Abstract
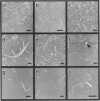
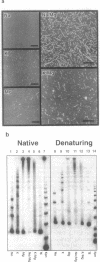
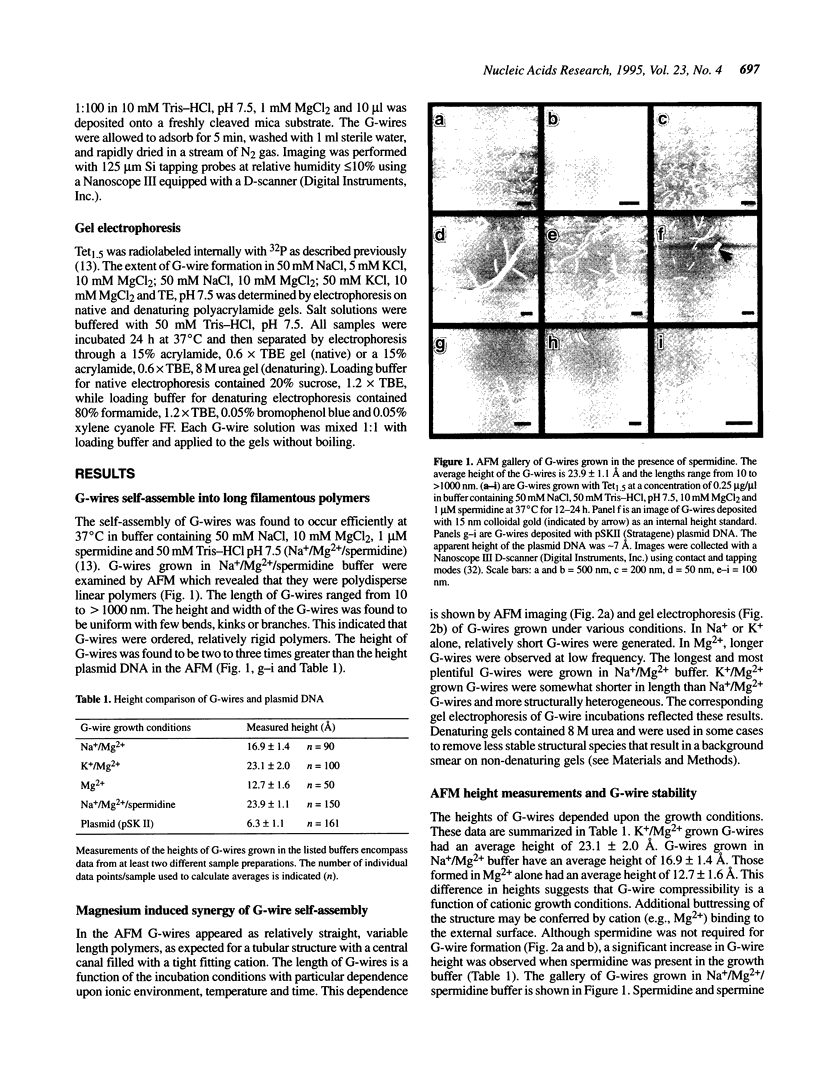
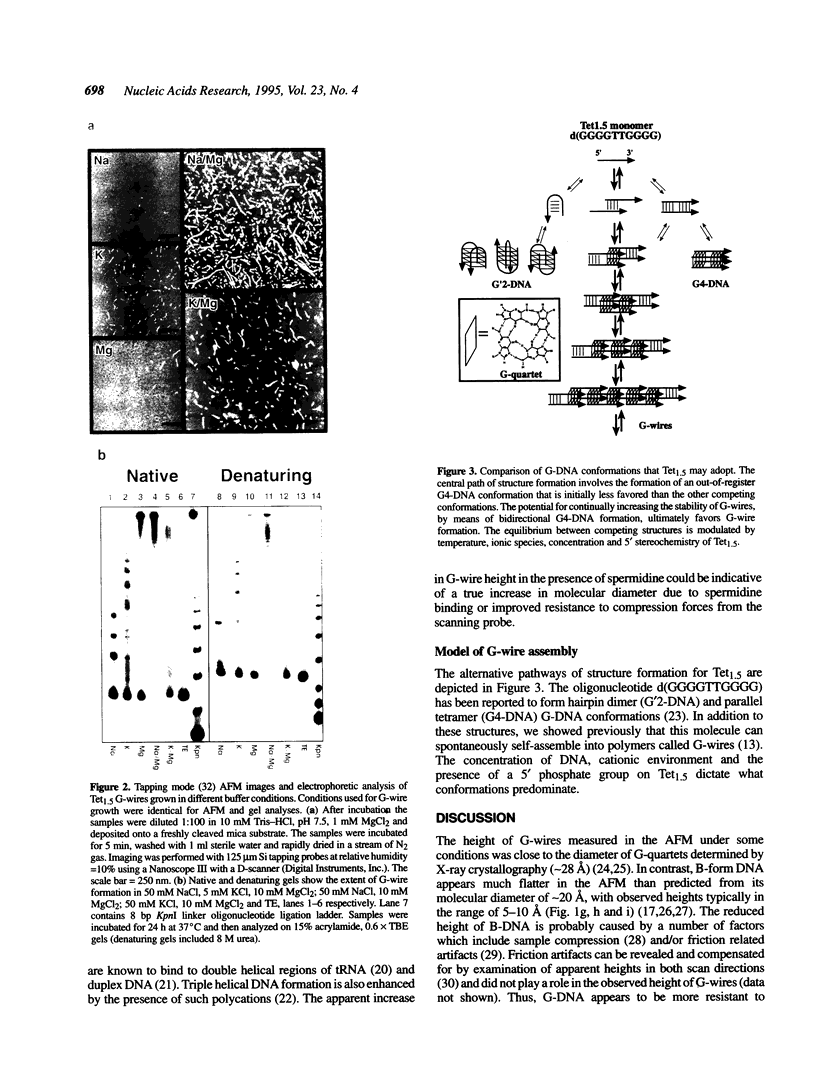
G-DNA is a polymorphic family of quadruple helical nucleic acid structures containing guanine tetrad motifs [G-quartets; Williamson, J.R., Raghuraman, M.K. and Cech, T.R. (1989) Cell 59, 871-880; Williamson, J.R. (1993) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 3124-3124]. Guanine rich oligonucleotides that are self-complimentary, as found in many telomeric G-strand repeat sequences, form G-DNA in the presence of monovalent and/or divalent metal cations. In this report we use the atomic force microscope (AFM) to explore the structural characteristics of long, linear polymers formed by the telomeric oligonucleotide d(GGGGTTGGGG) in the presence of specific metal cations. In the AFM these polymers, termed G-wires, appear as filaments whose height and length are determined by the metal ions present during the self-assembly process. The highly ordered, controllable self-assembly of G-wires could provide a basis for developing advanced biomaterials.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M. J., Dong X. F., O'Neill T. E., Yau P., Kowalczykowski S. C., Gatewood J., Balhorn R., Bradbury E. M. Atomic force microscope measurements of nucleosome cores assembled along defined DNA sequences. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 24;32(33):8390–8396. doi: 10.1021/bi00084a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amato I. Designer solids: haute couture in chemistry. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):753–755. doi: 10.1126/science.260.5109.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balagurumoorthy P., Brahmachari S. K., Mohanty D., Bansal M., Sasisekharan V. Hairpin and parallel quartet structures for telomeric sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):4061–4067. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnig G, Quate CF, Gerber C. Atomic force microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1986 Mar 3;56(9):930–933. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante C. Direct observation and manipulation of single DNA molecules using fluorescence microscopy. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:415–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.002215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante C., Vesenka J., Tang C. L., Rees W., Guthold M., Keller R. Circular DNA molecules imaged in air by scanning force microscopy. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):22–26. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. H., Seeman N. C. Synthesis from DNA of a molecule with the connectivity of a cube. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):631–633. doi: 10.1038/350631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du S. M., Seeman N. C. The construction of a trefoil knot from a DNA branched junction motif. Biopolymers. 1994 Jan;34(1):31–37. doi: 10.1002/bip.360340105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadiri M. R., Granja J. R., Milligan R. A., McRee D. E., Khazanovich N. Self-assembling organic nanotubes based on a cyclic peptide architecture. Nature. 1993 Nov 25;366(6453):324–327. doi: 10.1038/366324a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampel K. J., Crosson P., Lee J. S. Polyamines favor DNA triplex formation at neutral pH. Biochemistry. 1991 May 7;30(18):4455–4459. doi: 10.1021/bi00232a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Bezanilla M., Zenhausern F., Adrian M., Sinsheimer R. L. Atomic force microscopy of DNA in aqueous solutions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):505–512. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Vesenka J., Siegerist C., Kelderman G., Morrett H., Sinsheimer R. L., Elings V., Bustamante C., Hansma P. K. Reproducible imaging and dissection of plasmid DNA under liquid with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1180–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Hardin C. C., Walk S. K., Tinoco I., Jr, Blackburn E. H. Telomeric DNA oligonucleotides form novel intramolecular structures containing guanine-guanine base pairs. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):899–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90577-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C., Zhang X., Ratliff R., Moyzis R., Rich A. Crystal structure of four-stranded Oxytricha telomeric DNA. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):126–131. doi: 10.1038/356126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughlan G., Murchie A. I., Norman D. G., Moore M. H., Moody P. C., Lilley D. M., Luisi B. The high-resolution crystal structure of a parallel-stranded guanine tetraplex. Science. 1994 Jul 22;265(5171):520–524. doi: 10.1126/science.8036494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu M., Guo Q., Kallenbach N. R. Structure and stability of sodium and potassium complexes of dT4G4 and dT4G4T. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 10;31(9):2455–2459. doi: 10.1021/bi00124a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh T. C., Henderson E. G-wires: self-assembly of a telomeric oligonucleotide, d(GGGGTTGGGG), into large superstructures. Biochemistry. 1994 Sep 6;33(35):10718–10724. doi: 10.1021/bi00201a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid N., Behr J. P. Location of spermine and other polyamines on DNA as revealed by photoaffinity cleavage with polyaminobenzenediazonium salts. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 30;30(17):4357–4361. doi: 10.1021/bi00231a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C. Construction of three-dimensional stick figures from branched DNA. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;10(7):475–486. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. Novel DNA superstructures formed by telomere-like oligomers. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):65–70. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thundat T., Allison D. P., Warmack R. J., Ferrell T. L. Imaging isolated strands of DNA molecules by atomic force microscopy. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Jul;42-44(Pt B):1101–1106. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90409-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venczel E. A., Sen D. Parallel and antiparallel G-DNA structures from a complex telomeric sequence. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 22;32(24):6220–6228. doi: 10.1021/bi00075a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesenka J., Manne S., Giberson R., Marsh T., Henderson E. Colloidal gold particles as an incompressible atomic force microscope imaging standard for assessing the compressibility of biomolecules. Biophys J. 1993 Sep;65(3):992–997. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81171-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitesides G. M., Mathias J. P., Seto C. T. Molecular self-assembly and nanochemistry: a chemical strategy for the synthesis of nanostructures. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1312–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.1962191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R. G-quartets in biology: reprise. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3124–3124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Raghuraman M. K., Cech T. R. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: the G-quartet model. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagil G., Sussman J. L. Structural models for non-helical DNA. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1719–1725. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04416.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Shao Z. Effect of probe force on the resolution of atomic force microscopy of DNA. Ultramicroscopy. 1993 Jul;50(2):157–170. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(93)90006-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]