Abstract
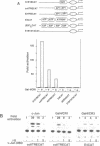
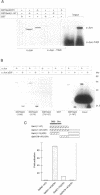
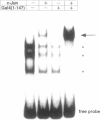
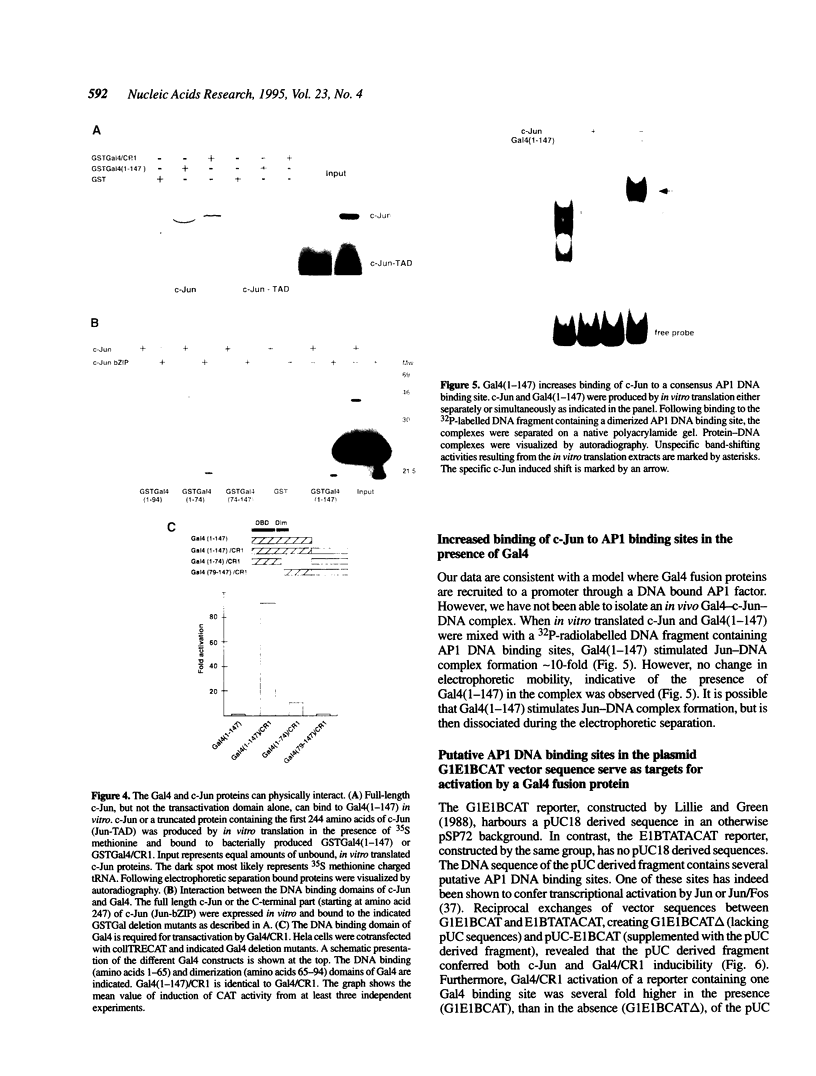
Different Gal4 fusion proteins, expressing unrelated transcription activator domains, were found to activate transcription from promoters containing dimerized AP1 DNA binding sites. Transactivation was dependent on the first 74 amino acids of Gal4. A direct interaction between Gal4 and c-Jun was demonstrated using a GSTGal4 fusion protein and in vitro translated human c-Jun. The interaction required the zinc finger containing DNA binding domain of Gal4 and the basic-leucine zipper region of c-Jun. These results demonstrated that the specificity of Gal4 fusion proteins in transient transfection experiments in mammalian cells is not restricted to reporters containing Gal4 binding sites, but also includes promoters containing AP1 binding sites. Furthermore, the Gal4 fusion proteins also activated transcription from a pUC18 vector fragment containing several putative AP1 binding sites. Finally, our results indicate that Gal4 activator proteins binding to Gal4 binding sites and to DNA bound AP1 factors can co-operatively activate transcription.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. G., Dynan W. S. Quantitative studies of the effect of HTLV-I Tax protein on CREB protein--DNA binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 11;22(15):3194–3201. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.15.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):129–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Tjian R. Control of c-Jun activity by interaction of a cell-specific inhibitor with regulatory domain delta: differences between v- and c-Jun. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D. M., Jones N. C. Heterodimer formation between CREB and JUN proteins. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):295–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Ransone L., Scharfmann R., Dwarki V. J., Tapscott S. J., Weintraub H., Verma I. M. Functional antagonism between c-Jun and MyoD proteins: a direct physical association. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):507–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90187-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondesson M., Mannervik M., Akusjärvi G., Svensson C. An adenovirus E1A transcriptional repressor domain functions as an activator when tethered to a promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 11;22(15):3053–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.15.3053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. H., Alani R., Preis L. H., Szabo E., Birrer M. J. Suppression of oncogene-induced transformation by a deletion mutant of c-jun. Oncogene. 1993 Apr;8(4):877–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatton B., Bocco J. L., Goetz J., Gaire M., Lutz Y., Kedinger C. Jun and Fos heterodimerize with ATFa, a member of the ATF/CREB family and modulate its transcriptional activity. Oncogene. 1994 Feb;9(2):375–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T., Curran T. Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3720–3724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Wu C. L., Fattaey A. R., Lees J. A., Dynlacht B. D., Ngwu C., Harlow E. Heterodimerization of the transcription factors E2F-1 and DP-1 leads to cooperative trans-activation. Genes Dev. 1993 Oct;7(10):1850–1861. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.10.1850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Stein R. c-jun inhibits transcriptional activation by the insulin enhancer, and the insulin control element is the target of control. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):655–662. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu W., Kerppola T. K., Chen P. L., Curran T., Chen-Kiang S. Fos and Jun repress transcription activation by NF-IL6 through association at the basic zipper region. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):268–276. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. Leucine zippers of fos, jun and GCN4 dictate dimerization specificity and thereby control DNA binding. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):568–571. doi: 10.1038/340568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A., Yancheva N., Wasylyk B. Transformation suppressor activity of a Jun transcription factor lacking its activation domain. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):635–638. doi: 10.1038/352635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez G., Schaufele F., Webb P., Holloway J. M., Baxter J. D., Kushner P. J. Positive and negative modulation of Jun action by thyroid hormone receptor at a unique AP1 site. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):3042–3049. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.3042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucibello F. C., Slater E. P., Jooss K. U., Beato M., Müller R. Mutual transrepression of Fos and the glucocorticoid receptor: involvement of a functional domain in Fos which is absent in FosB. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2827–2834. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07471.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmorstein R., Carey M., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. DNA recognition by GAL4: structure of a protein-DNA complex. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):408–414. doi: 10.1038/356408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall-Heyman H., Engel G., Ljungdahl S., Shoshan M. C., Svensson C., Wasylyk B., Linder S. Tumorigenic and metastatic properties of two ras-oncogene transfected rat fibrosarcoma cell lines defective in c-jun. Oncogene. 1994 Dec;9(12):3655–3663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberg M., Schuermann M., Hunter J. B., Müller R. Two functionally different regions in Fos are required for the sequence-specific DNA interaction of the Fos/Jun protein complex. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):589–590. doi: 10.1038/338589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe J. W., Rhodes D. Beyond zinc fingers: steroid hormone receptors have a novel structural motif for DNA recognition. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Aug;16(8):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90121-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Yang N., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Functional antagonism between oncoprotein c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1217–1226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90397-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. E., Papavassiliou A. G., Bohmann D. Different TRE-related elements are distinguished by sets of DNA-binding proteins with overlapping sequence specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 11;21(7):1581–1585. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.7.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-García I., Rabbitts T. H. The LIM domain: a new structural motif found in zinc-finger-like proteins. Trends Genet. 1994 Sep;10(9):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touray M., Ryan F., Jaggi R., Martin F. Characterisation of functional inhibition of the glucocorticoid receptor by Fos/Jun. Oncogene. 1991 Jul;6(7):1227–1234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner S., Green M. R. HTLV-I Tax protein stimulation of DNA binding of bZIP proteins by enhancing dimerization. Science. 1993 Oct 15;262(5132):395–399. doi: 10.1126/science.8211160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]