Abstract
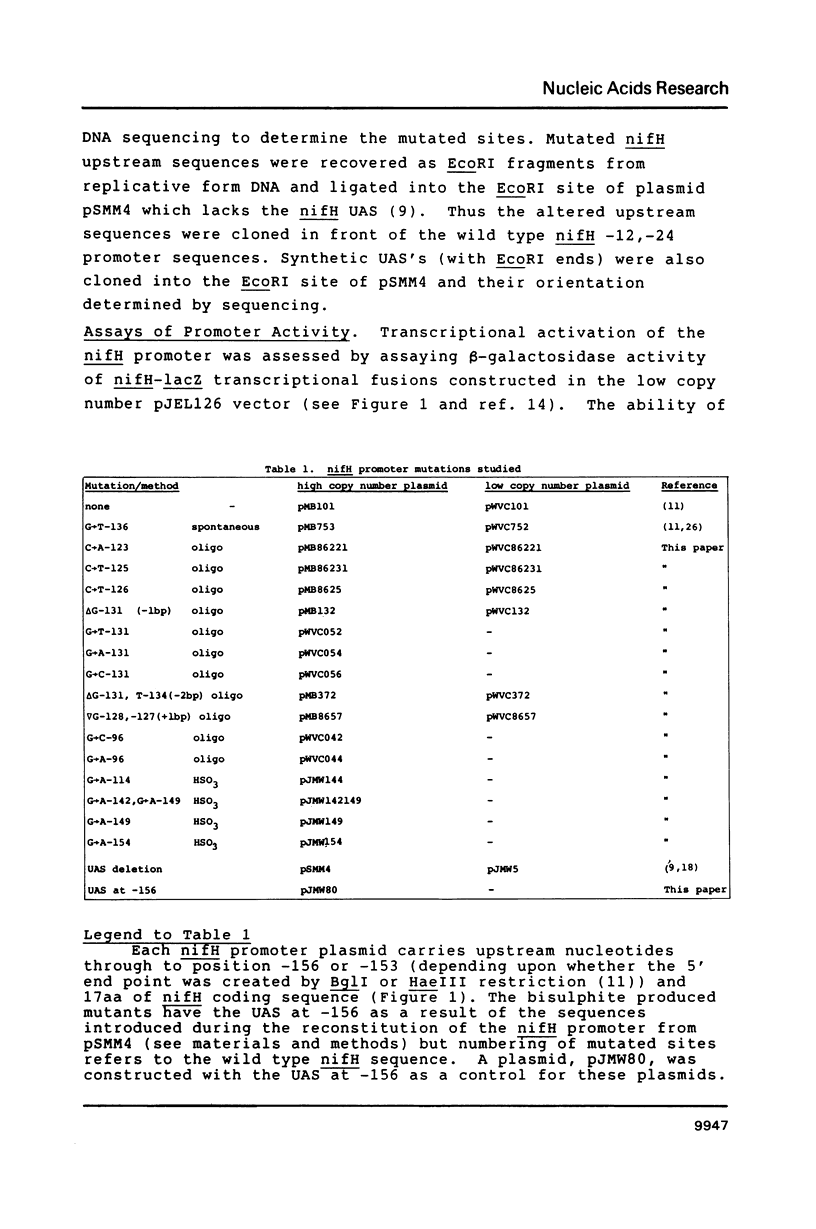
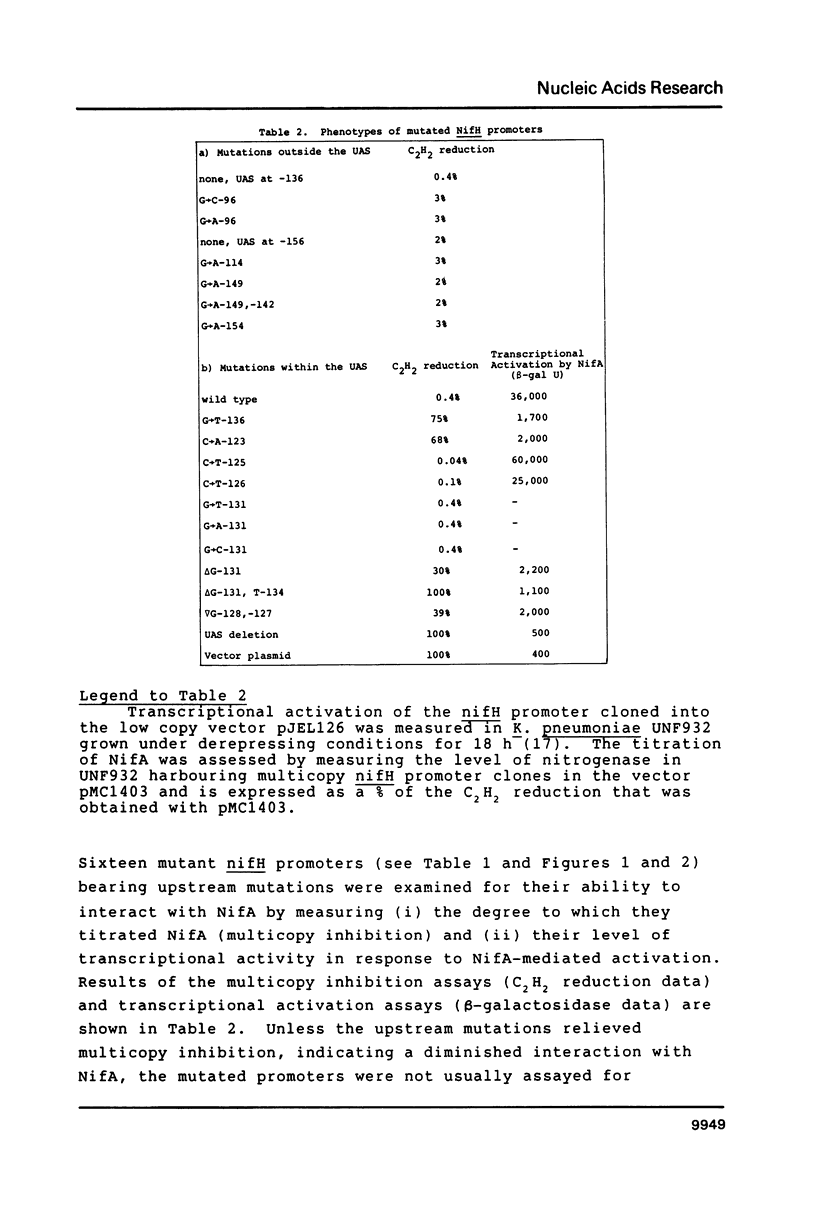
Upstream sequences of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifH promoter were mutagenised and activation of the mutated promoters by the nif-specific transcriptional activator protein NifA examined in vivo. Of the sixteen mutations analysed, only those within the nifH upstream activator sequence (UAS), characterised by a TGT-N10-ACA motif, influenced nifH promoter activity. Mutations altering the two-fold rotational symmetry of the UAS or the spacing between the TGT and ACA motifs reduced promoter activity, consistent with the UAS functioning as a NifA binding site. The bases flanking the TGT-ACA motif of the UAS also appear to influence activation by NifA. Substituting the nifH UAS with a binding site for the transcriptional activator NtrC resulted in improved NtrC-dependent activation of the nifH promoter demonstrating that the activator specificity of the nifH promoter is dependent upon the presence of the appropriate upstream sequences to which the activator binds.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Mutations affecting regulation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifH (nitrogenase reductase) promotor. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):143–147. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.143-147.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan-Wollaston V., Cannon M. C., Beynon J. L., Cannon F. C. Role of the nifA gene product in the regulation of nif expression in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):776–778. doi: 10.1038/294776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Cannon W. Frameshifts close to the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifH promoter prevent multicopy inhibition by hybrid nifH plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):492–498. doi: 10.1007/BF00331620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Cannon W., Woodcock J. Transcriptional activation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase promoter may involve DNA loop formation. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Sep;1(2):243–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Khan H., Dixon R. Site-directed mutagenesis of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifL and nifH promoters and in vivo analysis of promoter activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7621–7638. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. Tandem promoters determine regulation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae glutamine synthetase (glnA) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7811–7830. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M., Whitty P., Wootton J. Sequence and domain relationships of ntrC and nifA from Klebsiella pneumoniae: homologies to other regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):441–447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Regulation of nitrogen fixation genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:567–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes T., Merrick M., Dixon R. Interaction of purified NtrC protein with nitrogen regulated promoters from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(3):492–498. doi: 10.1007/BF00331345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman J., Wong P. K., Sei K., Keener J., Kustu S. Products of nitrogen regulatory genes ntrA and ntrC of enteric bacteria activate glnA transcription in vitro: evidence that the ntrA product is a sigma factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7525–7529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. P., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA by purified Escherichia coli components: core RNA polymerase and the products of glnF, glnG, and glnL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8453–8457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan H., Buck M., Dixon R. Deletion loop mutagenesis of the nifL promoter from Klebsiella pneumoniae: role of the -26 to -12 region in promoter function. Gene. 1986;45(3):281–288. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koudelka G. B., Harrison S. C., Ptashne M. Effect of non-contacted bases on the affinity of 434 operator for 434 repressor and Cro. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):886–888. doi: 10.1038/326886a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magasanik B. Genetic control of nitrogen assimilation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:135–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.001031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Magasanik B. Covalent modification of the glnG product, NRI, by the glnL product, NRII, regulates the transcription of the glnALG operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5909–5913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ow D. W., Xiong Y., Gu Q., Shen S. C. Mutational analysis of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase promoter: sequences essential for positive control by nifA and ntrC (glnG) products. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):868–874. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.868-874.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitzer L. J., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA in E. coli is stimulated by activator bound to sites far from the promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):785–792. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90553-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel G. E., Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Nitrogen fixation by Klebsiella pneumoniae is inhibited by certain multicopy hybrid nif plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):45–56. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.45-56.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton R. P., Ptashne M. Changing the binding specificity of a repressor by redesigning an alpha-helix. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):601–605. doi: 10.1038/316601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Popham D., Keener J., Kustu S. In vitro transcription of the nitrogen fixation regulatory operon nifLA of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2876–2880. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2876-2880.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


