Abstract
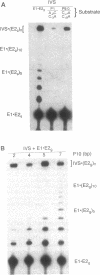
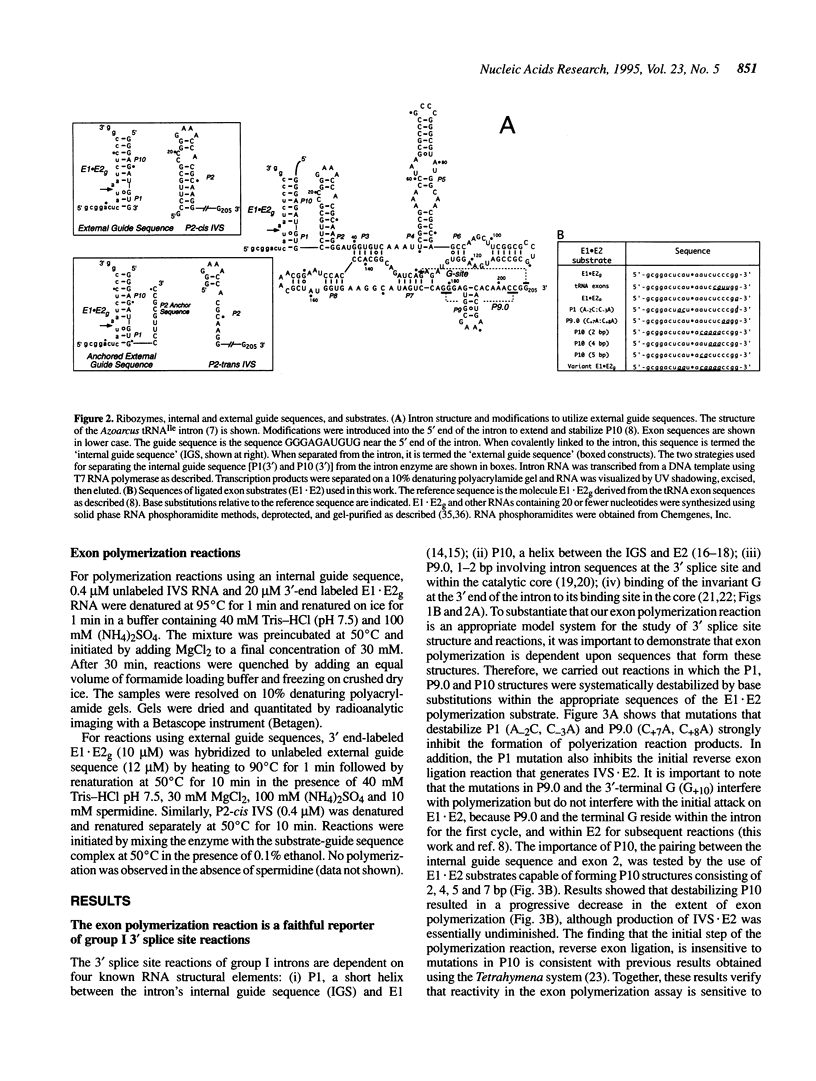
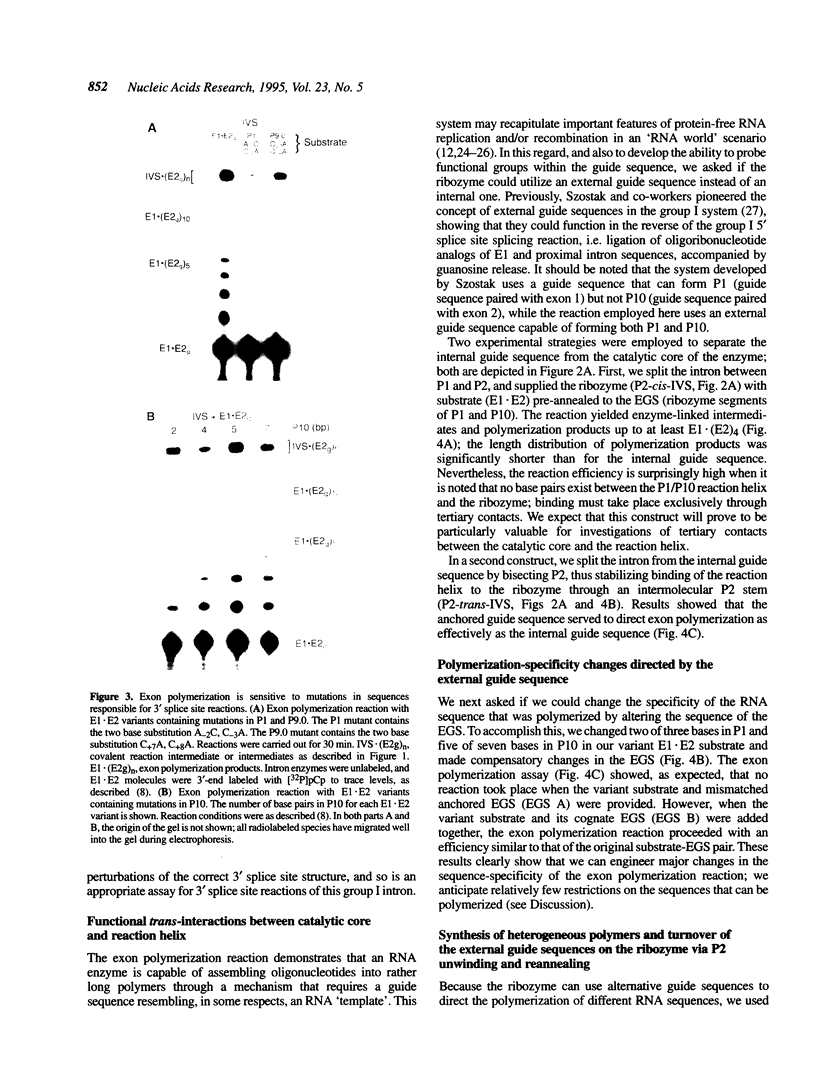
A group I intron from a bacterial tRNA precursor has been converted into an RNA enzyme that catalyzes the efficient polymerization of oligoribonucleotide analogs of tRNA exons using a reaction scheme consisting of multiple cycles of reverse and forward exon ligation reactions. Here, we present results showing that this system represents a novel and useful tool for the analysis of 3' splice site reactions of group I ribozymes. First, analysis of variant substrates containing base substitutions in group I secondary structure elements P1, P9.0 and P10 confirms that exon polymerization is dependent on these structures, and therefore constitutes an appropriate and relevant model system for studying the exon ligation step of splicing. Second, to probe interactions between the intron's catalytic core and the bases and backbone of the P1/P10 reaction helix, two successful strategies for separating the internal guide sequence from the intron core were devised. One such strategy uses a construct in which the reaction helix interacts functionally with the catalytic core using only tertiary contacts. Further stabilization of this interaction through the inclusion of a 7 bp intermolecular P2 helix generates increased reaction efficiency. Third, when provided with two reaction helices, the ribozyme synthesizes mixed polymers through a mechanism that involves sequential binding and release of the duplexes. Fourth, in these reactions, turnover of the external guide sequence requires unwinding and annealing of the P2 helix, suggesting that P2 unwinding may occur during group I splicing. These results provide novel experimental tools to probe the relatively poorly understood 3' splice site reactions of group I introns, and may be relevant to ribozyme-catalyzed assembly and recombination of oligomers in prebiotic scenarios.
Full text
PDF

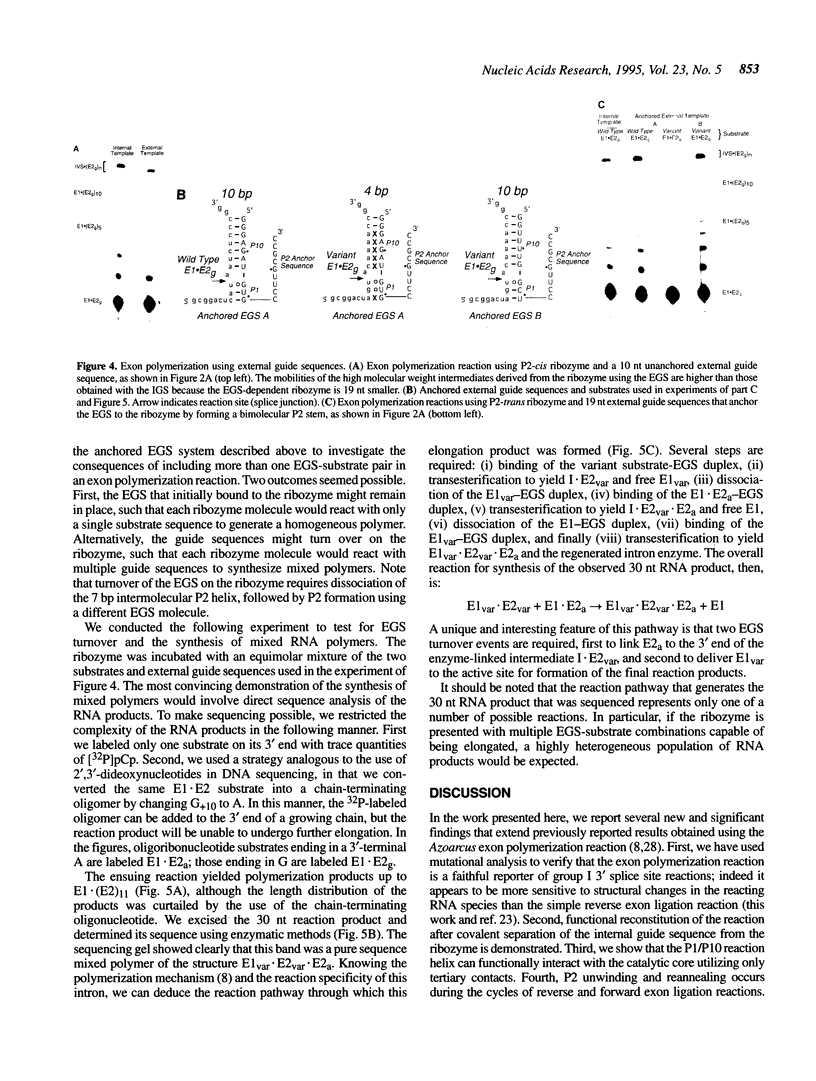
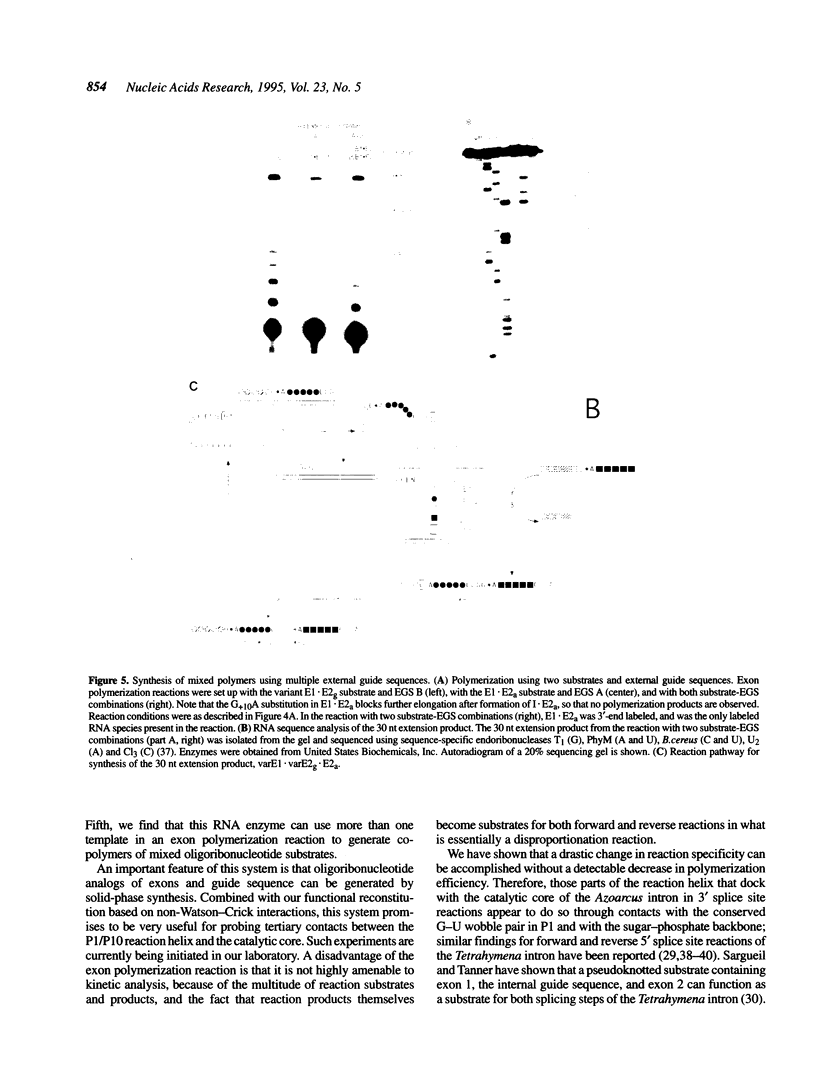

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartel D. P., Doudna J. A., Usman N., Szostak J. W. Template-directed primer extension catalyzed by the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3390–3394. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaudry A. A., Joyce G. F. Directed evolution of an RNA enzyme. Science. 1992 Jul 31;257(5070):635–641. doi: 10.1126/science.1496376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Cech T. R. One binding site determines sequence specificity of Tetrahymena pre-rRNA self-splicing, trans-splicing, and RNA enzyme activity. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90443-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Cech T. R. RNA as an RNA polymerase: net elongation of an RNA primer catalyzed by the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Science. 1988 Mar 18;239(4846):1412–1416. doi: 10.1126/science.2450400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Perrotta A. T. Group I intron self-splicing with adenosine: evidence for a single nucleoside-binding site. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):434–437. doi: 10.1126/science.2017681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzal-Herranz A., Chowrira B. M., Polsenberg J. F., Burke J. M. 2'-Hydroxyl groups important for exon polymerization and reverse exon ligation reactions catalyzed by a group I ribozyme. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 7;32(35):8981–8986. doi: 10.1021/bi00086a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua P. C., Turner D. H. Comparison of binding of mixed ribose-deoxyribose analogues of CUCU to a ribozyme and to GGAGAA by equilibrium dialysis: evidence for ribozyme specific interactions with 2' OH groups. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 5;30(44):10632–10640. doi: 10.1021/bi00108a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. M., Berzal-Herranz A. In vitro selection and evolution of RNA: applications for catalytic RNA, molecular recognition, and drug discovery. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):106–112. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. M., Esherick J. S., Burfeind W. R., King J. L. A 3' splice site-binding sequence in the catalytic core of a group I intron. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):80–82. doi: 10.1038/344080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. A model for the RNA-catalyzed replication of RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4360–4363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Herschlag D., Piccirilli J. A., Pyle A. M. RNA catalysis by a group I ribozyme. Developing a model for transition state stabilization. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17479–17482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Self-splicing of group I introns. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:543–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowrira B. M., Berzal-Herranz A., Burke J. M. Novel RNA polymerization reaction catalyzed by a group I ribozyme. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3599–3605. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06033.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowrira B. M., Burke J. M. Binding and cleavage of nucleic acids by the "hairpin" ribozyme. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 3;30(35):8518–8522. doi: 10.1021/bi00099a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Waring R. B., Ray J. A., Brown T. A., Scazzocchio C. Making ends meet: a model for RNA splicing in fungal mitochondria. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):719–724. doi: 10.1038/300719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doudna J. A., Couture S., Szostak J. W. A multisubunit ribozyme that is a catalyst of and template for complementary strand RNA synthesis. Science. 1991 Mar 29;251(5001):1605–1608. doi: 10.1126/science.1707185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doudna J. A., Szostak J. W. RNA-catalysed synthesis of complementary-strand RNA. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):519–522. doi: 10.1038/339519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doudna J. A., Usman N., Szostak J. W. Ribozyme-catalyzed primer extension by trinucleotides: a model for the RNA-catalyzed replication of RNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 2;32(8):2111–2115. doi: 10.1021/bi00059a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R., Ellington A. D., Szostak J. W. In vitro genetic analysis of the Tetrahymena self-splicing intron. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):406–408. doi: 10.1038/347406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R., Szostak J. W. Selection of a ribozyme that functions as a superior template in a self-copying reaction. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1910–1915. doi: 10.1126/science.1470913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschlag D., Eckstein F., Cech T. R. Contributions of 2'-hydroxyl groups of the RNA substrate to binding and catalysis by the Tetrahymena ribozyme. An energetic picture of an active site composed of RNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 17;32(32):8299–8311. doi: 10.1021/bi00083a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Sullivan F. X., Cech T. R. Intermolecular exon ligation of the rRNA precursor of Tetrahymena: oligonucleotides can function as 5' exons. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchino Y., Nishimura S. Enzymatic RNA sequencing. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:154–163. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Hanna M., Green R., Bartel D. P., Szostak J. W. The guanosine binding site of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):391–395. doi: 10.1038/342391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Netter P., Xu M. Q., Shub D. A. Mechanism of 3' splice site selection by the catalytic core of the sunY intron of bacteriophage T4: the role of a novel base-pairing interaction in group I introns. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):777–788. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partono S., Lewin A. S. Splicing of COB intron 5 requires pairing between the internal guide sequence and both flanking exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8192–8196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle A. M., Cech T. R. Ribozyme recognition of RNA by tertiary interactions with specific ribose 2'-OH groups. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):628–631. doi: 10.1038/350628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold-Hurek B., Shub D. A. Self-splicing introns in tRNA genes of widely divergent bacteria. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):173–176. doi: 10.1038/357173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchings B. W., Lewin A. S. Mutational evidence for competition between the P1 and the P10 helices of a mitochondrial group I intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20(9):2349–2353. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.9.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargueil B., Tanner N. K. A shortened form of the Tetrahymena thermophila group I intron can catalyze the complete splicing reaction in trans. J Mol Biol. 1993 Oct 20;233(4):629–643. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaringe S. A., Francklyn C., Usman N. Chemical synthesis of biologically active oligoribonucleotides using beta-cyanoethyl protected ribonucleoside phosphoramidites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5433–5441. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. A., Cech T. R. Tertiary interactions with the internal guide sequence mediate docking of the P1 helix into the catalytic core of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 14;32(49):13593–13604. doi: 10.1021/bi00212a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W. In vitro genetics. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Mar;17(3):89–93. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasiouka K. I., Burke J. M. A modified group I intron can function as both a ribozyme and a 5' exon in a trans-exon ligation reaction. Gene. 1994 Jun 24;144(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90195-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodson S. A., Cech T. R. Reverse self-splicing of the tetrahymena group I intron: implication for the directionality of splicing and for intron transposition. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):335–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90971-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Been M. D., Cech T. R. The Tetrahymena ribozyme acts like an RNA restriction endonuclease. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):429–433. doi: 10.1038/324429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Cech T. R. The intervening sequence RNA of Tetrahymena is an enzyme. Science. 1986 Jan 31;231(4737):470–475. doi: 10.1126/science.3941911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]