Abstract
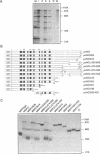
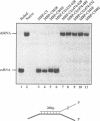
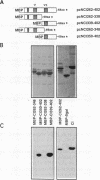
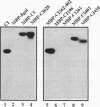
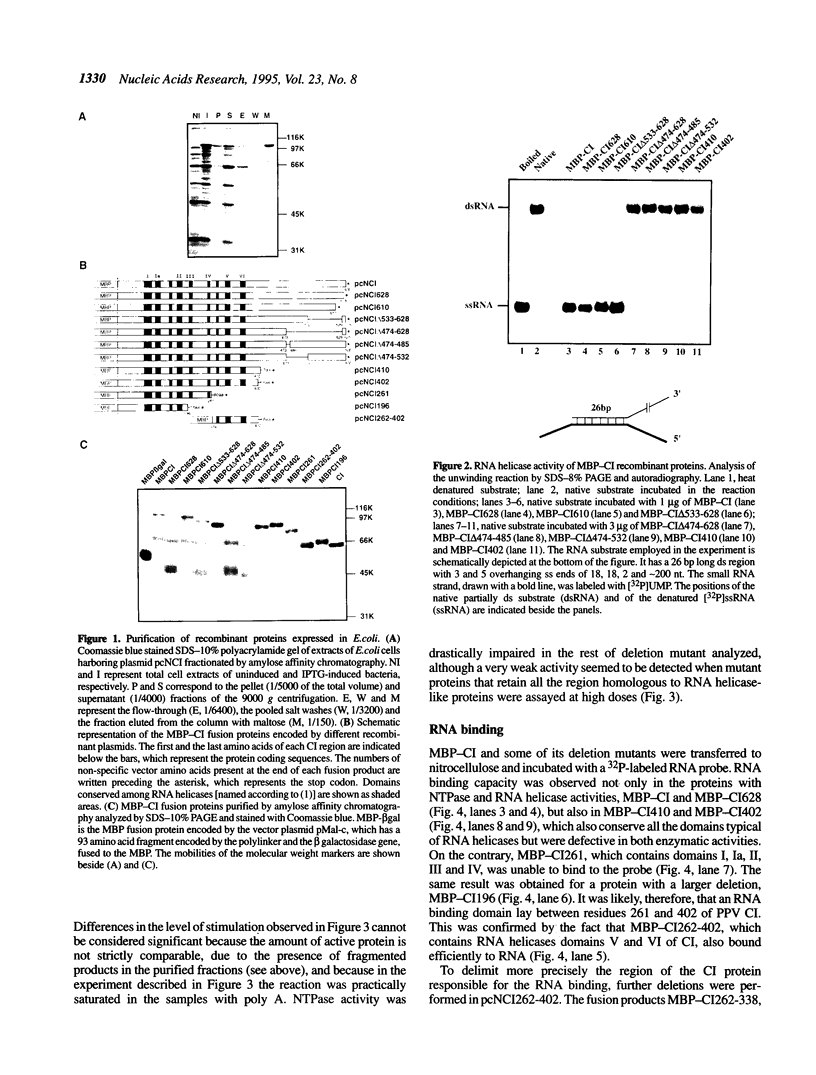
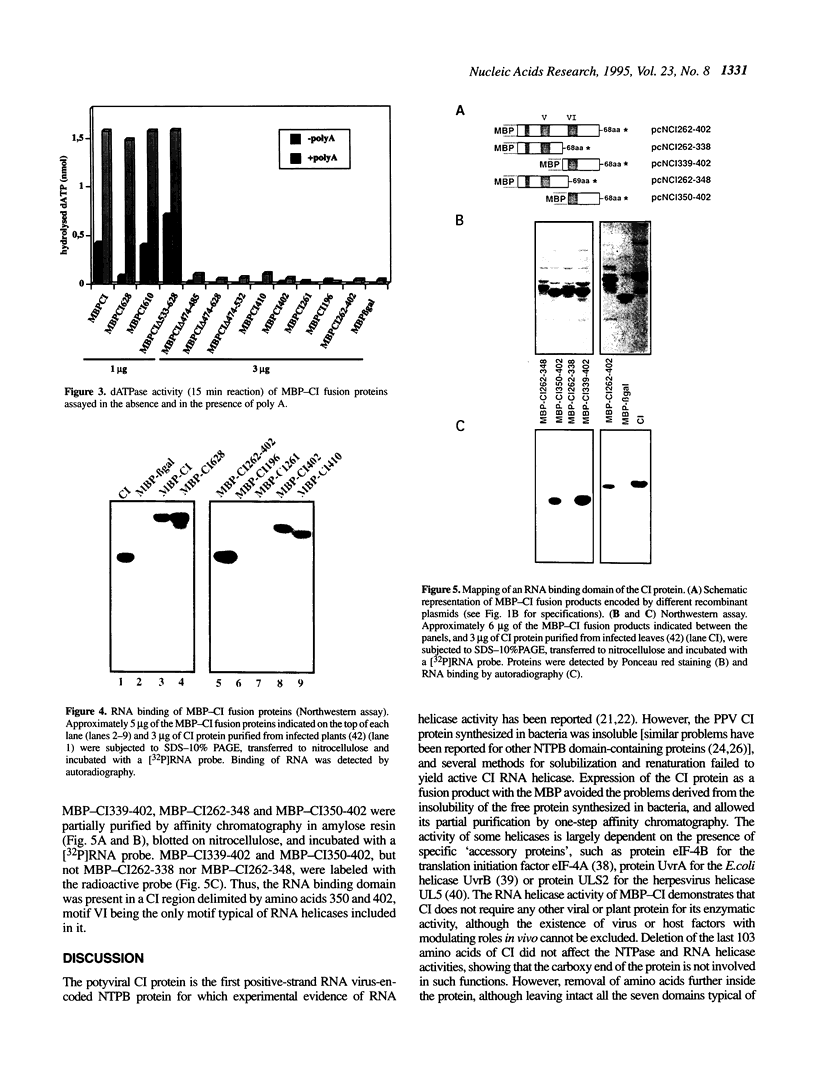
The plum pox potyvirus (PPV) cylindrical inclusion (CI) protein fused to the maltose binding protein (MBP) has been synthesized in Escherichia coli and purified by affinity chromatography in amylose resin. In the absence of any other viral factors, the fusion product had NTPase, RNA binding and RNA helicase activities. These in vitro activities were not affected by removal of the last 103 amino acids of the CI protein. However, other deletions in the C-terminal part of the protein, although leaving intact all the region conserved in RNA helicases, drastically impaired the ability to unwind dsRNA and to hydrolyze NTPs. A mutant protein lacking the last 225 residues retained the competence to interact with RNA. Further deletions mapped boundaries of the RNA binding domain within residues 350 and 402 of the PPV CI protein. This region includes the arginine-rich motif VI, the most carboxy terminal conserved domain of RNA helicases of the superfamily SF2. These results indicate that NTP hydrolysis is not an essential component for RNA binding of the PPV CI protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blum S., Schmid S. R., Pause A., Buser P., Linder P., Sonenberg N., Trachsel H. ATP hydrolysis by initiation factor 4A is required for translation initiation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Company M., Arenas J., Abelson J. Requirement of the RNA helicase-like protein PRP22 for release of messenger RNA from spliceosomes. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):487–493. doi: 10.1038/349487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M. S., Lehman I. R. Association of DNA helicase and primase activities with a subassembly of the herpes simplex virus 1 helicase-primase composed of the UL5 and UL52 gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1105–1109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagles R. M., Balmori-Melián E., Beck D. L., Gardner R. C., Forster R. L. Characterization of NTPase, RNA-binding and RNA-helicase activities of the cytoplasmic inclusion protein of tamarillo mosaic potyvirus. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Sep 1;224(2):677–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.t01-1-00677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Knippers R. Structure and function of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:55–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García J. A., Riechmann J. L., Laín S. Proteolytic activity of the plum pox potyvirus NIa-like protein in Escherichia coli. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):362–369. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90426-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbach R. Genome similarities between plant and animal RNA viruses. Microbiol Sci. 1987 Jul;4(7):197–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V. Viral proteins containing the purine NTP-binding sequence pattern. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8413–8440. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Wolf Y. I. A new superfamily of putative NTP-binding domains encoded by genomes of small DNA and RNA viruses. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 12;262(1):145–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80175-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grakoui A., McCourt D. W., Wychowski C., Feinstone S. M., Rice C. M. Characterization of the hepatitis C virus-encoded serine proteinase: determination of proteinase-dependent polyprotein cleavage sites. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2832–2843. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2832-2843.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koonin E. V. Similarities in RNA helicases. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):290–290. doi: 10.1038/352290c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laín S., Martín M. T., Riechmann J. L., García J. A. Novel catalytic activity associated with positive-strand RNA virus infection: nucleic acid-stimulated ATPase activity of the plum pox potyvirus helicaselike protein. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.1-6.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laín S., Riechmann J. L., García J. A. RNA helicase: a novel activity associated with a protein encoded by a positive strand RNA virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):7003–7006. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.7003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laín S., Riechmann J. L., García J. A. The complete nucleotide sequence of plum pox potyvirus RNA. Virus Res. 1989 Jun;13(2):157–172. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(89)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laín S., Riechmann J. L., Martín M. T., García J. A. Homologous potyvirus and flavivirus proteins belonging to a superfamily of helicase-like proteins. Gene. 1989 Oct 30;82(2):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzayan C., Wimmer E. Biochemical studies on poliovirus polypeptide 2C: evidence for ATPase activity. Virology. 1994 Feb 15;199(1):176–187. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mushegian A. R., Koonin E. V. Cell-to-cell movement of plant viruses. Insights from amino acid sequence comparisons of movement proteins and from analogies with cellular transport systems. Arch Virol. 1993;133(3-4):239–257. doi: 10.1007/BF01313766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh E. Y., Grossman L. Characterization of the helicase activity of the Escherichia coli UvrAB protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1336–1343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pause A., Méthot N., Sonenberg N. The HRIGRXXR region of the DEAD box RNA helicase eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A is required for RNA binding and ATP hydrolysis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6789–6798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pause A., Méthot N., Svitkin Y., Merrick W. C., Sonenberg N. Dominant negative mutants of mammalian translation initiation factor eIF-4A define a critical role for eIF-4F in cap-dependent and cap-independent initiation of translation. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 1;13(5):1205–1215. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06370.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pause A., Sonenberg N. Mutational analysis of a DEAD box RNA helicase: the mammalian translation initiation factor eIF-4A. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2643–2654. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05330.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riechmann J. L., Laín S., García J. A. Infectious in vitro transcripts from a plum pox potyvirus cDNA clone. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):710–716. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90537-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez P. L., Carrasco L. Poliovirus protein 2C has ATPase and GTPase activities. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8105–8110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen F., Edery I., Meerovitch K., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Sonenberg N. Bidirectional RNA helicase activity of eucaryotic translation initiation factors 4A and 4F. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1134–1144. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. R., Linder P. D-E-A-D protein family of putative RNA helicases. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(3):283–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. R., Linder P. Translation initiation factor 4A from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: analysis of residues conserved in the D-E-A-D family of RNA helicases. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3463–3471. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S. Vaccinia virus RNA helicase: an essential enzyme related to the DE-H family of RNA-dependent NTPases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10935–10939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzich J. A., Tamura J. K., Palmer-Hill F., Warrener P., Grakoui A., Rice C. M., Feinstone S. M., Collett M. S. Hepatitis C virus NS3 protein polynucleotide-stimulated nucleoside triphosphatase and comparison with the related pestivirus and flavivirus enzymes. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6152–6158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6152-6158.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura J. K., Warrener P., Collett M. S. RNA-stimulated NTPase activity associated with the p80 protein of the pestivirus bovine viral diarrhea virus. Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):1–10. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrener P., Tamura J. K., Collett M. S. RNA-stimulated NTPase activity associated with yellow fever virus NS3 protein expressed in bacteria. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):989–996. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.989-996.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Czaya G., Färber P. M., Hegemann J. H. In vitro synthesis of West Nile virus proteins indicates that the amino-terminal segment of the NS3 protein contains the active centre of the protease which cleaves the viral polyprotein after multiple basic amino acids. J Gen Virol. 1991 Apr;72(Pt 4):851–858. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-4-851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G. The NS 3 nonstructural protein of flaviviruses contains an RNA triphosphatase activity. Virology. 1993 Nov;197(1):265–273. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G. The carboxy-terminal part of the NS 3 protein of the West Nile flavivirus can be isolated as a soluble protein after proteolytic cleavage and represents an RNA-stimulated NTPase. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):707–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90440-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskerchen M., Collett M. S. Pestivirus gene expression: protein p80 of bovine viral diarrhea virus is a proteinase involved in polyprotein processing. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):341–350. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90850-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yáez R. J., Rodríguez J. M., Boursnell M., Rodríguez J. F., Viñuela E. Two putative African swine fever virus helicases similar to yeast 'DEAH' pre-mRNA processing proteins and vaccinia virus ATPases D11L and D6R. Gene. 1993 Dec 8;134(2):161–174. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90090-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]