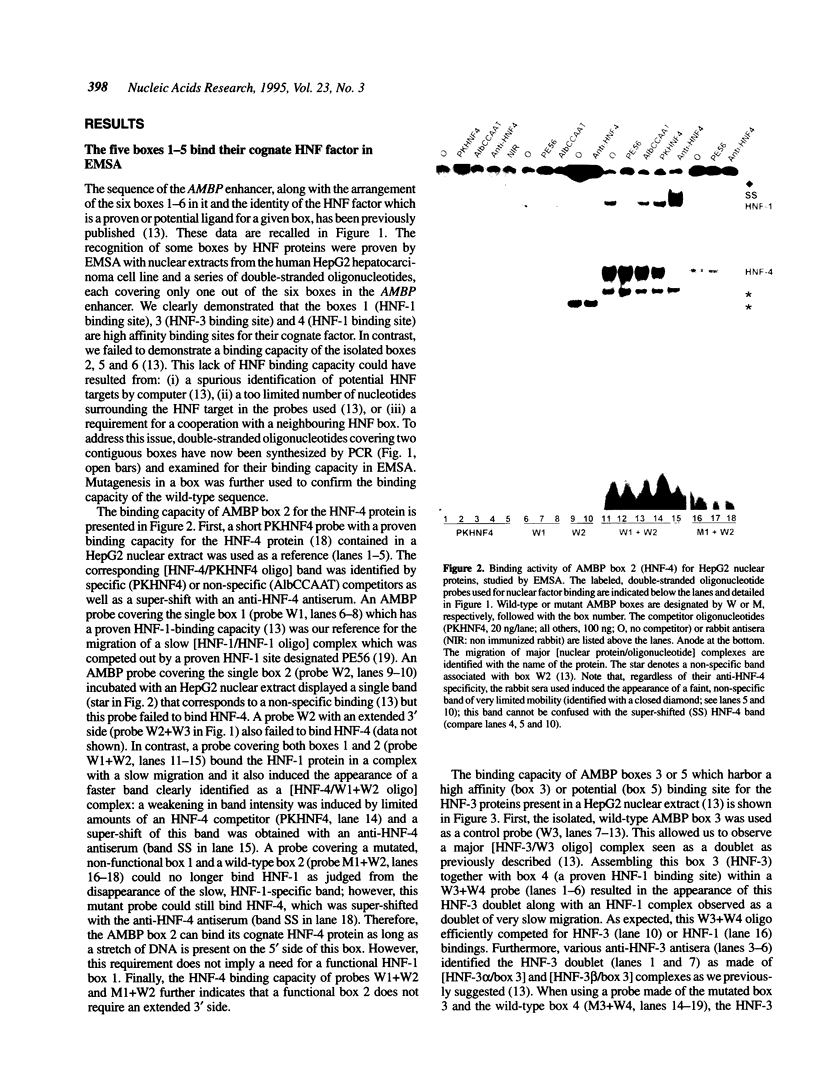
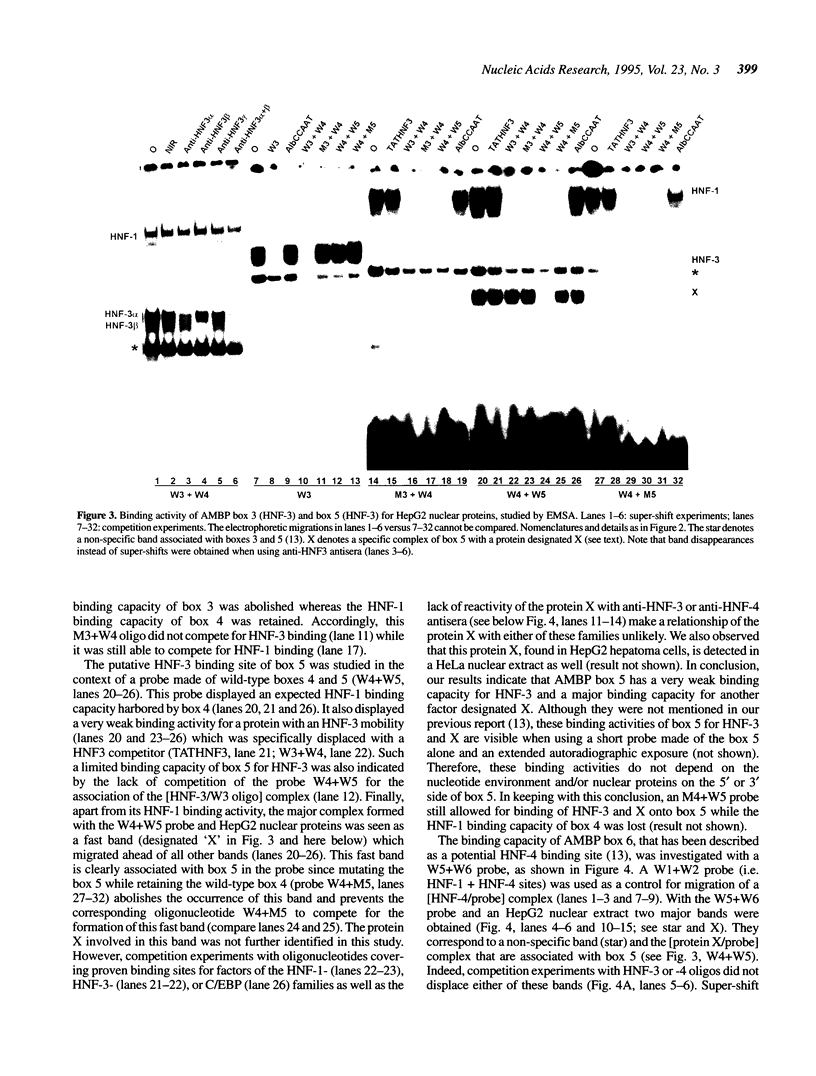
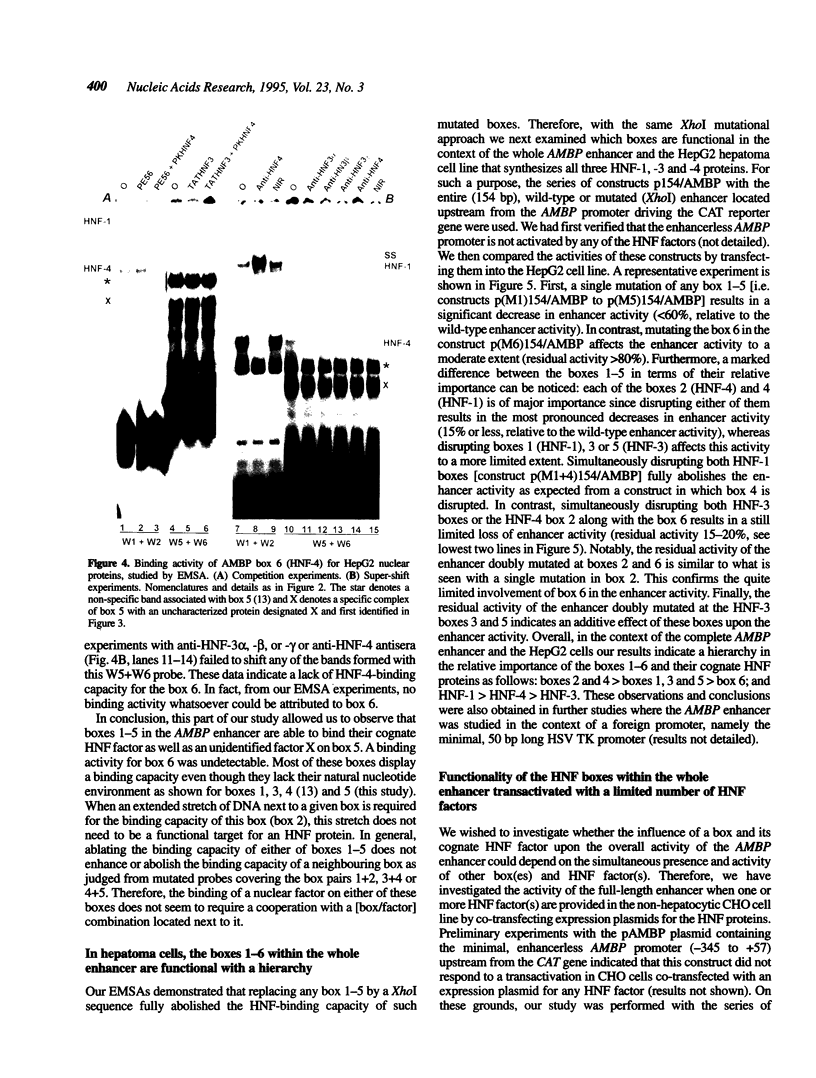
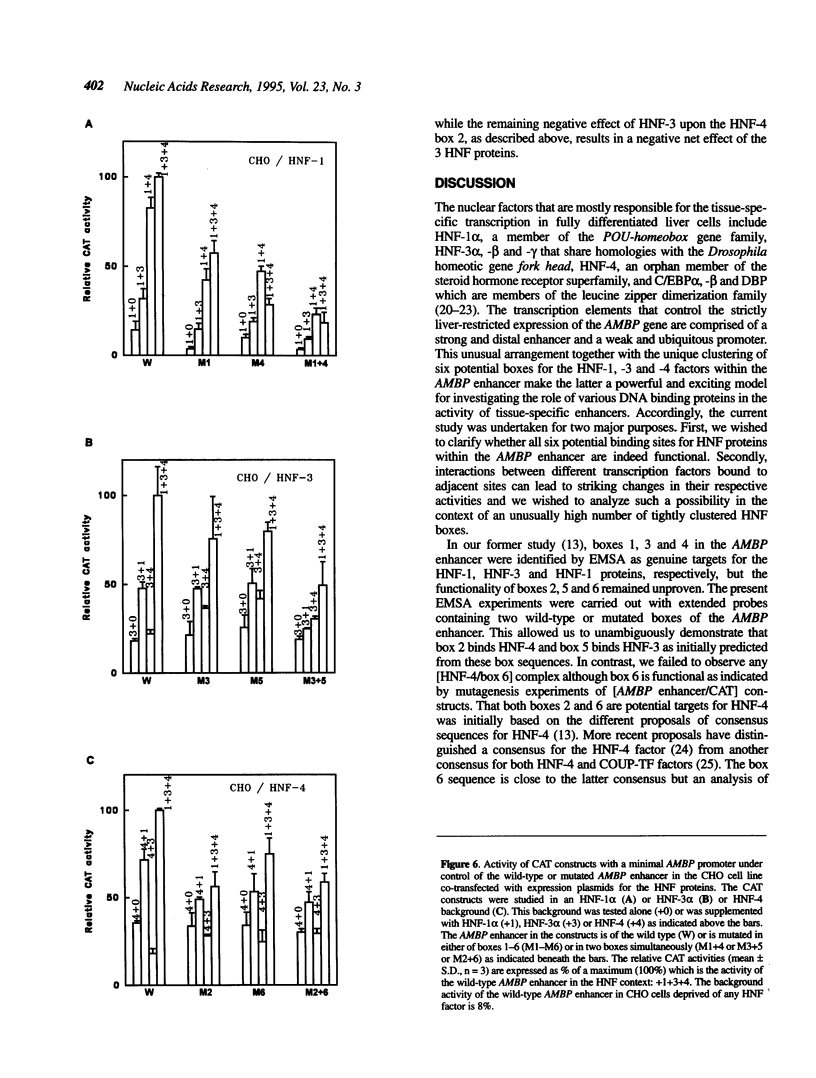
Abstract
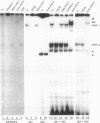
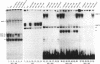
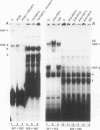
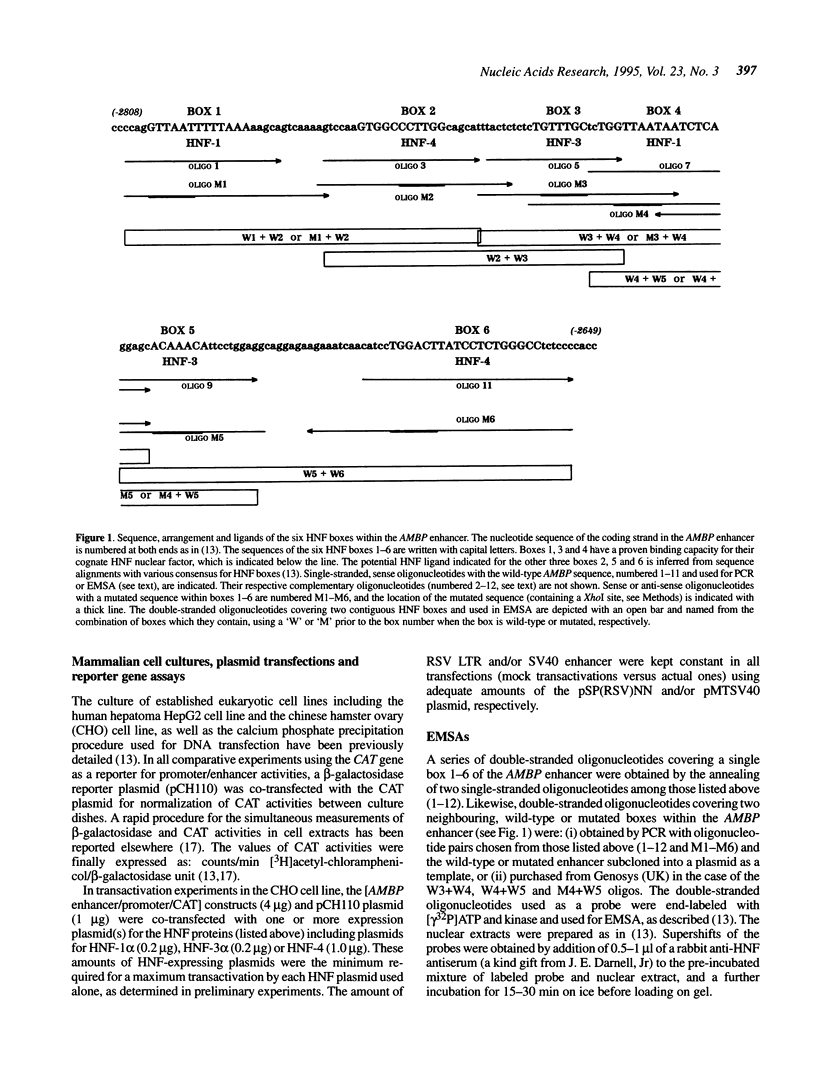
Alpha-1-microglobulin and bikunin are two plasma glycoproteins encoded by an alpha-1-microglobulin/bikunin precursor (AMBP) gene. The strict liver-specific expression of the AMBP gene is controlled by a potent enhancer made of six clustered boxes numbered 1-6 that have been reported to be proven or potential binding sites for the hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors HNF-1, -4, -3, -1, -3, -4, respectively. In the present study, electromobility shift assays of wild-type or mutated probes demonstrated that the boxes 1-5 have a binding capacity for their cognate HNF protein. Box 5 is also a target for another, as yet unidentified, factor. A functional analysis of the wild-type or mutated enhancer, driving its homologous promoter and a reporter CAT gene in the HepG2 hepatoma cell line, demonstrated that all six boxes participate in the enhancer activity, with the primary influence of box 4 (HNF-1) and box 2 (HNF-4). A similar analysis in the HNF-free CHO cell line co-transfected with one or several HNF factors further demonstrated various interplays between boxes: box 3 (HNF-3 alpha and beta) has a negative influence over the major HNF-4 box 2 as well as a positive influence over the major HNF-1 box 4.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerström B., Lögdberg L. An intriguing member of the lipocalin protein family: alpha 1-microglobulin. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jun;15(6):240–243. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90037-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach I., Yaniv M. More potent transcriptional activators or a transdominant inhibitor of the HNF1 homeoprotein family are generated by alternative RNA processing. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4229–4242. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Klüppel M., Schmidt A., Schütz G., Luckow B. Reporter constructs with low background activity utilizing the cat gene. Gene. 1992 Jan 2;110(1):129–130. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90456-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Mao S. J., Larsen W. J. Identification of a factor in fetal bovine serum that stabilizes the cumulus extracellular matrix. A role for a member of the inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor family. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12380–12386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daveau M., Rouet P., Scotte M., Faye L., Hiron M., Lebreton J. P., Salier J. P. Human inter-alpha-inhibitor family in inflammation: simultaneous synthesis of positive and negative acute-phase proteins. Biochem J. 1993 Jun 1;292(Pt 2):485–492. doi: 10.1042/bj2920485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diarra-Mehrpour M., Bourguignon J., Sesboü R., Salier J. P., Léveillard T., Martin J. P. Structural analysis of the human inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor light-chain gene. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 20;191(1):131–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escribano J., Grubb A., Méndez E. Identification of retinol as one of the protein HC chromophores. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 30;155(3):1424–1429. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godovac-Zimmermann J. The structural motif of beta-lactoglobulin and retinol-binding protein: a basic framework for binding and transport of small hydrophobic molecules? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):64–66. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregori C., Kahn A., Pichard A. L. Activity of the rat liver-specific aldolase B promoter is restrained by HNF3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 11;22(7):1242–1246. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.7.1242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ham J., Dostatni N., Arnos F., Yaniv M. Several different upstream promoter elements can potentiate transactivation by the BPV-1 E2 protein. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2931–2940. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07843.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Rowader K. E., Stevens K., Jiang C., Milos P., Zaret K. S. Modulation of liver-specific transcription by interactions between hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 and nuclear factor 1 binding DNA in close apposition. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2401–2410. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumeyer J. F., Polazzi J. O., Kotick M. P. The mRNA for a proteinase inhibitor related to the HI-30 domain of inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor also encodes alpha-1-microglobulin (protein HC). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):7839–7850. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Nishiyori A., Murakami T., Tsukamoto T., Hata S., Osumi T., Okamura R., Mori M., Takiguchi M. Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter-transcription factor (COUP-TF) represses transcription from the promoter of the gene for ornithine transcarbamylase in a manner antagonistic to hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 (HNF-4). J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11125–11133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Clark K. L., Burley S. K., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/fork head or "winged helix" proteins: a family of transcription factors of diverse biologic function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10421–10423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist A., Bratt T., Altieri M., Kastern W., Akerström B. Rat alpha 1-microglobulin: co-expression in liver with the light chain of inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 28;1130(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90462-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeehan W. L., Sakagami Y., Hoshi H., McKeehan K. A. Two apparent human endothelial cell growth factors from human hepatoma cells are tumor-associated proteinase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5378–5383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson C. E., Shim E. Y., Friedman D. S., Zaret K. S. An active tissue-specific enhancer and bound transcription factors existing in a precisely positioned nucleosomal array. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):387–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80079-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D. B., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1, a member of a novel class of dimerizing homeodomain proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):677–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger S., Halaas J. L., Breslow J. L., Sladek F. M. Orphan receptor HNF-4 and bZip protein C/EBP alpha bind to overlapping regions of the apolipoprotein B gene promoter and synergistically activate transcription. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16831–16838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura N., Tanaka K. Analysis of the rat hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF) 1 gene promoter: synergistic activation by HNF4 and HNF1 proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 11;21(16):3731–3736. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.16.3731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyori A., Tashiro H., Kimura A., Akagi K., Yamamura K., Mori M., Takiguchi M. Determination of tissue specificity of the enhancer by combinatorial operation of tissue-enriched transcription factors. Both HNF-4 and C/EBP beta are required for liver-specific activity of the ornithine transcarbamylase enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1323–1331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin S., Gilliland G. Site-specific mutagenesis using asymmetric polymerase chain reaction and a single mutant primer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7433–7438. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymondjean M., Pichard A. L., Gregori C., Ginot F., Kahn A. Interplay of an original combination of factors: C/EBP, NFY, HNF3, and HNF1 in the rat aldolase B gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6145–6153. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouet P., Raguenez G., Salier J. P. Optimized assays for quantifying transient expressions of co-transfected beta-galactosidase and CAT reporter genes. Biotechniques. 1992 Nov;13(5):700–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouet P., Raguenez G., Tronche F., Yaniv M., N'Guyen C., Salier J. P. A potent enhancer made of clustered liver-specific elements in the transcription control sequences of human alpha 1-microglobulin/bikunin gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20765–20773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salier J. P., Chan P., Raguenez G., Zwingman T., Erickson R. P. Developmentally regulated transcription of the four liver-specific genes for inter-alpha-inhibitor family in mouse. Biochem J. 1993 Nov 15;296(Pt 1):85–91. doi: 10.1042/bj2960085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salier J. P., Diarra-Mehrpour M., Sesboue R., Bourguignon J., Benarous R., Ohkubo I., Kurachi S., Kurachi K., Martin J. P. Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding the heavy chain of human inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor (I alpha TI): unambiguous evidence for multipolypeptide chain structure of I alpha TI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8272–8276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salier J. P. Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor: emergence of a family within the Kunitz-type protease inhibitor superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Nov;15(11):435–439. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90282-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K. J., Wilson D. R., Shih C., Darlington G. J. The transcription factor HNF1 acts with C/EBP alpha to synergistically activate the human albumin promoter through a novel domain. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1177–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthopoulos K. G., Mirkovitch J. Gene regulation in rodent hepatocytes during development, differentiation and disease. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Sep 1;216(2):353–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]