Abstract
Mdm2 is a multifunctional protein that modulates nuclear receptor-mediated transactivation. In this study, we show that Mdm2 significantly enhanced estrogen receptor α (ERα) and ERα/specificity protein (Sp)-mediated transactivation in MCF-7 and ZR-75 breast cancer cells. This was demonstrated by both Mdm2 overexpression and knockdown experiments by RNA interference. ERα interacted with wild-type Mdm2 and deletion mutants of Mdm2 containing amino acids 1–342 (C-terminal deletion) and 134–490 (N-terminal deletion), but not 134–342. In contrast, only wild-type but not mutant Mdm2 enhanced ERα-mediated transactivation. Protein-protein interactions in vitro were 17β-estradiol (E2)-independent, whereas fluorescent resonance energy transfer (FRET) experiments in living cells showed that E2 enhanced ERα-Mdm2 interactions. Subsequent RNA interference and mammalian two-hybrid experiments suggested that Mdm2 did not directly interact with endogenous coactivators such as the steroid receptor coactivators but played a role in enhancing ERα-mediating gene expression and estrogen-responsiveness through interactions with ERα.
Keywords: Mdm2, ERα, ERα/Sp, coactivation
INTRODUCTION
Murine Double Minute Clone 2 (Mdm2) was initially cloned from a transformed 3T3 cell line, and later identified as a p53-interacting protein (Cahilly-Snyder et al. 1987; Fakharzadeh et al. 1991; Momand et al. 1992). It was subsequently shown that overexpression of Mdm2 resulted in cell transformation and oncogenicity and this was due, in part, to suppression of the tumor suppressor gene p53. The complex interrelationships between Mdm2 and p53 have been extensively investigated (Levav-Cohen et al. 2005; Brooks & Gu 2006). Mdm2 exhibits E3-ubiquitin ligase activity which increases ubiquitination of p53 and, in combination with other factors, the resulting proteasome-dependent degradation of p53 decreases expression of this tumor suppressor gene under non-stressed conditions (Ashcroft et al. 1999; Kubbutat et al. 1999). The role of Mdm2 in regulating p53 expression is also apparent in transgenic mice where Mdm2 knockout animals exhibit embryolethality which is reversed by inactivation of p53 (Jones et al. 1995; Montes de Oca Luna et al. 1995; de Rozieres et al. 2000). Under conditions of cellular stress, the physical and functional interactions of Mdm2 and p53 are inhibited, thereby allowing p53 to activate gene expression pathways, such as inhibition of cell cycle progress and induction of apoptosis, that allow the cells to respond to stressors. The interactions between p53 and Mdm2 are complex and are modified under various conditions and in a cell/tissue context-dependent manner (Brooks & Gu 2006).
Since Mdm2 inhibits p53 function as a tumor suppressor gene, it is not surprising that expression of Mdm2 plays a role in cancer and in cancer prognosis (Levav-Cohen et al. 2005). Overexpression of Mdm2 is frequently observed in many different cancers; however, the prognosis for patients in which Mdm2 levels are high is dependent on multiple factors including the type of tumor and its origin. For example, Mdm2 overexpression through gene amplification in gliomas predicts poor survival (Korkolopoulou et al. 1997; Rainov et al. 1997; Schiebe et al. 2000), whereas overexpression through gene amplification in breast cancer is observed only in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive tumors for which there is a good prognosis for survival (Bueso-Ramos et al. 1996; Lukas et al. 2001; Hori et al. 2002). The variability of Mdm2 as a prognostic indicator for cancer survival is complex and may be due to interactions with other unknown factors.
A number of p53-independent functions of Mdm2 have been identified and show that this protein can modify different signaling pathways. Mdm2 interacts with and inhibits the function of retinoblastoma (Rb) protein and other Rb family members (Hsieh et al. 1999) and this affects E2F1-DP1 mediated responses (Martin et al. 1995) and also enhances the transcriptional activation of cyclin A (Leveillard & Wasylyk 1997). Mdm2 also modulates ligand-dependent activation of several steroid hormone receptors including the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), androgen receptor (AR), and estrogen receptor (ER) (Liu et al. 2000; Saji et al. 2001; Sengupta & Wasylyk 2004). Mdm2 overexpression in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells enhances their estrogen-dependent growth and, in p53-deficient Saos-2 osteosarcoma cells and MCF-7 cells, Mdm2 enhances 17β-estradiol (E2)-dependent activation of a construct containing an estrogen response element (ERE) insert (Saji et al. 2001).
This study shows by RNA interference that Mdm2 enhances E2-dependent growth and transactivation in breast cancer cells using constructs containing three-tandem estrogen responsive elements (EREs) or GC-rich motifs (pSp13) activated by ERα or ERα/Sp1, respectively. Mdm2 overexpression also coactivates ERα and ERα/Sp1, and results suggest that the coactivation response is primarily through direct interactions of Mdm2 with ERα and Mdm2-dependent enhanced interactions of ERα with coactivators.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell Lines, Chemicals, and Biochemicals
The ZR-75 (ZR-75.1), MCF-7, and T47D human breast cancer cell lines were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA). Cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 or DMEM (Sigma) supplemented with 5 or 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and medium was further supplemented with antibiotic/antimycotic solution (Sigma). Prior to transfection, RPMI or DMEM medium was replaced by Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium/F-12 (Sigma) supplemented with charcoal-stripped 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). Cells were maintained at 37°C with a humidified CO2/air (5:95) mixture. Small inhibitory RNA (siRNA) duplexes for mdm2 (siMDM2), p53 (sip53), luciferase (siGL2), and the scrambled siRNA (siCT) were purchased either from Ambion (Austin, TX) or Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). The sequence for siGL2: 5'-CGU ACG CGG AAU ACU UCG ATT-3'; for siMdm2: 5'-GAA CAA GAG ACC CTG GTT A-3'; for sip53: 5'-GAG GUU GGC UCU GAC UGU A-3'; for scrambled RNA (siCT): 5'-ACU CUA UCU GCA CGC UGA CTT-3'.
Plasmids and Cloning
pERE3, pSp13, pCAD, and pE2F1 were previously generated in our lab. pcDNA-Mdm2 (490 aa) was kindly provided from Dr. Lane (University of Dundee, United Kingdom). The Mdm2 deletion mutants (135–490 aa, 135–342 aa, and 1–342 aa) were generated by cloning Mdm2 deletion mutant amplified PCR products into EcoRI/XhoI sites of pcDNA3.1His plasmid. Mdm2 deletion mutants were generated by PCR using following primer sets: 1–342 aa: (F) 5'- GAA TTC ATG TGC AAT ACC AAC ATG TC-3', (R) 5'-CTC GAG TTT TTC AGA GAT TTC CAC-3'; 134–490 aa: (F) 5'-GAA TTC CCT TTG CAA GCG CCA CCA G-3', (R) 5'- CTC GAG CTA GTT GAA GTA AGT TAG CAC-3'; 135–342 aa: (F) 5'- GAA TTC CCT TTG CAA GCG CCA CCA G-3', (R) 5'-CTC GAG TTT TTC AGA GAT TTC CAC-3'. These gemerated Xpress tagged expression plasmids were also used for in vitro coimmunoprecipitation assays. pMMdm2 and VP-Mdm2 expression plasmids were generated by PCR amplification of Mdm2 wild-type and cloned into ECoRI and HindIII sites of pM and VP-16 vectors (Clontech, Palo Alto, CA). For ECFP-Mdm2 vector generation, the amplified Mdm2 PCR product was digested with EcoRI and XhoI, and cloned into CFP-C1 vector (Clontech). The GAL4-coactivator fusion plasmids pMSRC1, pMGripwt, and pMAIB1 were kindly provided by Dr. Shigeaki Kato (University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan), and pMGripLxxLL (fused to the yeast GAL4 DBD) was obtained from Dr. Donald McDonnell (Duke University, Durham, NC).
Transient Transfection Assays
Cells were seeded onto 12-well plates in phenol-free Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium/F-12 supplemented with 5% charcoal-stripped FBS. After 24 hr, cells were transfected by lipofectamine 2000 reagent (Invitrogen) with 250 ng of an appropriate reporter plasmid (pERE3, pSp13, pCAD, pE2F1, or GAL4-luciferase), 50 ng of a CMV β-galactosidase expression plasmid, and other appropriate expression plasmids (125 ng/well) [ERα, Mdm2 wild-type and mutants (1–342 aa, 134–490 aa, 134–490 aa), pMERα, pMMdm2, VP-ERα or VP-Mdm2. Empty vectors or non-specific (siCT) oligonucleotides were used as controls in all transfection experiments. After transfection for 24 hr, cells were treated with Me2SO or 10 nmol/L E2 with 5% stripped serum media for 24 hr. In cells transfected with siRNA(s), E2 was added after 36–48 hr for accomplishing efficient knockdown of target gene. Cells were then harvested, and luciferase activity (relative to β-galactosidase activity) was determined. Normalized luciferase values were obtained by dividing the luciferase by the β-galactosidase activities for a given sample. Results are expressed as means ± SE for at least three separate experiments for each treatment group.
In vitro Coimmunoprecipitation Assay
[35S]ERα, [35S]Mdm2wt, [35S]Mdm2(1–342 aa), [35S]Mdm2 (134–342 aa), or [35S]Mdm2 (134–490 aa) were in vitro translated using the T7 QuikCoupled Transcription Translation System (Promega Corp.). Mdm2 wild-type and all mutants were Xpress-tagged. [35S]ERα (1 μl) and 35S-labeled Mdm2 wild-type or deletion mutant protein (0.5 μl) were coincubated in coimmunoprecipitation buffer (sterilized PBS + 0.01% IGEPAL CA630) with E2 to give a final concentration of 100 nM E2. After incubation for 1 hr at 4°C, 25 μl of a 50% slurry of protein G-sepharose beads (Amersham Biosciences) were added to the incubation solution, followed by incubation for 2 hr on a rocker at 4°C. Samples were then centrifuged and washed; the final pellet was boiled in 30 μl of 2× SDS sample buffer; and proteins were separated on a 8% SDS-PAGE and visualized by autoradiography.
Western Blot Analysis
Depletion of Mdm2 protein was determined, 48 hr after transfection with siRNA for Mdm2, breast cancer cells were harvested with RIPA lysis buffer (1× PBS, 1% Nonidet P-40 or Igepal CA-630, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1 mg/ml phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride in isopropanol, aprotinin, 100 nM sodium orthovanadate), and equal amounts of protein from each group were boiled with sample buffer and loaded onto 8% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. The membrane was blocked and probed with primary antibodies for Mdm2 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) O/N at 4°C. Membrane was visualized using the ECL detection system (PerkinElmer Life Sciences).
Cell Proliferation Assay
MCF-7 or ZR-75 cells (5×104 per well) were plated in 12-well plates and allowed to attach for 24 hr, and then cells were transfected with either control siRNA or Mdm2 siRNA. After 24 hr, the medium was changed to charcoal stripped 5% FBS DMEM medium containing either vehicle (DMSO) or estrogen (10 nM). Fresh medium was added every 48 hr. Cells were then trypsinized and counted at the indicated times using a Coulter Z1 particle counter. Each experiment was done in triplicate and results are expressed as means ± SE for each treatment group.
Quantitative RT PCR
RNA was harvested from T47D cells using the RNeasy mini or micro kits (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA). First-strand cDNA synthesis was performed with 1 μg RNA using Reverse Transcription Kit from Promega (Madison, WI). Real-time PCR was performed using SYBR Green PCR Master Mix reagent, the ABI PRISM 7000 sequence detection system, and software (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). The primer sets were: for CAD: (F) 5'-ACC ACG ACA CCT GAA AGA CC-3', (R) 5'-TAC TGG TGG TGG AGG GTA GC-3'; for pS2: (F) 5'-CAC CAT GGA GAA CAG GTG A-3', (R) 5'-AGC CCT TAT TTG CAC ACT GG-3'; for cyclin D1: (F) 5'-CGA TGC CAA CCT CCT CAA CGA-3' (R) 5'-TCG CAG ACC TCC AGC ATC CA-3'; for β-actin: (F) 5'-GGG GTG TTG AAG GTC TCA AA-3'; for E2F1: (F) 5'-ATG TTT TCC TGT GCC CTG AG-3', (R) 5'-ATC TGT GGT GAG GGA TGA GG-3'.
FRET (fluorescence resonance energy transfer) analysis
Cells were grown in two-well Lab-Tek Chambered Coverglass slides (Nalge Nunc International, Rochester, NY) in DME/F12 medium supplemented with 5% charcoal-stripped serum and then transfected with CFP-Mdm2/YFP-ERα or CFP-Sp1/ YFP-ERα sets. All the procedures for measuring FRET efficiency were previously described (Kim et al. 2005). Briefly, after transfection for 24 hr, cells were put on the stage of a Bio-Rad 2000 MP microscope system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA) equipped with a Nikon T#300 inverted microscope. The images were acquired between 5 and 15 min before and after the addition of 10 nM E2. FRET efficiency data were collected using two photon 820 nmol/L excitation wavelength. Emission of CFP (CFP channel, donor signal) was collected using a 500DCLP dichroic and 450/80 nm filter, whereas emission of YFP (FRET channel, acceptor signal) was collected using a 528/50 nm filter. CFP-Sp1/YFP-ERα set was used as positive control after E2 treatment in this experiment. For FRET analysis, MetaMorph software version 6.0 (Universal Imaging Corp., Downingtown, PA) was used and FRET signals were corrected by subtracting the background signal as well as the donor bleed through signal. At least 50 cells per treatment were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical differences between different treatments were determined using Student's t-test or analysis of variance (Fisher's protected Least Significant Difference), and the levels of significance are shown (p<0.05). The results are expressed as mean ± SE for at least three replicate determinations for each experiment.
RESULTS
Mdm2 enhances E2-dependent transactivation
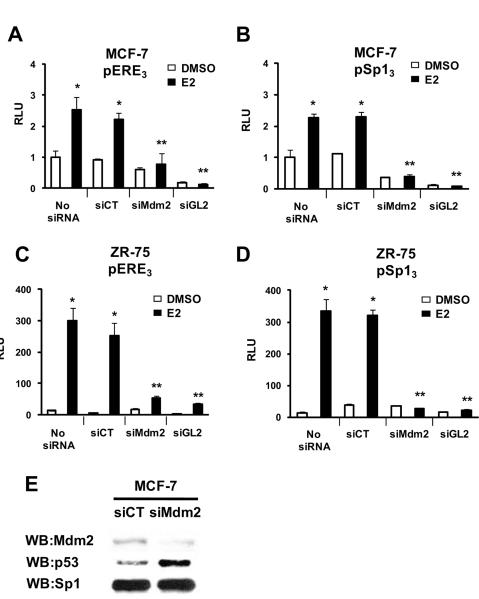
Previous studies showed that E2-responsiveness was enhanced in MCF-7 cells overexpressing Mdm2 and similar results were observed in Saos-2 cells transfected with ERα and Mdm2 expression plasmids and an ERE reporter construct (Saji et al. 2001). In this study, we first examined the effects of endogenous Mdm2 on E2-induced transactivation in ZR-75 breast cancer cells transfected with pERE3 (Fig. 1A) or pSp13 (Fig. 1B) constructs containing three tandem EREs or concensus GC-rich Sp1 binding sites linked to the luciferase gene, respectively. These constructs in which ERα or ERα/Sp1 activate their respective promoters represent two of the major genomic pathways of estrogen action in breast cancer cells (Hall et al. 2001; Safe & Kim 2004). The results show that small inhibitory RNA for Mdm2 significantly decreased E2-induced transactivation in cells transfected with pERE3 or pSp13 compared to cells transfected with siCT (non-specific oligonucleotide) or untransfected cells. As a positive control, siGL2 (small inhibitory RNA for luciferase) also decreased luciferase activity. Endogenous luciferase activity in cells transfected with pSp13 was not affected by siMdm2, suggesting that coactivation of ERα/Sp may be due to interactions of Mdm2 with ERα, not with Sp proteins. Figures 1C and 1D show that Mdm2 knockdown (siMdm2) inhibited E2-induced transactivation in ZR-75 cells transfected with the pERE3 or pSp13 constructs; similar results were observed in ZR-75 cells transfected with E2-responsive GC-rich constructs containing promoter inserts from the E2F1 and CAD genes (Wang et al. 1999; Khan et al. 2003; Ngwenya & Safe 2003) (Suppl. Fig. 1). Moreover, in a mammalian two-hybrid assay in ZR-75 cells, we did not observe Sp1-Mdm2 interactions (data not shown). Results in Figure 1E show that siMdm2 inhibited siMdm2 protein expression in MCF-7 cells, increased p53 protein expression, and did not affect levels of Sp1 protein.
Figure 1.
Mdm2 knockdown inhibits estrogen-induced ERα and ERα/Sp-mediated transactivation. MCF-7 cells were transfected with pERE3 (A) or pSp13 (B) and ZR-75 cells were transfected with pERE3 (C) or pSp13 (D) andand various (or no) oligonucleotides and treated with DMSO or 10 nM E2. Luciferase activity was determined as described in the Materials and Methods. Significant (p < 0.05) induction by E2 (*) or inhibition by iMdm2 or iGL2 (**) are indicated. Results are expressed as means ± SE for at least 3 separate determinations for each treatment group. Minimal activity was observed in cells transfected with the empty vector, and treatment with DMSO or E2 did not induce activity. (E) Mdm2 knockdown. MCF-7 cells were transfected with a non-specific (siCT) or siMdm2 oligonucleotide, and whole cell lysates were analyzed by western blots as described in the Materials and Methods. MCF-7 cells were used for whole cell lysate analysis due to higher transfection efficiency compared to ZR-75 cells.
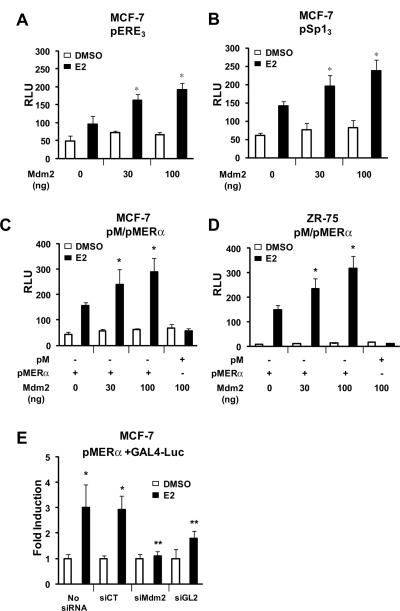
The effects of overexpression of Mdm2 on coactivation of ERα and ERα/Sp was investigated in MCF-7 cells transfected with pERE3 (Fig. 2A) or pSp13 (Fig. 2B), and the results showed that Mdm2 significantly enhanced ERα and ERα/Sp-mediated transactivation and similar results were observed in ZR-75 cells (data not shown). Coactivation of ERα by Mdm2 was further investigated in MCF-7 (Fig. 2C) and ZR-75 (Fig. 2D) cells transfected with Mdm2, a GAL4-ERα chimeric protein (pMER), and a construct (GAL4-luc) containing five tandem GAL4 response elements. The results show that E2 significantly induced transactivation in both cell lines and this response was further enhanced by Mdm2 expression. Moreover, E2-induced transactivation in MCF-7 cells transfected with pMER and GAL4-luc was significantly decreased after cotransfection with siMdm2 or siGL2 that knocks down luciferase (Fig. 2E), confirming that Mdm2 coactivates ERα-mediated transactivation.
Figure 2.
Mdm2 coactivates ERα and ERα/Sp-dependent transactivation. MCF-7 cells were treated with DMSO or E2, transfected with pERE3 (A) or pSp13 (B) and different amounts of Mdm2 expression plasmid, and luciferase activity was determined as described in the Materials and Methods. Effects of Mdm2 expression in MCF-7 (C) and ZR-75 (D) cells or Mdm2 knockdown in MCF-7 (E) cells on activation of pM-ERα. Cells were treated with DMSO or 10 nM E2, transfected with pMER and Mdm2 expression plasmid, a GAL4-luc reporter construct, and oligonucleotides (as indicated); luciferase activated determined as outlined in the Materials and Methods. Results are expressed as means ± SE for at least 3 replicate determinations for each treatment group as significant (p < 0.05) coactivation by Mdm2 (*) or inhibition by iMdm2 or iGL2 (**) are indicated.
Mdm2 interacts with ERα
It was previously reported that in a mammalian two-hybrid assay in Saos-2 cells using pM-ERα and VP-Mdm2, E2 induced transactivation (interaction); however, in GST pulldown studies ERα interacted with Mdm2 in the presence or absence of ligand (Saji et al. 2001). Results in Figure 3A show that in mammalian two-hybrid assays in ZR-75 cells, there was increased transactivation in cells transfected with pM-Mdm2 and VP-ERα compared to cells transfected with pM-Mdm2 and VP and this interaction did not require addition of E2. Moreover, in coimmunoprecipitation experiments with in vitro expressed 35S-labeled ERα and Mdm2 (Xpress-tagged), both proteins interacted in the presence or absence of E2 (Fig. 3B). The interactions of ERα and Mdm2 in living cells were also investigated by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) in cells transfected with a CFP-Mdm2 construct and a YFP-ERα construct. In preliminary experiments, we showed that like Mdm2, ECFP-Mdm2 also enhanced E2-dependent transactivation in ZR-75 cells transfected with pM-ERα/GAL4-luc (Fig. 3C). FRET analysis was determined in MCF-7 cells transfected with CFP-Mdm2 and YFP-ERα (Fig. 3D). The FRET efficiencies obtained are illustrated in Figure 3E and show that E2 significantly enhanced this response indicating that although both proteins directly interact in the absence of E2, treatment with hormone clearly enhances this interaction and facilitates the energy transfer between the CFP and YFP moieties in both proteins. As a positive control for this experiment, we also show that E2 enhances YFP-ERα interactions with CFP-Sp1 as previously reported (Kim et al. 2005). There was clearly a parallel between the significant effects of E2 on FRET efficiencies associated with YFP-ERα–CFP-Sp1 and YFP-ERα–CFP-Mdm2 and the E2-independent interaction of ERα with both Sp1 (Kim et al. 2005) and Mdm2 (Figs. 3A and 3B) in coimmunoprecipitation experiments.
Figure 3.
Interactions of Mdm2 and ERα. (A) Mammalian two hybrid assay. Cells were transfected with various constructs and a GAL4-luc reporter gene and luciferase activity determined as described in the Materials and Methods. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of Mdm2 and ERα. [35S]ERα and [35S]Mdm2 (Xpress-tagged) were in vitro expressed, treated with or without E2, and coimmunoprecipitated with Xpress antibodies and then analyzed by western blots as described in the Materials and Methods. (C) Coactivation of pMER by Mdm2. ZR-75 cells were treated with DMSO or 10 nM E2 transfected with pMER/GAL4-luc and Mdm2 or ECFP-Mdm2, and luciferase activity determined as outlined in the Materials and Methods. (D) Mdm2:ERα interactions - FRET anlaysis. ZR-75 cells were treated with DMSO or 10 nM E2, transfected with CFP-Mdm2 or YFP-ERα expression plasmids, and E2-dependent interactions were determined by FRET as described in the Materials and Methods. (E) FRET efficiencies. ZR-75 cells were treated with DMSO or 10 nM E2 and transfected with various constructs, and FRET efficiencies were determined as described in the Materials and Methods. Results of transfection studies (A, C and E) are means ± SE for at least 3 replicate determinations for each treatment group, and significant (p<0.05) induction is indicated (*).
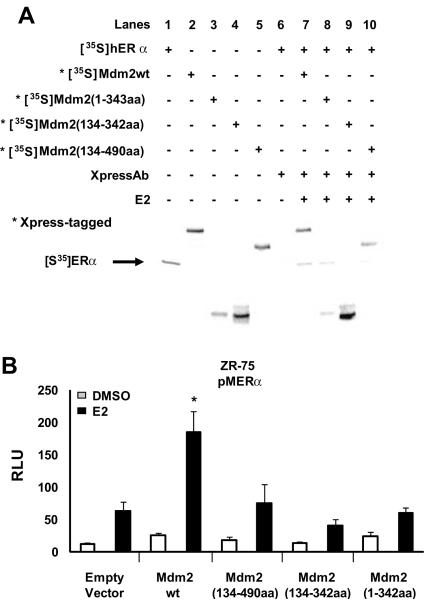
Mdm2 contains several domains that interact with other proteins and also a zinc finger and a C-terminal RING finger domain that functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase (Ashcroft et al. 1999; Kubbutat et al. 1999). We initially examined the interactions of wild-type and deletion variants of Mdm2 (Xpress-tagged) with ERα, and Figure 4A illustrates the electrophoretic mobilities and interactions between 35S-labeled ER and 35S-labeled wild-type Mdm2 and variants expressing amino acids 1 – 342 [Mdm2(1–342aa)], 134 – 342 [Mdm2(134–342aa)], and 134 – 490 [Mdm2(134–490aa)]. Coimmunoprecipitation experiments showed that ERα interacted with wild-type Mdm2 (lane 7), Mdm2(1–342aa) (lane 8), Mdm2(134–490aa) (lane 10) but not Mdm2(134–342aa) (lane 9). Lanes 1 – 6 illustrate the 35S-labeled proteins alone. Thus, ERα interacts with both C- and N-terminal domains of Mdm2 but not the 134–342aa region which binds CBP/p300 (Grossman et al. 1998). In contrast, coactivation studies in ZR-75 cells transfected with pM-ERα showed that only wild-type, but not the deletion variants of Mdm2, coactivated ERα (Fig. 4B). These results suggest that multiple regions of Mdm2 are required for coactivation of ERα.
Figure 4.
Physical and function interaction of ERα with wild-type and variant Mdm2. (A) In vitro interactions. Various [35S]-labeled proteins were in vitro expressed, coimmunoprecipitated, and analyzed by western blots as outlined in the Material and Methods, and only wild-type and variant Mdm2 were Xpress-tagged. (B) Coactivation of ERα by wild-type and deletion mutant forms of Mdm2. ZR-75 cells were treated with DMSO or 10 nM E2, transfected with pMER/GAL4-luc and various wild-type and deletion mutant Mdm2 expression plasmids, and luciferase activity determined as outlined in the Materials and Methods. Results are expressed as means ± SE for at least 3 replicate determinations for each treatment group, and significant (p < 0.05) coactivation is indicated (*).
Mdm2 enhances interactions of ER α with steroid receptor coactivators
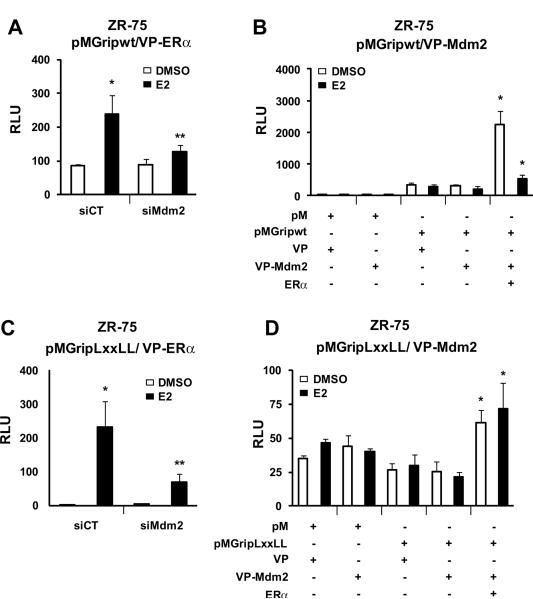
Steroid receptor coactivators (SRCs), mediator proteins, and p300 associate with ER as complexes that interact cyclically with E2-responsive gene promoters, and Mdm2 has been identified as a component of these complexes (Metivier et al. 2003; Reid et al. 2003). The role of Mdm2 and its interactions with coactivators has been further investigated in mammalian two-hybrid assays using coactivator-Gal4 chimeras (pM-coactivators), VP-ERα and Gal4-luc in ZR-75 cells. In cells transfected with pMGRIP(wt), VP-ERα and Gal4-luc treatment with E2 induced transactivation; however, E2-dependent interactions were significantly inhibited in cells cotransfected with siMdm2, suggesting that interactions of GRIP (SRC-2) and ERα are mediated, in part, by Mdm2 (Fig. 5A). Interactions of GRIP and Mdm2 were also investigated in a mammalian two-hybrid assay in ZR-75 cells transfected with pMGRIP/GAL4-luc and VP-Mdm2, and the results show that Mdm2 and GRIP do not interact in the presence or absence of E2 (Fig. 5B). However, after cotransfection with ERα, there was a significant increase in transactivation which was observed in the absence or presence of E2 but was more pronounced in the former case. These results suggest that, although GRIP and Mdm2 do not exhibit binding in a two-hybrid assay, expression of ERα significantly enhanced interactions between GRIP and Mdm2. ER-coactivator interactions are dependent, in part, on interactions between NR-box (LXXLL) motifs in coactivators (Torchia et al. 1997; Voegel et al. 1998) with ERα, and Figure 5C shows that E2 induces transactivation in ZR-75 cells transfected with VP-ERα and pMGRIP(LXXLL)/GAL4-luc where pMGRIP(LXXLL) is a chimera containing GAL4 fused to aa629 to 760 from GRIP/SRC-2 which contains an LXXLL motif. E2-dependent interactions of ERα and GRIP(LXXLL) in the mammalian two hybrid assay were inhibited after cotransfection with siMdm2, suggesting that Mdm2 facilitates ERα interactions with the NR box motif of GRIP. pMGRIP(LXXLL) did not interact with VP-Mdm2 in a two-hybrid assay; however, cotransfection with ERα in the presence or absence of E2 enhanced transactivation (Fig. 5D). These results suggest that ERα enhances Mdm2 interactions with the NR box motif of GRIP.
Figure 5.
Effects of Mdm2 on coactivation of ERα by GRIP (SRC-2). ZR-75 cells were treated with DMSO or 10 nM E2, and transfected with pMGripwt/VPERα and iCT or iMdm2 oligonucleotides (A) or pMGripwt/VP16-Mdm2, empty vectors and hERα (B), and luciferase activity was determined as described in the Materials and Methods. ZR-75 cells were treated with DMSO or 10 nM E2, transfected with pMGripLXXLL/VPERα and iCT or iMdm2 oligonucleotides (C) or pMGripLXXLL/VP16-Mdm2, empty vectors and ERα (D), and luciferase activity determined as described in the Materials and Methods. Results are expressed as means ± SE for at least 3 replicate determinations for each treatment group, and significantly (p<0.05) enhanced interactions by ERα (*) or decreased activity by iMdm2 (**) are indicated.
The role of Mdm2 in the interaction of ERα with SRC-1 and SRC-3(AIB-1) was also investigated in mammalian two-hybrid assays in ZR-75 cells (Fig. 6), and the results were similar to those observed for ERα and GRIP. E2 induced transactivation in cells transfected with pMSRC1/GAL4-luc plus VP-ERα (Fig. 6A) or pMAIB1/GAL4-luc plus VP-ERα (Fig. 6B). Cotransfection with siMdm2 inhibited basal and induced activity, and the inhibition was most pronounced for AIB1-ER interactions. Interactions of pMSRC1 and VP-Mdm2 (Fig. 6C) or pMAIB1 and VP-Mdm2 (Fig. 6D) were not observed in mammalian two hybrid assays; however, cotransfection with ERα significantly enhanced transactivation in the absence or presence of E2. The hormone-induced response was more pronounced with pMAIB1 compared to pMSRC-1; moreover, E2 decreased transactivation in ZR-75 cells transfected with pMSRC1, VP16-MDM2 and ERα, suggesting that liganded ERα may inhibit SRC1-MDM2 interactions. These results demonstrate that although Mdm2 does not interact with SRCs, this protein plays a key role in enhancing ERα interactions with the SRC coactivators. Results in Figure 6E demonstrate that E2 also induces transactivation in ZR-75 cells transfected pMp300/GAL4-luc and VP-ER; however, iMdm2 slightly enhances both basal and E2-induced activity. These results demonstrate the specificity of the SRC-ERα-Mdm2 compared to that observed for p300-ERα-Mdm2 interactions where Mdm2 plays a key role in coactivator ERα interactions but not p300-ERα interactions. The “constitutive” inhibitory effect may be due to the competitive binding of both ERα and Mdm2 to p300 (Hanstein et al. 1996; Grossman et al. 1998).
Figure 6.
Effects of Mdm2 on coactivation of ERα by other coactivators and p300. ZR-75 cells were treated with DMSO or 10 nM E2, transfected with pMSRC1/VP-ERα (A) or pMAIB1/VP-ERα (B), GAL4luc and iCT or iMdm2 oligonucleotides, and luciferase activity was determined as outlined in the Materials and Methods. Effects of ERα on Mdm2 coactivator interactions. ZR-75 cells were treated with DMSO or 10 nM E2, transfected with pMSRC1/VP-Mdm2 or pMAIB1/VP-Mdm2, empty vectors or ERα and GAL4-luc, and luciferase activity was determined as described in the Materials and Methods. (E) Effect of Mdm2 knockdown on ERα-p300 interactions. ZR-75 cells were treated with DMSO or 10 nM E2, transfected with pMp300/VP-ERα and GAL-luc, and luciferase activity determined as outlined in the Materials and Methods. Results are expressed as means ± SE for at least 3 replicate determinations for each treatment group and significantly (p<0.05) enhanced activity after transfections with ERα (*) or decreased activity after transfection with iMdm2 (**) are indicated.
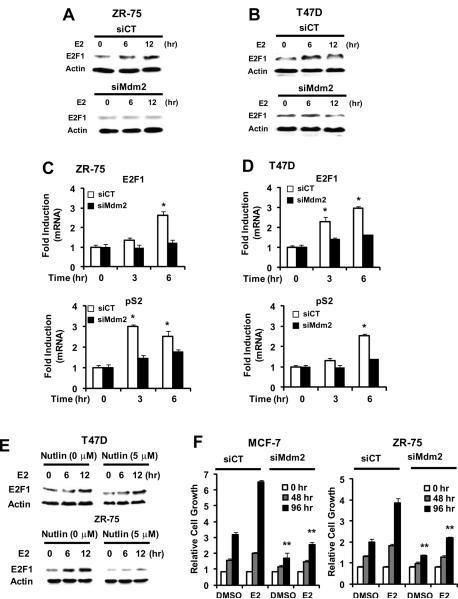
Mdm2 enhances E2-dependent activation of pS2 and E2F1 and cell proliferation
The functional effects of Mdm2 on hormone-induced gene expression were investigated in p53-expressing ZR-75 cells and T47D cells that do not express functional p53. In ZR-75 (Fig. 7A) and T47D (Fig 7B) cells transfected with siMdm2, induction of E2F1 protein expression was decreased after loss of Mdm2. The role of Mdm2 in hormone-induced expression of E2F1 and pS2 mRNA levels in ZR-75 (Fig. 7C) and T47D (Fig. 7D) cells was also determined, and the hormone-induced responses were significantly decreased in cells transfected with siMdm2. Moreover, using a similar approach, knockdown of Mdm2 by RNA interference in T47D cells decreased induction of CAD and cyclin D1 by E2 (Suppl. Fig. 2A). Since p53 inhibits estrogen-responsiveness, it is possible that the loss of hormone-induced transactivation in breast cancer cells transfected with siMdm2 may be due, in part, to activation of p53. Results in Supplementary Figures 2B and 2C compare the effects of hormone-induced transactivation in MCF-7 cells transfected with sip53, siMdm2 and their combination. E2 induced pS2 and E2F1 gene expression in MCF-7 cells treated with E2 and this response was decreased after cotransfection with siMdm2 or siMdm2 plus sip53, but unaffected by sip53 alone (Suppl. Fig. 2B). Similar results were observed for induction of luciferase activity in cells transfected with pSp13 and pERE3 (Suppl. Fig. 2C), demonstrating that the effects of siMdm2 were p53-independent. Nutlin-3 is an Mdm2 antagonist that dissociates the Mdm2-p53 complex, resulting in activation of p53 (Vassilev et al. 2004). In T47D cells that do not express wild-type p53, addition of Nutlin-3 did not affect induction of E2F1 by E2 (Fig. 7E). In contrast, Nutlin-3 significantly decreased basal and E2-inducible E2F1 in ZR-75 cells that express wild-type p53 (Fig. 7D), demonstrating that inhibition of Mdm2, like knockdown of Mdm2 (Figs. 1 and 2), decreased hormonal activation of E2F1. The effects of Mdm2 knockdown on basal and E2-induced proliferation was also investigated in MCF-7 and ZR-75 cells (Fig. 7F). The results show that loss of Mdm2 in these cells decreased both basal and hormone-induced cell growth after 96 hr, further demonstrating the critical role for Mdm2 in both cell lines. These results confirm the important role of Mdm2 as a coregulator of hormone-induced gene expression in breast cancer cells.
Figure 7.
Mdm2 regulates ERα- and E2-dependent genes and responses in breast cancer cells. Effects of siMdm2 on E2F1 protein levels in ZR-75 (A) and T47D (B) cells. Cells were transfected with siCT (non-specific) or siMdm2, treated with 10 nM E2 for 0, 6 or 12 hr, and whole cell lysates were analyzed for E2F1 and β-actin (loading control) by western blots as described in the Materials and Methods. Effects of siMdm2 on E2F1 and pS2 mRNA levels in ZR-75 (C) and T47D (D) cells. Cells were transfected with siCT (non-specific) or siMdm2, treated with DMSO or 10 nM E2 for the indicated times, and mRNA levels were determined by real time PCR as described in the Materials and Methods. Results are expressed as means ± SE for replicate (3) determinations and significant (p<0.05) induction by E2 (*) and inhibition by siMdm2 (**) is indicated. (E) Effects of nutlin. T47D or ZR-75 cells were treated with DMSO or 10 nM E2 in the presence or absence of 5 μM nutlin and analyzed for E2F1 and β-actin (loading control) by western blots. (F) siMdm2 inhibits growth and hormone-induced cell proliferation. MCF-7 or ZR-75 cells were transfected with siCT or siMdm2 treated with DMSO or 10 nM E2, and cells were counted at various time points as described in the Materials and Methods. Results are expressed as means ± SE for replicate (3) determinations and significant induction by E2 (compared to DMSO) (*) and inhibition by siMdm2 (**) are indicated.
DISCUSSION
Coactivators and other coregulatory proteins play a critical role in hormone receptor-dependent gene expression, and these nuclear proteins are essential factors for ligand-induced transcriptional activation (Blanco et al. 1998; O'Malley 2007). Initial studies describing coactivation of nuclear receptors by SRCs demonstrated several essential features of coactivator function. These included identification of NR-boxes required for specific coactivator-receptor interactions (Torchia et al. 1997; Voegel et al. 1998), histone acetyltransferase activity of some SRCs which facilitates interaction of receptor-coregulatory complexes with promoter DNA, and interactions of coactivators with multiple domains of nuclear receptors and with other nuclear cofactors (Blanco et al. 1998; O'Malley 2007). This complexity associated with SRCs has been further magnified by ongoing studies which have identified many other classes of coactivators which manifest their activities through ATP-dependent chromatin modeling, histone methylation, or modification of receptors through ubiquitination or sumoylation (Blanco et al. 1998; O'Malley 2007; O'Malley & Kumar 2009).
The interactions of different functional classes of nuclear factors in ERα-mediated transcriptional activation has been extensively investigated in chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays which demonstrate an ordered cycling of distinct cofactor/ERα complexes on and off the E2-responsive pS2 gene promoter (Shang et al. 2000; Burakov et al. 2002; Metivier et al. 2003; Reid et al. 2003). Mdm2 which exhibits ubiquitin E3 ligase activity is involved in this cycling process, and previous studies show that Mdm2 overexpression coactivates ERα-dependent transactivation in cells transfected with ERE-promoter constructs (Saji et al. 2001). Research in this laboratory and others have demonstrated that E2 also activates genes in breast cancer cells through ERα/Sp interactions with GC-rich promoters (O'Malley 2007), and we have been investigating coactivation of ERα and ERα/Sp in breast cancer cells transfected with pERE3 and pSp13, respectively (Kim et al. 2003; Wu et al. 2004; Lee et al. 2005; Lee & Safe 2007). Vitamin D interacting protein 150 (DRIP150) is a mediator complex protein (Koh et al. 2002; Kouzmenko et al. 2004) that coactivates ERα and ERα/Sp1, and this involves an α-helical NIFSEVRVYN (amino acids 795–804) motif within a twenty-three amino acid sequence (789–811) in the central region of DRIP150 which does not contain an LXXLL box (Lee et al. 2005; Lee & Safe 2007). DRIP150 had minimal effects on Sp-dependent transactivation and coactivated ERα and ERα/Sp1 primarily through interactions with ERα (Lee & Safe 2007). In this study, we demonstrate that E2-induced transactivation in breast cancer cells transfected with pSp13 or pERE3 was significantly inhibited by knockdown of Mdm2 by RNA interference (siMdm2) (Figs. 1A and 1B), and overexpression of MdM2 also enhanced transactivation in cells transfected with pSp13 or pERE3 constructs (Figs. 2A and 2B). We also observed that in ZR-75 and T47D cells transfected with siMdm2, there was a significant decrease in hormone-induced protein and mRNA levels (Fig. 7), demonstrating a role for Mdm2 in E2-induced gene expression. These results confirm coactivation of ERα by Mdm2 as previously reported (Saji et al. 2001) and also show that Mdm2 coactivates ERα/Sp1. Mdm2 did not interact with Sp1 and knockdown or overexpression of Mdm2 did not affect Sp-dependent transactivation (Figs. 1A, 1B, 2A and 2C), suggesting that coactivation of ERα and ERα/Sp is primarily associated with direct interactions between Mdm2 and ERα.
Mdm2 interacts with ERα in the presence or absence of E2 (Figs. 3A and 3B) and E2 also enhances ERα-Mdm2 interactions in living cells as determined by FRET analysis (Figs. 3D and 3E). It is clear from ChIP assays that ERα, Mdm2 and other nuclear coregulatory proteins cycle on and off E2-responsive gene promoters in breast cancer cells, and there is also evidence that specific subsets of coactivators may be selectively recruited to the pS2 promoter (Metivier et al. 2003). Since constitutively expressed and transiently overexpressed Mdm2 activated ERα and ERα/Sp1, it is possible that this protein may also act in concert with other nuclear cofactors such as the SRCs. Previous studies have demonstrated coactivation of ERα by SRCs (Blanco et al. 1998; Vassilev et al. 2004; O'Malley 2007) and co-recruitment of Mdm2 and SRCs to E2-responsive gene promoters and therefore, we hypothesized that Mdm2 acts, in part, through facilitating SRC-ERα interactions. Results in Figures 5 and 6 demonstrate that interactions of pMSRCs with VP-ERα are E2-dependent, and similar results were observed with interactions of VP-ER with the GRIP-1 LXXLL box [GAL4-GRIP(LXXLL)] (Fig. 5C). These hormone-dependent ER-SRC interactions were not surprising; however, using RNA interference with iMdm2, it was evident that Mdm2 facilitated ERα-SRC (Figs. 5A, 6A and 6C) but not ERα-p300 (Fig. 6E) interactions in a mammalian two-hybrid assay. Moreover, it was also apparent in mammalian two-hybrid assays in which cells were transfected with pMSRC and VP16-Mdm2 that Mdm2 did not directly interact with coactivators unless ERα was also overexpressed, and this resulted in increased transactivation in the presence or absence of E2 (Figs. 5B, 6B and 6D).
These results suggest a model for Mdm2 coactivation of ERα or ERα/Sp1 in which Mdm2 acts alone or in combination with SRCs to enhance transactivation. This resembles, in part, a similar model proposed for β-catenin which enhances nuclear receptor or transcription factor-mediated transactivation alone and in combination with other coactivators (Koh et al. 2002; Kouzmenko et al. 2004; Li et al. 2004; Yang et al. 2006). For example, β-catenin enhanced interactions between Lef1 (GAL4-Lef1) and GRIP-1 (VP-GRIP), and this was primarily due to coactivation and interactions of β-catenin with Lef1 but not GRIP-1. Similarly, this study shows that Mdm2 enhanced interactions between ERα and SRCs, and this was primarily associated with coactivation and interactions with ERα since Mdm2 and SRCs did not interact. The cooperative coactivation of nuclear receptors by coactivators and other nuclear factors is highly variable. For example, CARM-1 and p300 enhanced GRIP-1-dependent coactivation of ERα and the former proteins interact with GRIP-1 but not ERα (Chen et al. 2000). In contrast, the model for coactivation of ERα and ERα/Sp1 by SRCs and Mdm2 primarily involves Mdm2 interactions with ERα and not SRCs.
Current studies are investigating the role of Mdm2 in regulating expression of E2-responsive genes with ERE and GC-rich promoters and determining their cyclical interactions with gene promoters and other coactivators using ChIP assays. Our results clearly demonstrate that Mdm2 enhances ER-dependent transactivation and cell proliferation (Fig. 7), and in transactivation assays, the loss of hormone-responsiveness in cells transfected with siMdm2 was p53-independent (Suppl. Fig. 2). Cotransfection of cells with siMdm2 alone or siMdm2 plus sip53 gave similar results, whereas knockdown of p53 alone (sip53) slightly enhanced hormone-induced transactivation, and this was consistent with a recent study (Akaogi et al. 2009) and a report showing that p53 decreases hormone-induced transactivation (Liu et al. 1999). In breast cancer, the potential prognostic significance of Mdm2 or an Mdm2 promoter polymorphism (SNP309) that enhances Mdm2 expression has been inconsistent (Wilkening et al. 2007). However, examination of the publically available Nederlands Kanker Instituut (NKI) gene expression data from ER-positive breast cancer patients (van de Vijver et al. 2002) shows that low Mdm2 levels predict a higher overall and relapse-free survival compared to patients with high Mdm2 levels (Suppl. Fig. 3) and this observation is consistent with results of this study showing the critical role of Mdm2 in hormone-induced gene expression and growth of ER-positive breast cancer cells, suggesting that Mdm2 inhibitors may be efficacious for treatment of ER-positive breast cancer patients. However, it should also be noted that the loss of Mdm2 and the decreased MCF7 and ZR-75 cell proliferation (Fig. 7F) may also be due to the parallel activation of p53 after Mdm2 knockdown.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
FUNDING This research was supported by National Institutes of Health is gratefully acknowledged (ES04917).
Footnotes
DECLARATION OF INTEREST The authors have nothing to disclose.
REFERENCES
- Akaogi K, Nakajima Y, Ito I, Kawasaki S, Oie SH, Murayama A, Kimura K, Yanagisawa J. KLF4 suppresses estrogen-dependent breast cancer growth by inhibiting the transcriptional activity of ERalpha. Oncogene. 2009;28:2894–2902. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft M, Kubbutat MH, Vousden KH. Regulation of p53 function and stability by phosphorylation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999;19:1751–1758. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.3.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco JC, Minucci S, Lu J, Yang XJ, Walker KK, Chen H, Evans RM, Nakatani Y, Ozato K. The histone acetylase PCAF is a nuclear receptor coactivator. Genes Dev. 1998;12:1638–1651. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.11.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks CL, Gu W. p53 ubiquitination: Mdm2 and beyond. Mol. Cell. 2006;21:307–315. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.01.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bueso-Ramos CE, Manshouri T, Haidar MA, Yang Y, McCown P, Ordonez N, Glassman A, Sneige N, Albitar M. Abnormal expression of MDM-2 in breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1996;37:179–188. doi: 10.1007/BF01806499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burakov D, Crofts LA, Chang CPB, Freedman LP. Reciprocal recruitment of DRIP/mediator and p160 coactivator complexes in vivo by estrogen receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:14359–14362. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C200099200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahilly-Snyder L, Yang-Feng T, Francke U, George DL. Molecular analysis and chromosomal mapping of amplified genes isolated from a transformed mouse 3T3 cell line. Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 1987;13:235–244. doi: 10.1007/BF01535205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen DG, Huang SM, Stallcup MR. Synergistic, p160 coactivator-dependent enhancement of estrogen receptor function by CARM1 and p300. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:40810–40816. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005459200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rozieres S, Maya R, Oren M, Lozano G. The loss of mdm2 induces p53-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene. 2000;19:1691–1697. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakharzadeh SS, Trusko SP, George DL. Tumorigenic potential associated with enhanced expression of a gene that is amplified in a mouse tumor cell line. EMBO J. 1991;10:1565–1569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman SR, Perez M, Kung AL, Joseph M, Mansur C, Xiao ZX, Kumar S, Howley PM, Livingston DM. p300/MDM2 complexes participate in MDM2-mediated p53 degradation. Mol. Cell. 1998;2:405–415. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall JM, Couse JF, Korach KS. The multifaceted mechanisms of estradiol and estrogen receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:36869–36872. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R100029200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanstein B, Eckner R, DiRenzo J, Halachmi S, Liu H, Searcy B, Kurokawa R, Brown M. p300 is a component of an estrogen receptor coactivator complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1996;93:11540–11545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.21.11540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori M, Shimazaki J, Inagawa S, Itabashi M, Hori M. Overexpression of MDM2 oncoprotein correlates with possession of estrogen receptor α and lack of MDM2 mRNA splice variants in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2002;71:77–83. doi: 10.1023/a:1013350419426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh JK, Chan FS, O'Connor DJ, Mittnacht S, Zhong S, Lu X. RB regulates the stability and the apoptotic function of p53 via MDM2. Mol. Cell. 1999;3:181–193. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80309-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones SN, Roe AE, Donehower LA, Bradley A. Rescue of embryonic lethality in Mdm2-deficient mice by absence of p53. Nature. 1995;378:206–208. doi: 10.1038/378206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S, Abdelrahim M, Samudio I, Safe S. Estrogen receptor/Sp1 complexes are required for induction of cad gene expression by 17β-estradiol in breast cancer cells. Endocrinology. 2003;144:2325–2335. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-0149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K, Barhoumi R, Burghardt R, Safe S. Analysis of estrogen receptor α-Sp1 interactions in breast cancer cells by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005;19:843–854. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K, Nguyen T, Saville B, Safe S. Domains of estrogen receptor α (ERα) required for ERα/Sp1-mediated activation of GC-rich promoters by estrogens and antiestrogens in breast cancer cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003;17:804–817. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh SS, Li H, Lee YH, Widelitz RB, Chuong CM, Stallcup MR. Synergistic coactivator function by coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase (CARM) 1 and β-catenin with two different classes of DNA-binding transcriptional activators. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:26031–26035. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110865200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korkolopoulou P, Christodoulou P, Kouzelis K, Hadjiyannakis M, Priftis A, Stamoulis G, Seretis A, Thomas-Tsagli E. MDM2 and p53 expression in gliomas: a multivariate survival analysis including proliferation markers and epidermal growth factor receptor. Br. J. Cancer. 1997;75:1269–1278. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1997.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzmenko AP, Takeyama K, Ito S, Furutani T, Sawatsubashi S, Maki A, Suzuki E, Kawasaki Y, Akiyama T, Tabata T, Kato S. Wnt/β-catenin and estrogen signaling converge in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:40255–40258. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C400331200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubbutat MH, Ludwig RL, Levine AJ, Vousden KH. Analysis of the degradation function of Mdm2. Cell Growth Differ. 1999;10:87–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J, Safe S. Coactivation of estrogen receptor α (ER α)/Sp1 by vitamin D receptor interacting protein 150 (DRIP150) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007;461:200–210. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2006.12.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee JE, Kim K, Sacchettini JC, Smith CV, Safe S. DRIP150 coactivation of estrogen receptor α in ZR-75 breast cancer cells is independent of LXXLL motifs. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:8819–8830. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413184200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levav-Cohen Y, Haupt S, Haupt Y. Mdm2 in growth signaling and cancer. Growth Factors. 2005;23:183–192. doi: 10.1080/08977190500196218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveillard T, Wasylyk B. The MDM2 C-terminal region binds to TAFII250 and is required for MDM2 regulation of the cyclin A promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:30651–30661. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.49.30651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Kim JH, Koh SS, Stallcup MR. Synergistic effects of coactivators GRIP1 and β-catenin on gene activation: cross-talk between androgen receptor and Wnt signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:4212–4220. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M311374200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G, Schwartz JA, Brooks SC. p53 down-regulates ER-responsive genes by interfering with the binding of ER to ERE. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999;264:359–364. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu GZ, Schwartz JA, Brooks SC. Estrogen receptor protects p53 from deactivation by human double minute-2. Cancer Res. 2000;60:1810–1814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas J, Gao DQ, Keshmeshian M, Wen WH, Tsao-Wei D, Rosenberg S, Press MF. Alternative and aberrant messenger RNA splicing of the mdm2 oncogene in invasive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3212–3219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K, Trouche D, Hagemeier C, Sorensen TS, La Thangue NB, Kouzarides T. Stimulation of E2F1/DP1 transcriptional activity by MDM2 oncoprotein. Nature. 1995;375:691–694. doi: 10.1038/375691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metivier R, Penot G, Hubner MR, Reid G, Brand H, Kos M, Gannon F. Estrogen receptor-α directs ordered, cyclical, and combinatorial recruitment of cofactors on a natural target promoter. Cell. 2003;115:751–763. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00934-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson DC, George D, Levine AJ. The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell. 1992;69:1237–1245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montes de Oca Luna R, Wagner DS, Lozano G. Rescue of early embryonic lethality in mdm2-deficient mice by deletion of p53. Nature. 1995;378:203–206. doi: 10.1038/378203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngwenya S, Safe S. Cell context-dependent differences in the induction of E2F-1 gene expression by 17 β-estradiol in MCF-7 and ZR-75 cells. Endocrinology. 2003;144:1675–1685. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley BW. Coregulators: from whence came these “master genes”. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007;21:1009–1013. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley BW, Kumar R. Nuclear receptor coregulators in cancer biology. Cancer Res. 2009;69:8217–8222. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainov NG, Dobberstein KU, Bahn H, Holzhausen HJ, Lautenschlager C, Heidecke V, Burkert W. Prognostic factors in malignant glioma: influence of the overexpression of oncogene and tumor-suppressor gene products on survival. J. Neurooncol. 1997;35:13–28. doi: 10.1023/a:1005841520514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G, Hubner MR, Metivier R, Brand H, Denger S, Manu D, Beaudouin J, Ellenberg J, Gannon F. Cyclic, proteasome-mediated turnover of unliganded and liganded ERα on responsive promoters is an integral feature of estrogen signaling. Mol. Cell. 2003;11:695–707. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safe S, Kim K. Nuclear receptor-mediated transactivation through interaction with Sp proteins. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 2004;77:1–36. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6603(04)77001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saji S, Okumura N, Eguchi H, Nakashima S, Suzuki A, Toi M, Nozawa Y, Saji S, Hayashi S. MDM2 enhances the function of estrogen receptor α in human breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001;281:259–265. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.4339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiebe M, Ohneseit P, Hoffmann W, Meyermann R, Rodemann HP, Bamberg M. Analysis of mdm2 and p53 gene alterations in glioblastomas and its correlation with clinical factors. J. Neurooncol. 2000;49:197–203. doi: 10.1023/a:1006410702284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta S, Wasylyk B. Physiological and pathological consequences of the interactions of the p53 tumor suppressor with the glucocorticoid, androgen, and estrogen receptors. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004;1024:54–71. doi: 10.1196/annals.1321.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shang Y, Hu X, DiRenzo J, Lazar MA, Brown M. Cofactor dynamics and sufficiency in estrogen receptor-regulated transcription. Cell. 2000;103:843–852. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torchia J, Rose DW, Inostroza J, Kamei Y, Westin S, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG. The transcriptional co-activator p/CIP binds CBP and mediates nuclear-receptor function. Nature. 1997;387:677–684. doi: 10.1038/42652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver MJ, He YD, van't Veer LJ, Dai H, Hart AA, Voskuil DW, Schreiber GJ, Peterse JL, Roberts C, Marton MJ, Parrish M, Atsma D, Witteveen A, Glas A, Delahaye L, van d V, Bartelink H, Rodenhuis S, Rutgers ET, Friend SH, Bernards R. A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;347:1999–2009. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa021967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D, Podlaski F, Filipovic Z, Kong N, Kammlott U, Lukacs C, Klein C, Fotouhi N, Liu EA. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science. 2004;303:844–848. doi: 10.1126/science.1092472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voegel JJ, Heine MJ, Tini M, Vivat V, Chambon P, Gronemeyer H. The coactivator TIF2 contains three nuclear receptor-binding motifs and mediates transactivation through CBP binding-dependent and -independent pathways. EMBO J. 1998;17:507–519. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W, Dong L, Saville B, Safe S. Transcriptional activation of E2F1 gene expression by 17β-estradiol in MCF-7 cells is regulated by NF-Y - Sp1/estrogen receptor interactions. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999;13:1373–1387. doi: 10.1210/mend.13.8.0323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkening S, Bermejo JL, Hemminki K. MDM2 SNP309 and cancer risk: a combined analysis. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28:2262–2267. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgm191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Q, Burghardt R, Safe S. Vitamin D-interacting protein 205 (DRIP205) coactivation of estrogen receptor α (ERα) involves multiple domains of both proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:53602–53612. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409778200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang CK, Kim JH, Li H, Stallcup MR. Differential use of functional domains by coiled-coil coactivator in its synergistic coactivator function with β-catenin or GRIP1. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:3389–3397. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510403200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.