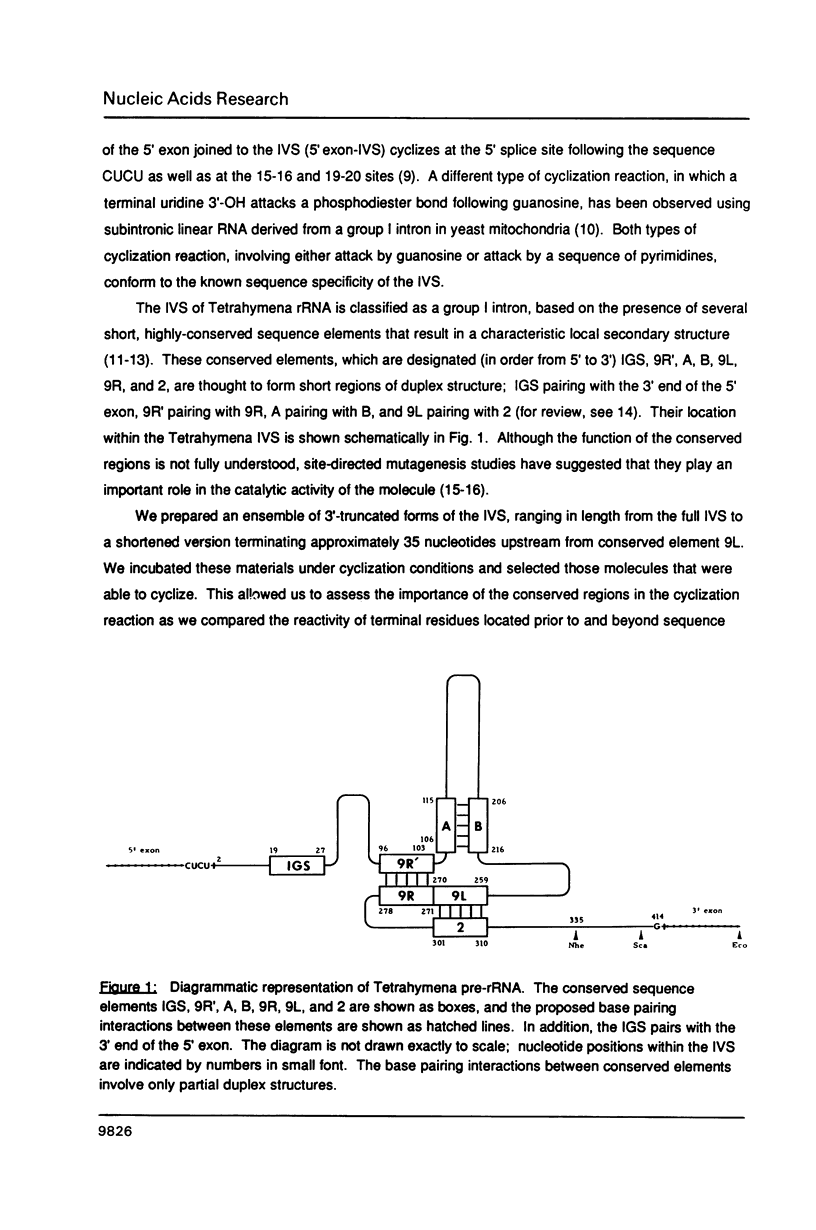
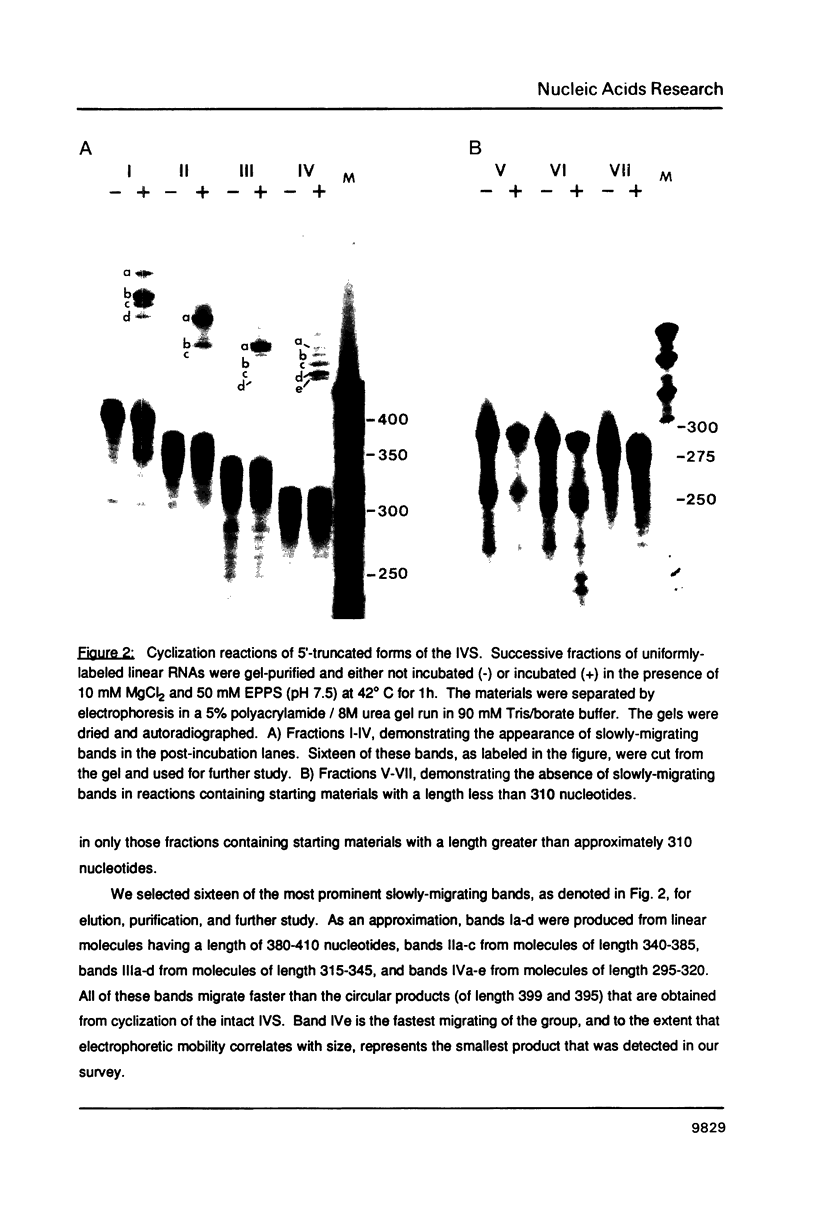
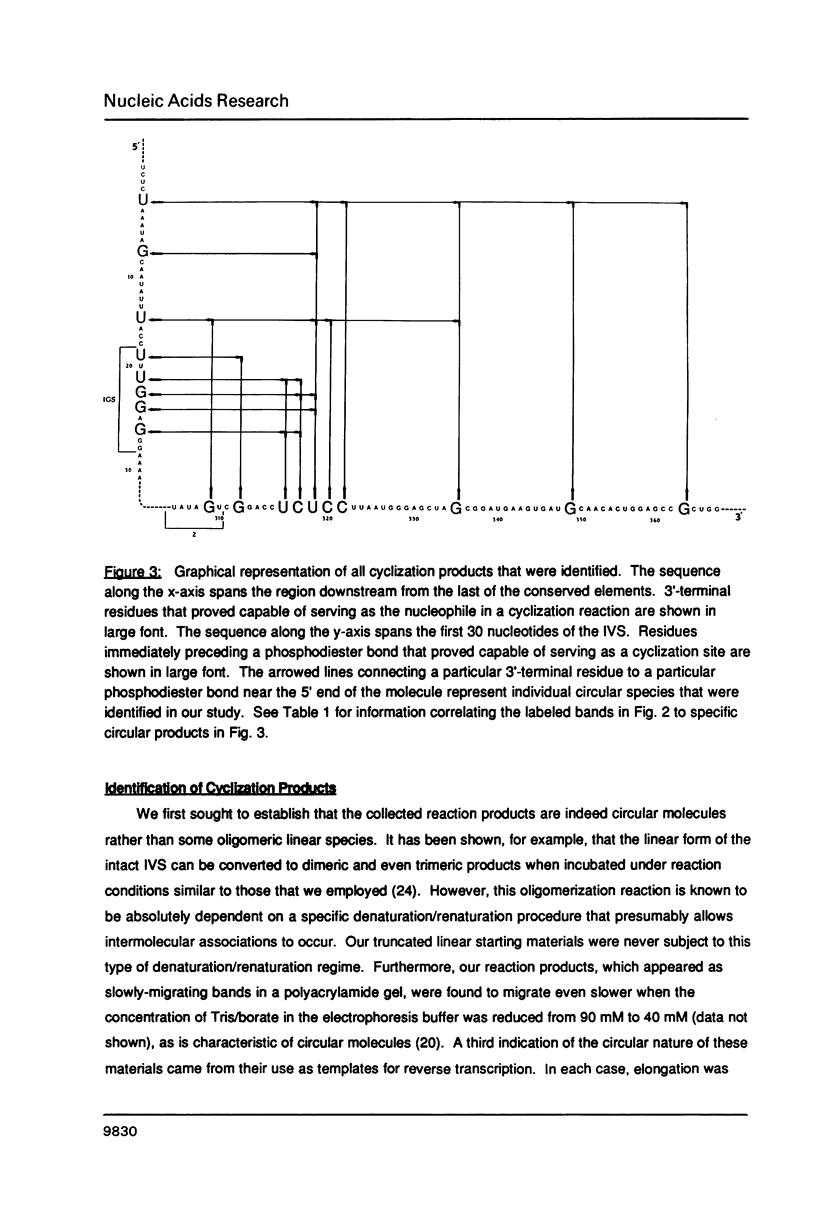
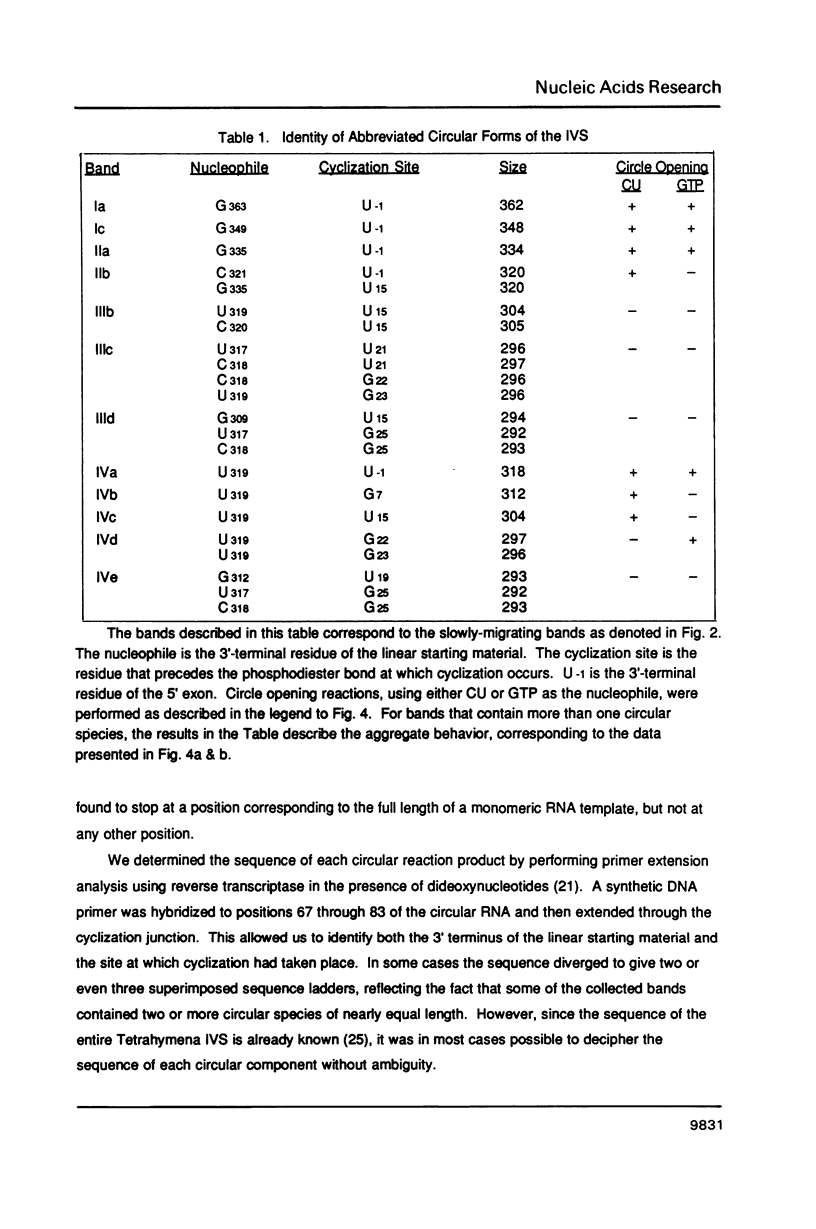
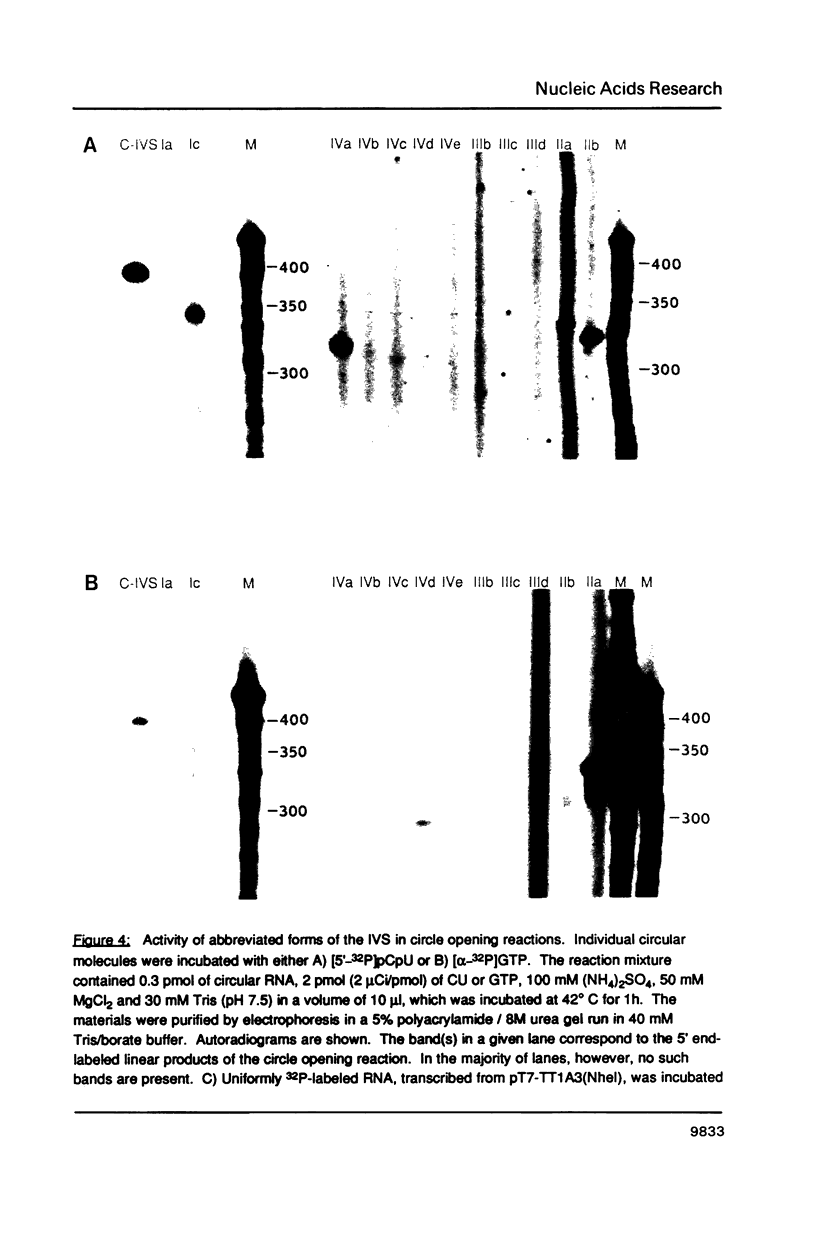
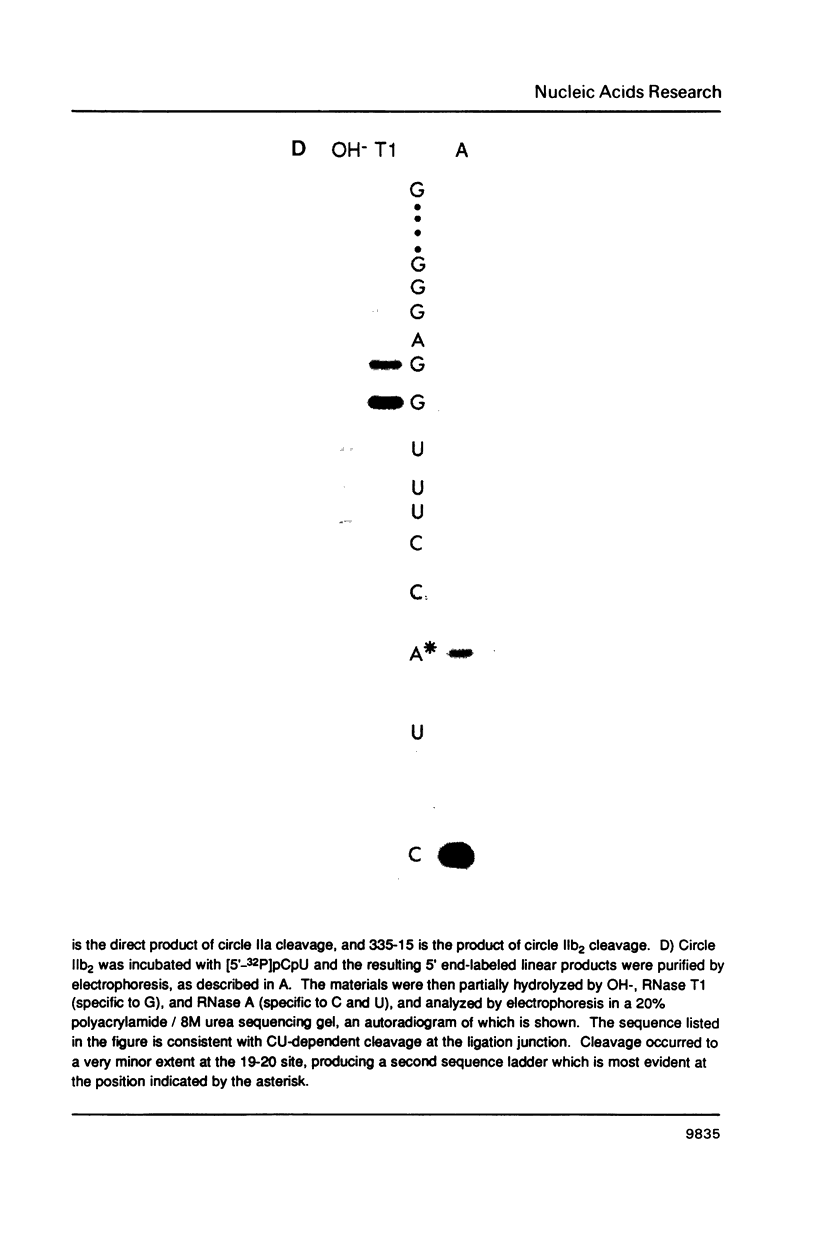
The precursor rRNA of Tetrahymena thermophila contains a group I intervening sequence (IVS) that catalyzes its own excision to yield mature rRNA. The excised IVS catalyzes a number of cleavage/ligation reactions that are analogous to the transesterification reactions of splicing. We examined the behavior of a variety of 3'-truncated forms of the IVS and found several abbreviated molecules that retained catalytic activity. The reactivity of these molecules indicates that the site at which cleavage/ligation occurs lies in close proximity to all of the conserved sequence elements within the catalytic core of the IVS.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Been M. D., Cech T. R. One binding site determines sequence specificity of Tetrahymena pre-rRNA self-splicing, trans-splicing, and RNA enzyme activity. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90443-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Cech T. R. Sites of circularization of the Tetrahymena rRNA IVS are determined by sequence and influenced by position and secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8389–8408. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. M., Irvine K. D., Kaneko K. J., Kerker B. J., Oettgen A. B., Tierney W. M., Williamson C. L., Zaug A. J., Cech T. R. Role of conserved sequence elements 9L and 2 in self-splicing of the Tetrahymena ribosomal RNA precursor. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90380-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler E. T., Chamberlin M. J. Bacteriophage SP6-specific RNA polymerase. I. Isolation and characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5772–5778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davanloo P., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Cloning and expression of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2035–2039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Waring R. B., Ray J. A., Brown T. A., Scazzocchio C. Making ends meet: a model for RNA splicing in fungal mitochondria. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):719–724. doi: 10.1038/300719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Gardiner K., Marsh T., Pace N., Altman S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Cech T. R. Secondary structure of the circular form of the Tetrahymena rRNA intervening sequence: a technique for RNA structure analysis using chemical probes and reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Sullivan F. X., Cech T. R. Intermolecular exon ligation of the rRNA precursor of Tetrahymena: oligonucleotides can function as 5' exons. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Sullivan F. X., Cech T. R. New reactions of the ribosomal RNA precursor of Tetrahymena and the mechanism of self-splicing. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):143–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Rosbash M. Efficient trans-splicing of a yeast mitochondrial RNA group II intron implicates a strong 5' exon-intron interaction. Science. 1986 Nov 28;234(4780):1099–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.2430332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan N. C., Gall J. G. The intervening sequence of the ribosomal RNA gene is highly conserved between two Tetrahymena species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2809–2822. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay P. S., Inoue T. Catalysis of splicing-related reactions between dinucleotides by a ribozyme. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):343–346. doi: 10.1038/327343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger K., Grabowski P. J., Zaug A. J., Sands J., Gottschling D. E., Cech T. R. Self-splicing RNA: autoexcision and autocyclization of the ribosomal RNA intervening sequence of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90414-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Conservation of RNA secondary structures in two intron families including mitochondrial-, chloroplast- and nuclear-encoded members. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Jacquier A., Dujon B. Comparison of fungal mitochondrial introns reveals extensive homologies in RNA secondary structure. Biochimie. 1982 Oct;64(10):867–881. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan F. X., Cech T. R. Reversibility of cyclization of the Tetrahymena rRNA intervening sequence: implication for the mechanism of splice site choice. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):639–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W. Enzymatic activity of the conserved core of a group I self-splicing intron. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):83–86. doi: 10.1038/322083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak H. F., Van der Horst G., Kamps A. M., Arnberg A. C. Interlocked RNA circle formation by a self-splicing yeast mitochondrial group I intron. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90360-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner N. K., Cech T. R. Guanosine binding required for cyclization of the self-splicing intervening sequence ribonucleic acid from Tetrahymena thermophila. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3330–3340. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Davies R. W. Assessment of a model for intron RNA secondary structure relevant to RNA self-splicing--a review. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):277–291. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Ray J. A., Edwards S. W., Scazzocchio C., Davies R. W. The Tetrahymena rRNA intron self-splices in E. coli: in vivo evidence for the importance of key base-paired regions of RNA for RNA enzyme function. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):371–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90151-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Been M. D., Cech T. R. The Tetrahymena ribozyme acts like an RNA restriction endonuclease. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):429–433. doi: 10.1038/324429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Cech T. R. Oligomerization of intervening sequence RNA molecules in the absence of proteins. Science. 1985 Sep 13;229(4718):1060–1064. doi: 10.1126/science.2412290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Cech T. R. The intervening sequence RNA of Tetrahymena is an enzyme. Science. 1986 Jan 31;231(4737):470–475. doi: 10.1126/science.3941911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Cech T. R. The intervening sequence excised from the ribosomal RNA precursor of Tetrahymena contains a 5-terminal guanosine residue not encoded by the DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2823–2838. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Grabowski P. J., Cech T. R. Autocatalytic cyclization of an excised intervening sequence RNA is a cleavage-ligation reaction. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):578–583. doi: 10.1038/301578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Kent J. R., Cech T. R. A labile phosphodiester bond at the ligation junction in a circular intervening sequence RNA. Science. 1984 May 11;224(4649):574–578. doi: 10.1126/science.6200938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Kent J. R., Cech T. R. Reactions of the intervening sequence of the Tetrahymena ribosomal ribonucleic acid precursor: pH dependence of cyclization and site-specific hydrolysis. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6211–6218. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]