Abstract
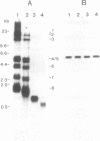
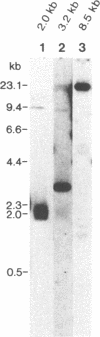
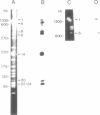
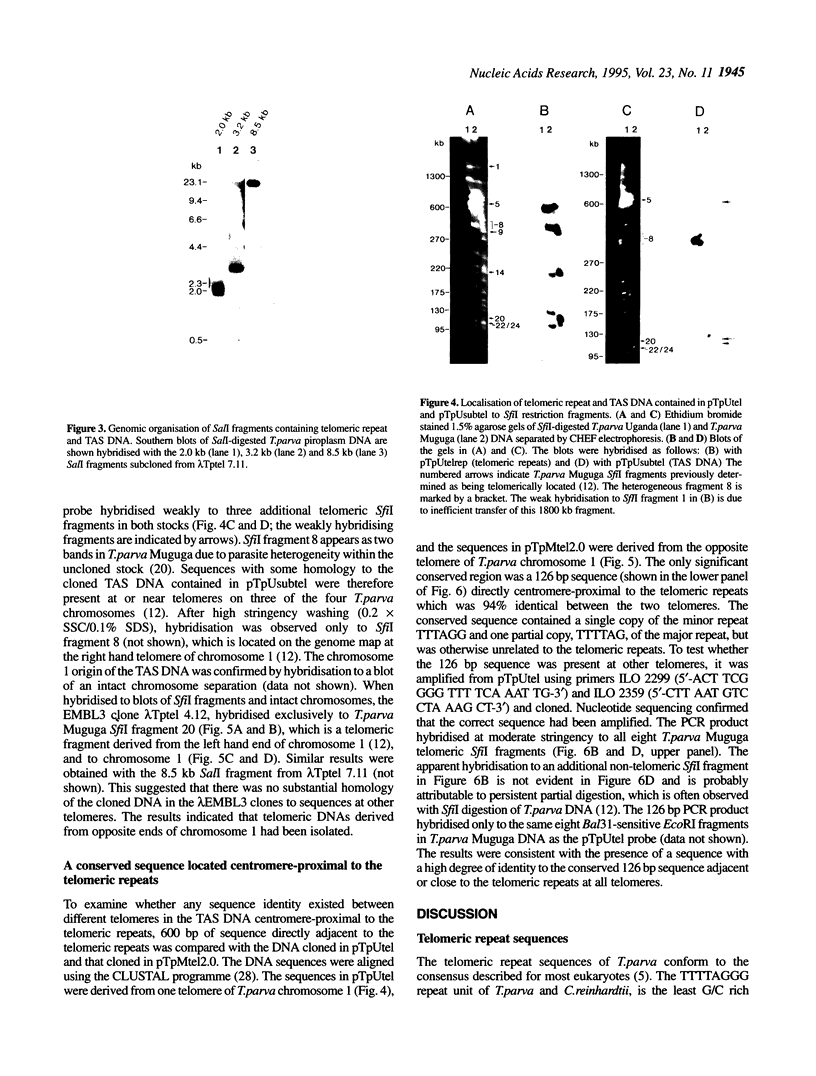
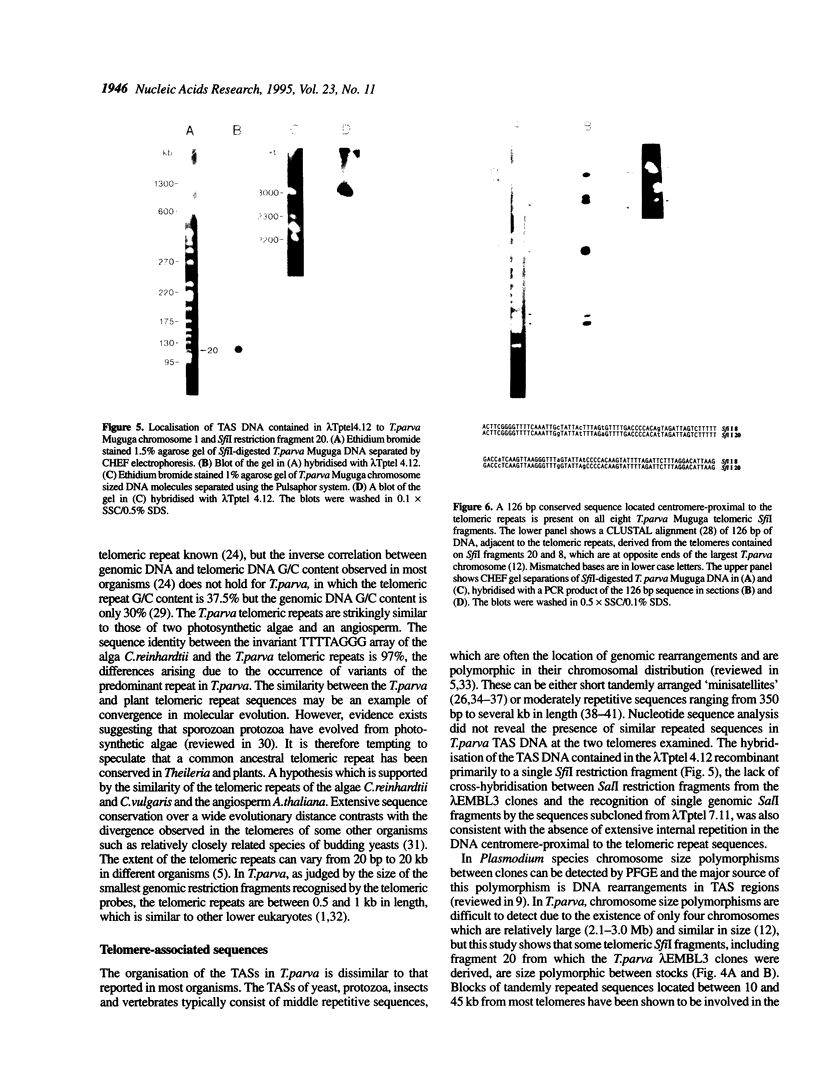
Bacteriophage lambda clones containing Theileria parva genomic DNA derived from two different telomeres were isolated and the nucleotide sequences of the telomeric repeats and adjacent telomere-associated (TAS) DNA were determined. The T.parva telomeric repeat sequences, a tandem array of TTTTAGGG or TTTAGGG interspersed with a few variant copies, showed a high degree of sequence identity to those of the photosynthetic algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (97% identity) and Chlorella vulgaris (87.7% identity) and the angiosperm Arabidopsis thaliana (84.4% identity). Unlike most organisms which have been studied, no significant repetitive sequences were found in the nucleotide sequences of TAS DNA located centromere-proximal to the telomeric repeats. Restriction mapping and hybridisation analysis of lambda EMBL3 clones containing 16 kilobases of TAS DNA derived from one telomere suggested that they did not contain long regions of repetitive DNA. The cloned TAS DNAs were mapped to T.parva Muguga genomic SfiI fragments 8 and 20, which are located at opposite ends of the largest T.parva chromosome. A 126 bp sequence located directly centromere-proximal to the telomeric repeats was 94% identical between the two cloned telomeres. The conserved 126 bp sequence was present on all T.parva Muguga telomeric SfiI fragments.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allsopp B. A., Allsopp M. T. Theileria parva: genomic DNA studies reveal intra-specific sequence diversity. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Feb;28(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann L., Raab M., Sperlich D. Evolution of a telomere associated satellite DNA sequence in the genome of Drosophila tristis and related species. Genetica. 1990;83(1):9–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00774684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Mason J. M. Genetics and molecular biology of telomeres. Adv Genet. 1992;30:185–249. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):569–573. doi: 10.1038/350569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., MacKinnon P. J., Villasanté A., Spurr N., Buckle V. J., Dobson M. J. Structure and polymorphism of human telomere-associated DNA. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90293-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. S., Tye B. K. A family of Saccharomyces cerevisiae repetitive autonomously replicating sequences that have very similar genomic environments. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 15;168(3):505–523. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80299-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. S., Tye B. K. Organization of DNA sequences and replication origins at yeast telomeres. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman M. J., McHale M. T., Arnau J., Watson A., Oliver R. P. Cloning and characterisation of telomeric DNA from Cladosporium fulvum. Gene. 1993 Sep 30;132(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90515-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad P. A., Iams K., Brown W. C., Sohanpal B., ole-MoiYoi O. K. DNA probes detect genomic diversity in Theileria parva stocks. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Oct;25(3):213–226. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Thompson J. K., Walliker D., Kemp D. J. Homologous recombination within subtelomeric repeat sequences generates chromosome size polymorphisms in P. falciparum. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):807–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90097-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dore E., Pace T., Ponzi M., Picci L., Frontali C. Organization of subtelomeric repeats in Plasmodium berghei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2423–2427. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz H., Haber J. E. Subtelomeric regions of yeast chromosomes contain a 36 base-pair tandemly repeated sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7105–7121. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janse C. J. Chromosome size polymorphism and DNA rearrangements in plasmodium. Parasitol Today. 1993 Jan;9(1):19–22. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(93)90158-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kibe M. K., ole-MoiYoi O. K., Nene V., Khan B., Allsopp B. A., Collins N. E., Morzaria S. P., Gobright E. I., Bishop R. P. Evidence for two single copy units in Theileria parva ribosomal RNA genes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994 Aug;66(2):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(94)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R. W., Ganesan R., Houtchens K., Tolar L. A., Sheen F. M. Transposons in place of telomeric repeats at a Drosophila telomere. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90318-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEachern M. J., Blackburn E. H. A conserved sequence motif within the exceptionally diverse telomeric sequences of budding yeasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3453–3457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami T., Spooner P. R., Irvin A. D., Ocama J. G., Dobbelaere D. A., Fujinaga T. Characterisation of stocks of Theileria parva by monoclonal antibody profiles. Res Vet Sci. 1983 Nov;35(3):334–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morzaria S. P., Spooner P. R., Bishop R. P., Musoke A. J., Young J. R. SfiI and NotI polymorphisms in Theileria stocks detected by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 May;40(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90042-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morzaria S. P., Young J. R. Restriction mapping of the genome of the protozoan parasite Theileria parva. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5241–5245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace T., Ponzi M., Dore E., Frontali C. Telomeric motifs are present in a highly repetitive element in the Plasmodium berghei genome. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jun;24(2):193–202. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petracek M. E., Lefebvre P. A., Silflow C. D., Berman J. Chlamydomonas telomere sequences are A+T-rich but contain three consecutive G-C base pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8222–8226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzi M., Pace T., Dore E., Frontali C. Identification of a telomeric DNA sequence in Plasmodium berghei. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2991–2995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards E. J., Chao S., Vongs A., Yang J. Characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana telomeres isolated in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):4039–4046. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.4039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards E. J., Goodman H. M., Ausubel F. M. The centromere region of Arabidopsis thaliana chromosome 1 contains telomere-similar sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3351–3357. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandell L. L., Zakian V. A. Loss of a yeast telomere: arrest, recovery, and chromosome loss. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90493-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotti R., Pace T., Ponzi M. A 40-kilobase subtelomeric region is common to most Plasmodium falciparum 3D7 chromosomes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Mar;58(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90084-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernick K. D., McCutchan T. F. Sequence and structure of a Plasmodium falciparum telomere. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Mar;28(2):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernick K. D., Walliker D., McCutchan T. F. Genetic hypervariability of telomere-related sequences is associated with meiosis in Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6973–6985. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., Gardner M. J., Feagin J. E., Williamson D. H. Have malaria parasites three genomes? Parasitol Today. 1991 Jun;7(6):134–136. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(91)90276-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Mehra V., Sweetser D., Buchanan T., Clark-Curtiss J., Davis R. W., Bloom B. R. Genes for the major protein antigens of the leprosy parasite Mycobacterium leprae. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):450–452. doi: 10.1038/316450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:579–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin D., Lanzer M., Ravetch J. V. The polymorphic subtelomeric regions of Plasmodium falciparum chromosomes contain arrays of repetitive sequence elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):619–623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lange T., Shiue L., Myers R. M., Cox D. R., Naylor S. L., Killery A. M., Varmus H. E. Structure and variability of human chromosome ends. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):518–527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ole-MoiYoi O. K. Theileria parva: an intracellular protozoan parasite that induces reversible lymphocyte transformation. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Aug;69(2):204–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]