Abstract
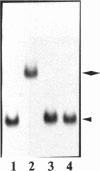
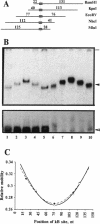
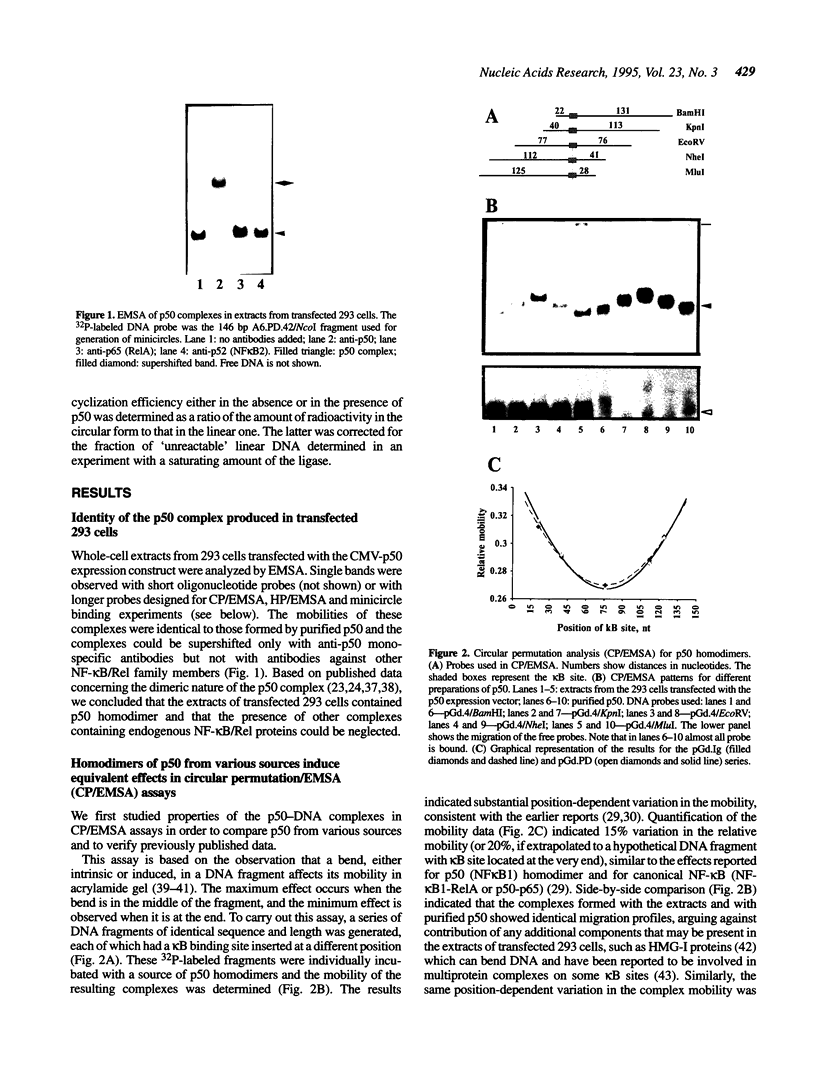
Transcription factors can distort the conformation of the DNA double helix upon binding to their target sites. Previously, studies utilizing circular permutation--electrophoretic mobility shift assay suggested that the homodimer of p50 (NF kappa B1), canonical NF-kappa B (p65-p50), as well as several non-canonical NF-kappa B/Rel complexes, may induce substantial DNA bending at the binding site. Here we have applied three additional experimental approaches, helical phasing analysis, minicircle binding and cyclization kinetics, and conclude that the homodimer of p50 introduces virtually no directed bend into the consensus kappa B sequences GGGACTTTCC or GGGAATTCCC.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
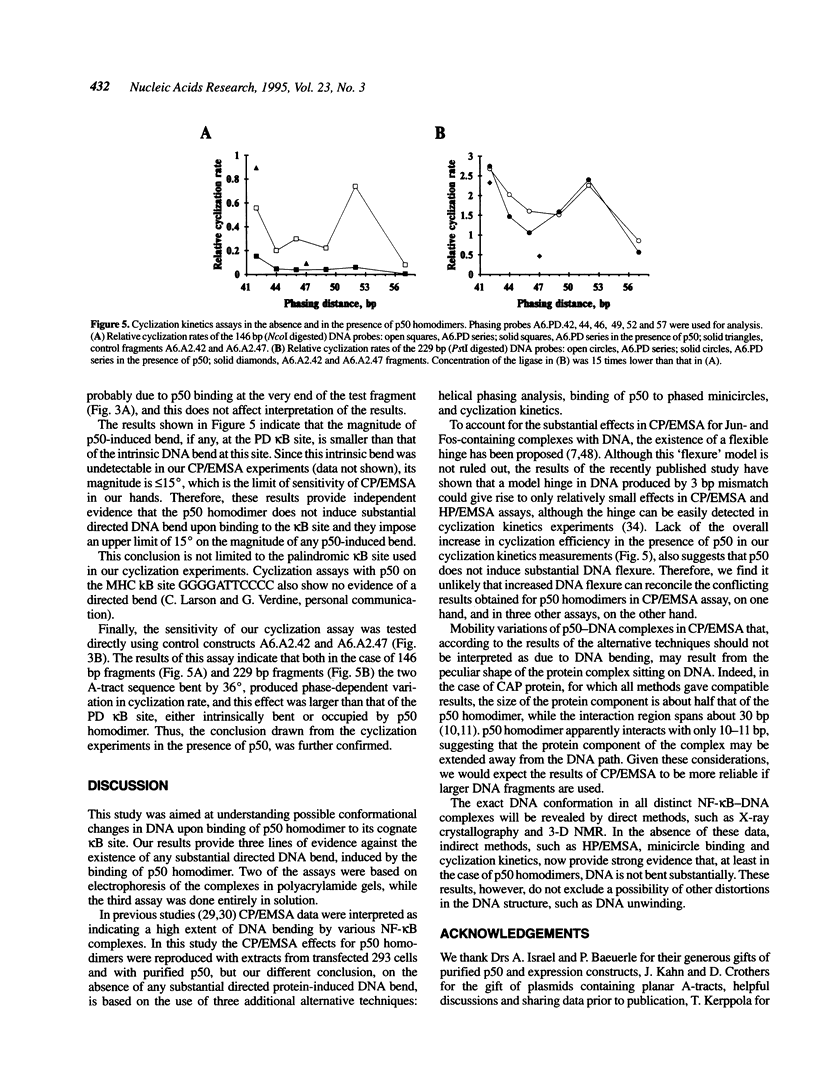
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
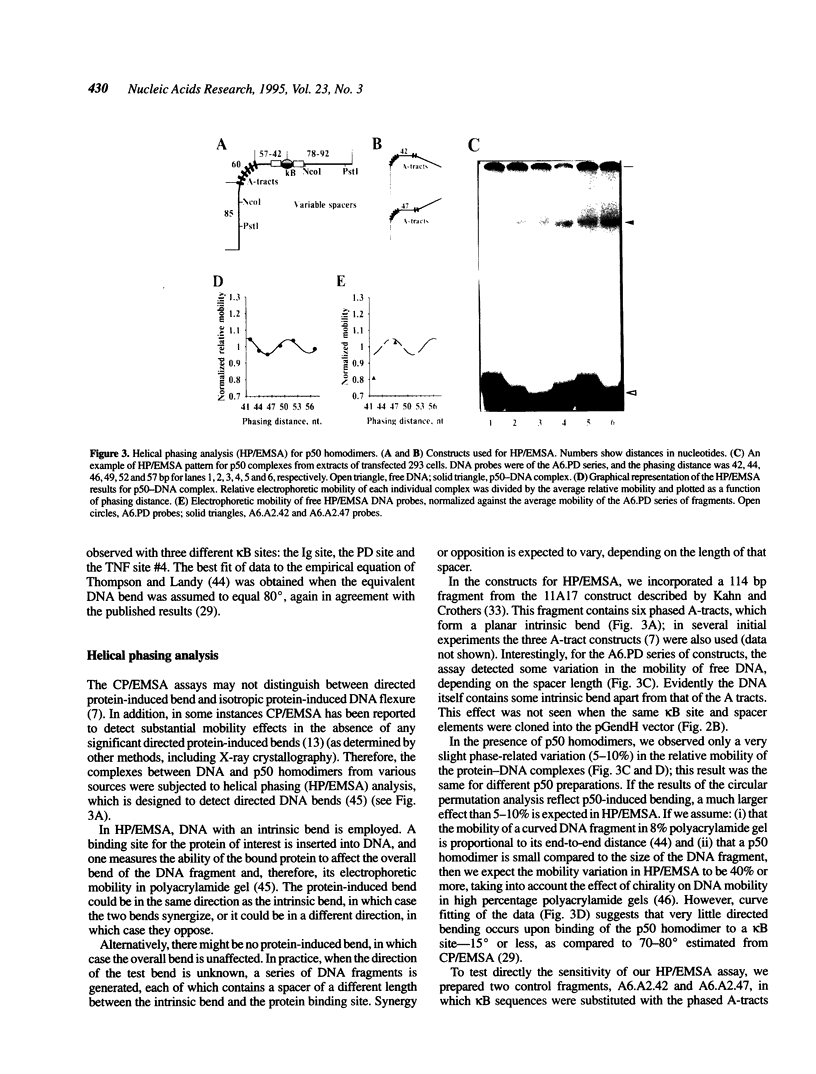
- Baeuerle P. A., Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Crothers D. M. Modulation of the stability of a gene-regulatory protein dimer by DNA and cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7387–7391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. L., Halden N. F., Lenardo M. J., Leonard W. J. Functionally distinct NF-kappa B binding sites in the immunoglobulin kappa and IL-2 receptor alpha chain genes. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):466–469. doi: 10.1126/science.2497520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Drak J., Kahn J. D., Levene S. D. DNA bending, flexibility, and helical repeat by cyclization kinetics. Methods Enzymol. 1992;212:3–29. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)12003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drak J., Crothers D. M. Helical repeat and chirality effects on DNA gel electrophoretic mobility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3074–3078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Brandl C. J., Struhl K., Harrison S. C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1223–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferré-D'Amaré A. R., Prendergast G. C., Ziff E. B., Burley S. K. Recognition by Max of its cognate DNA through a dimeric b/HLH/Z domain. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):38–45. doi: 10.1038/363038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Ampe C., Steitz T. A., Crothers D. M. Molecular characterization of the GCN4-DNA complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6034–6038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Cox J., Grosschedl R. The HMG domain of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 bends DNA and facilitates assembly of functional nucleoprotein structures. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90129-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. R., Lehn D. A., Elton T. S., Barr P. J., Reeves R. Complete murine cDNA sequence, genomic structure, and tissue expression of the high mobility group protein HMG-I(Y). J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18338–18342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. D., Crothers D. M. Protein-induced bending and DNA cyclization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6343–6347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. D., Yun E., Crothers D. M. Detection of localized DNA flexibility. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):163–166. doi: 10.1038/368163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. DNA bending by Fos and Jun: the flexible hinge model. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1210–1214. doi: 10.1126/science.1957173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. Fos-Jun heterodimers and Jun homodimers bend DNA in opposite orientations: implications for transcription factor cooperativity. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90621-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. Selective DNA bending by a variety of bZIP proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5479–5489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Nikolov D. B., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of a TATA element. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):520–527. doi: 10.1038/365520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Zwieb C., Wu C., Adhya S. Bending of DNA by gene-regulatory proteins: construction and use of a DNA bending vector. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Geiger J. H., Hahn S., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of a yeast TBP/TATA-box complex. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):512–520. doi: 10.1038/365512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Drak J., Rice J. A., Crothers D. M. Determination of the extent of DNA bending by an adenine-thymine tract. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4227–4234. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuprash D. V., Nedospasov S. A. Vzaimodeistvie transkriptsionnykh faktorov seveistva NF-kappa B/rel s DNK privodit k ee znachitel'nomu izgibu v uchastke sviazyvaniia. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1992;322(2):421–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König P., Richmond T. J. The X-ray structure of the GCN4-bZIP bound to ATF/CREB site DNA shows the complex depends on DNA flexibility. J Mol Biol. 1993 Sep 5;233(1):139–154. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. Bending and flexibility of kinetoplast DNA. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):3988–3995. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Johnson H. N., Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. The DNA binding domain and bending angle of E. coli CAP protein. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X. P., Eberhardt N. L., Pfahl M. DNA bending by retinoid X receptor-containing retinoid and thyroid hormone receptor complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6509–6519. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyubchenko Y., Shlyakhtenko L., Chernov B., Harrington R. E. DNA bending induced by Cro protein binding as demonstrated by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5331–5334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauxion F., Sen R. Alteration of a single nucleotide allows efficient binding of H2TF1/KBF1 to the immunoglobulin kappa enhancer B motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3548–3552. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- När A. M., Boutin J. M., Lipkin S. M., Yu V. C., Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. The orientation and spacing of core DNA-binding motifs dictate selective transcriptional responses to three nuclear receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a five-finger GLI-DNA complex: new perspectives on zinc fingers. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1701–1707. doi: 10.1126/science.8378770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins N. D., Schmid R. M., Duckett C. S., Leung K., Rice N. R., Nabel G. J. Distinct combinations of NF-kappa B subunits determine the specificity of transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1529–1533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Martín J., Espinosa M. The RepA repressor can act as a transcriptional activator by inducing DNA bends. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1375–1382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07657.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Ernst M. K. In vivo control of NF-kappa B activation by I kappa B alpha. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4685–4695. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Zorbas H., Winnacker E. L., Baeuerle P. A. The NF-kappa B transcription factor induces DNA bending which is modulated by its 65-kD subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6497–6502. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1001–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1653449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos D., Maniatis T. The high mobility group protein HMG I(Y) is required for NF-kappa B-dependent virus induction of the human IFN-beta gene. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90554-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban M. B., Baeuerle P. A. The role of the p50 and p65 subunits of NF-kappa B in the recognition of cognate sequences. New Biol. 1991 Mar;3(3):279–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler D. S., Dang C. V. Opposite orientations of DNA bending by c-Myc and Max. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7635–7639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Architectural transcription factors. Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1100–1101. doi: 10.1126/science.8178167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. DNA bend direction by phase sensitive detection. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):178–181. doi: 10.1038/328178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vliet P. C., Verrijzer C. P. Bending of DNA by transcription factors. Bioessays. 1993 Jan;15(1):25–32. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]