Abstract
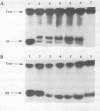
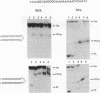
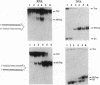
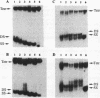
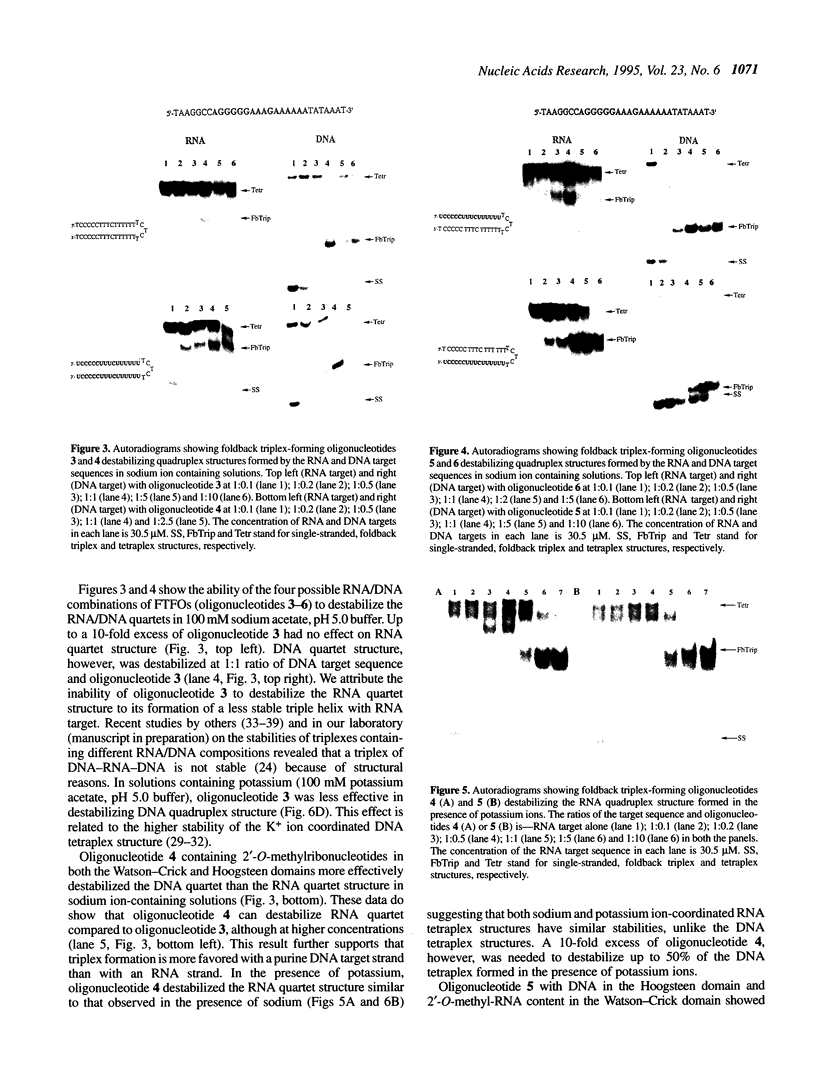
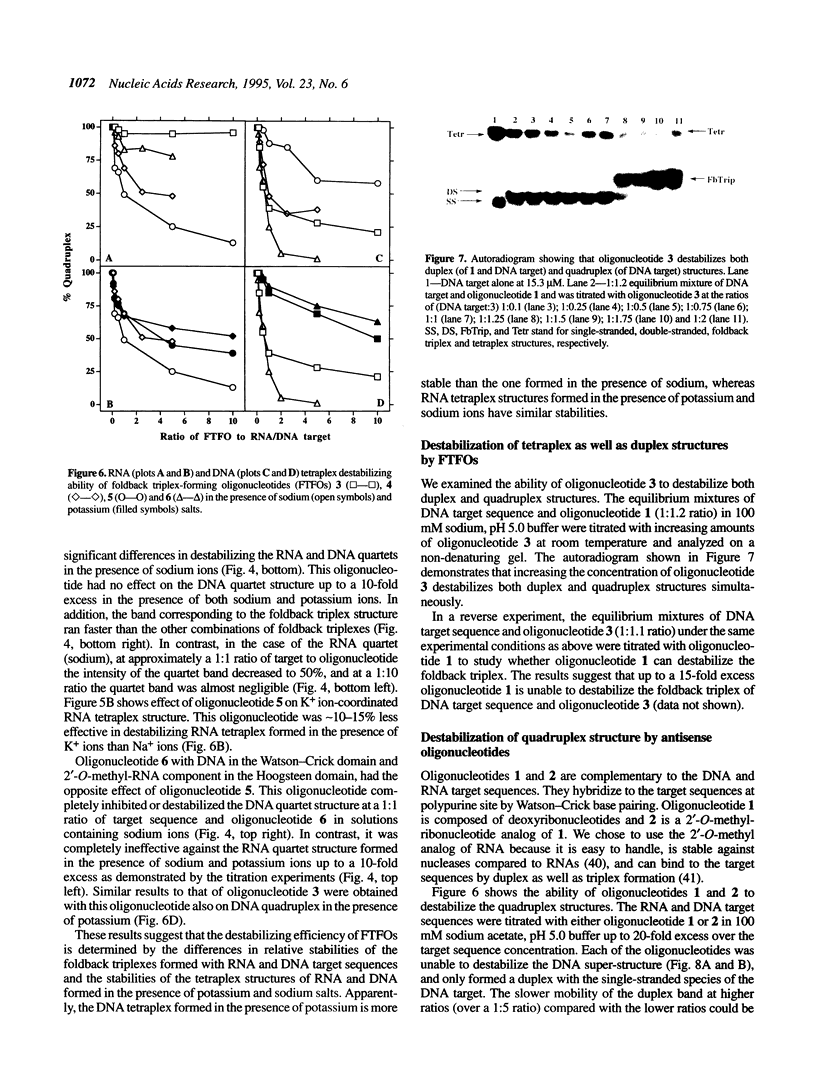
Oligonucleotides that can hybridize to single-stranded complementary polypurine nucleic acid targets by Watson-Crick base pairing as well as by Hoogsteen base pairing, referred to here as foldback triplex-forming oligonucleotides (FTFOs), have been designed. These oligonucleotides hybridize with target nucleic acid sequences with greater affinity than antisense oligonucleotides, which hybridize to the target sequence only by Watson-Crick hydrogen bonding [Kandimalla, E. R. and Agrawal, S. Gene(1994) 149, 115-121 and references cited therein]. FTFOs have been studied for their ability to destabilize quadruplexes formation by RNA or DNA target sequences. The influence of various DNA/RNA compositions of FTFOs on their ability to destabilize RNA and DNA quadruplexes has been examined. The ability of the FTFOs to destabilize quadruplex structures is related to the structurally and thermodynamically stable foldback triplex formed between the FTFO and its target sequence. Antisense oligonucleotides (DNA or RNA) that can form only a Watson-Crick double helix with the target sequence are unable to destabilize quadruplex structures of RNA and DNA target sequences and are therefore limited in their repertoire of target sequences. The quadruplex destabilization ability of FTFOs is dependent on the nature of the cation present in solution. The RNA quadruplex destabilization ability of FTFOs is -20% higher in the presence of sodium ion than potassium ion. The use of FTFOs, which can destabilize quadruplex structure, opens up new areas for development of oligonucleotide-based therapeutics, specifically, targeting guanine-rich sequences that exist at the ends of pro- and eukaryotic chromosomes and dimerization regions of retroviral RNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal S. Antisense oligonucleotides as antiviral agents. Trends Biotechnol. 1992 May;10(5):152–158. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(92)90203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal S., Tang J. Y. GEM 91--an antisense oligonucleotide phosphorothioate as a therapeutic agent for AIDS. Antisense Res Dev. 1992 Winter;2(4):261–266. doi: 10.1089/ard.1992.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awang G., Sen D. Mode of dimerization of HIV-1 genomic RNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 26;32(42):11453–11457. doi: 10.1021/bi00093a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudin F., Marquet R., Isel C., Darlix J. L., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Functional sites in the 5' region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA form defined structural domains. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 20;229(2):382–397. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayever E., Iversen P. L., Bishop M. R., Sharp J. G., Tewary H. K., Arneson M. A., Pirruccello S. J., Ruddon R. W., Kessinger A., Zon G. Systemic administration of a phosphorothioate oligonucleotide with a sequence complementary to p53 for acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome: initial results of a phase I trial. Antisense Res Dev. 1993 Winter;3(4):383–390. doi: 10.1089/ard.1993.3.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):569–573. doi: 10.1038/350569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker D. J., Vickers T. A., Bruice T. W., Freier S. M., Jenison R. D., Manoharan M., Zounes M. Pseudo--half-knot formation with RNA. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):958–961. doi: 10.1126/science.1502560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escudé C., François J. C., Sun J. S., Ott G., Sprinzl M., Garestier T., Hélène C. Stability of triple helices containing RNA and DNA strands: experimental and molecular modeling studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 11;21(24):5547–5553. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.24.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannangeli C., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Oligonucleotide clamps arrest DNA synthesis on a single-stranded DNA target. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10013–10017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han H., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical RNA and RNA.DNA by triple helix formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin C. C., Henderson E., Watson T., Prosser J. K. Monovalent cation induced structural transitions in telomeric DNAs: G-DNA folding intermediates. Biochemistry. 1991 May 7;30(18):4460–4472. doi: 10.1021/bi00232a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandimalla E. R., Agrawal S. Single-strand-targeted triplex formation: stability, specificity and RNase H activation properties. Gene. 1994 Nov 4;149(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90419-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C., Zhang X., Ratliff R., Moyzis R., Rich A. Crystal structure of four-stranded Oxytricha telomeric DNA. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):126–131. doi: 10.1038/356126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Cheong C., Moore P. B. Tetramerization of an RNA oligonucleotide containing a GGGG sequence. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):331–332. doi: 10.1038/351331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S. The stability of polypurine tetraplexes in the presence of mono- and divalent cations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6057–6060. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu M., Guo Q., Kallenbach N. R. Thermodynamics of G-tetraplex formation by telomeric DNAs. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 19;32(2):598–601. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. E., Egholm M., Berg R. H., Buchardt O. Sequence-selective recognition of DNA by strand displacement with a thymine-substituted polyamide. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1497–1500. doi: 10.1126/science.1962210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyutin I. G., Kovalsky O. I., Budowsky E. I., Dickerson R. E., Rikhirev M. E., Lipanov A. A. G-DNA: a twice-folded DNA structure adopted by single-stranded oligo(dG) and its implications for telomeres. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):867–870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats A. C., Roy C., Wang P. A., Erard M., Housset V., Gabus C., Paoletti C., Darlix J. L. cis elements and trans-acting factors involved in dimer formation of murine leukemia virus RNA. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):774–783. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.774-783.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghunathan G., Miles H. T., Sasisekharan V. Symmetry and molecular structure of a DNA triple helix: d(T)n.d(A)n.d(T)n. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 19;32(2):455–462. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. W., Crothers D. M. Stability and properties of double and triple helices: dramatic effects of RNA or DNA backbone composition. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1463–1466. doi: 10.1126/science.1279808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. A sodium-potassium switch in the formation of four-stranded G4-DNA. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):410–414. doi: 10.1038/344410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):364–366. doi: 10.1038/334364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. Novel DNA superstructures formed by telomere-like oligomers. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):65–70. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu M., Konishi A., Shimada Y., Inoue H., Ohtsuka E. Oligo(2'-O-methyl)ribonucleotides. Effective probes for duplex DNA. FEBS Lett. 1992 May 11;302(2):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80428-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. W., Feigon J. Quadruplex structure of Oxytricha telomeric DNA oligonucleotides. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):164–168. doi: 10.1038/356164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sproat B. S., Lamond A. I., Beijer B., Neuner P., Ryder U. Highly efficient chemical synthesis of 2'-O-methyloligoribonucleotides and tetrabiotinylated derivatives; novel probes that are resistant to degradation by RNA or DNA specific nucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3373–3386. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Cheng Y. C. Antisense oligonucleotides as therapeutic agents--is the bullet really magical? Science. 1993 Aug 20;261(5124):1004–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.8351515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist W. I., Heaphy S. Evidence for interstrand quadruplex formation in the dimerization of human immunodeficiency virus 1 genomic RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3393–3397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundquist W. I., Klug A. Telomeric DNA dimerizes by formation of guanine tetrads between hairpin loops. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):825–829. doi: 10.1038/342825a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Patel D. J. Guanine residues in d(T2AG3) and d(T2G4) form parallel-stranded potassium cation stabilized G-quadruplexes with anti glycosidic torsion angles in solution. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 8;31(35):8112–8119. doi: 10.1021/bi00150a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xodo L. E., Manzini G., Quadrifoglio F. Spectroscopic and calorimetric investigation on the DNA triplex formed by d(CTCTTCTTTCTTTTCTTTCTTCTC) and d(GAGAAGAAAGA) at acidic pH. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3557–3564. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]