Abstract
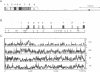
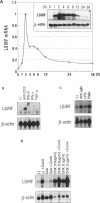
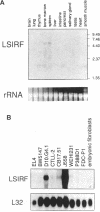
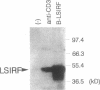
Interferon regulatory factor (IRF) genes encode a family of DNA-binding proteins that are involved in the transcriptional regulation of type-I interferon and/or interferon-inducible genes. We report here the characterization of LSIRF, a new member of the IRF gene family cloned from mouse spleen by the polymerase chain reaction using degenerate primers. LSIRF was found to encode a 51 kDa protein that shares a high degree of amino acid sequence homology in the DNA-binding domain with other IRF family members. LSIRF expression was detectable only in lymphoid cells. In contrast to other IRF genes, LSIRF expression was not induced by interferons, but rather by antigen-receptor mediated stimuli such as plant lectins, CD3 or IgM crosslinking. In in vitro DNA binding studies, LSIRF was able to bind to the interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE) of the MHC class I promoter. The expression pattern and DNA binding activities suggest that LSIRF plays a role in ISRE-targeted signal transduction mechanisms specific to lymphoid cells.
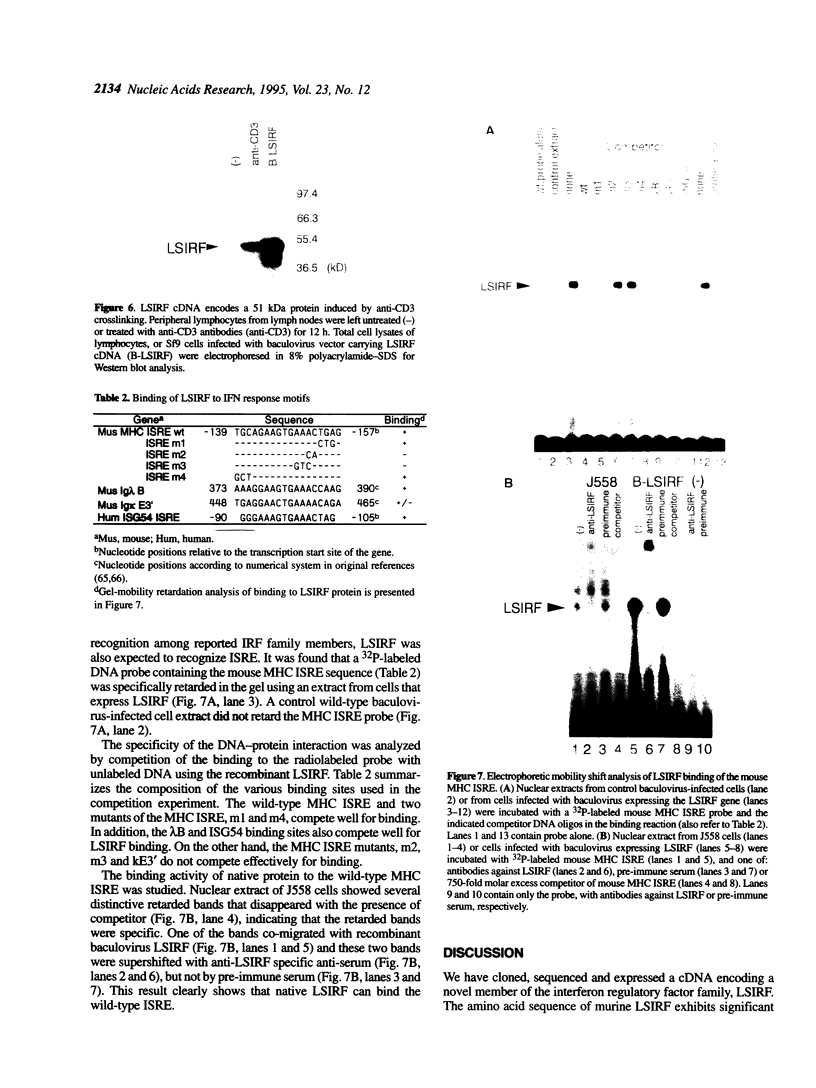
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G. The isochore organization of the human genome. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:637–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovolenta C., Driggers P. H., Marks M. S., Medin J. A., Politis A. D., Vogel S. N., Levy D. E., Sakaguchi K., Appella E., Coligan J. E. Molecular interactions between interferon consensus sequence binding protein and members of the interferon regulatory factor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5046–5050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher P., Trifonov E. N. Compilation and analysis of eukaryotic POL II promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):10009–10026. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.10009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Ephrussi A., Gilbert W., Tonegawa S. Cell-type-specific contacts to immunoglobulin enhancers in nuclei. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):798–801. doi: 10.1038/313798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumano A., Paige C. J., Iscove N. N., Brady G. Bipotential precursors of B cells and macrophages in murine fetal liver. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):612–615. doi: 10.1038/356612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr, Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1415–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.8197455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Mirkovitch J., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of GAF, an IFN-gamma-regulated DNA-binding factor. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):927–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Garland J., Scott D., Scolnick E., Metcalf D. Growth of factor-dependent hemopoietic precursor cell lines. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):1036–1047. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driggers P. H., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Mak W. H., Marks M. S., Levi B. Z., Flanagan J. R., Appella E., Ozato K. An interferon gamma-regulated protein that binds the interferon-inducible enhancer element of major histocompatibility complex class I genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3743–3747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duran L. W., Pease L. R. Tracing the evolution of H-2 D region genes using sequences associated with a repetitive element. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):295–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dölz R. GCG: pattern recognition. Methods Mol Biol. 1994;24:117–127. doi: 10.1385/0-89603-246-9:117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbeis C. F., Singh H., Storb U. PU.1 is a component of a multiprotein complex which binds an essential site in the murine immunoglobulin lambda 2-4 enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6452–6461. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Schindler C., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr The proteins of ISGF-3, the interferon alpha-induced transcriptional activator, define a gene family involved in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7840–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Kimura Y., Miyamoto M., Barsoumian E. L., Taniguchi T. Induction of endogenous IFN-alpha and IFN-beta genes by a regulatory transcription factor, IRF-1. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):270–272. doi: 10.1038/337270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Sakakibara J., Sudo Y., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Taniguchi T. Evidence for a nuclear factor(s), IRF-1, mediating induction and silencing properties to human IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3397–3405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Shibuya H., Hotta H., Yamanishi K., Taniguchi T. Interferon-beta gene regulation: tandemly repeated sequences of a synthetic 6 bp oligomer function as a virus-inducible enhancer. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):357–367. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90288-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galson D. L., Hensold J. O., Bishop T. R., Schalling M., D'Andrea A. D., Jones C., Auron P. E., Housman D. E. Mouse beta-globin DNA-binding protein B1 is identical to a proto-oncogene, the transcription factor Spi-1/PU.1, and is restricted in expression to hematopoietic cells and the testis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2929–2941. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene J. M., Larin Z., Taylor I. C., Prentice H., Gwinn K. A., Kingston R. E. Multiple basal elements of a human hsp70 promoter function differently in human and rodent cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3646–3655. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagman J., Rudin C. M., Haasch D., Chaplin D., Storb U. A novel enhancer in the immunoglobulin lambda locus is duplicated and functionally independent of NF kappa B. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):978–992. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Fujita T., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Furia A., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Structurally similar but functionally distinct factors, IRF-1 and IRF-2, bind to the same regulatory elements of IFN and IFN-inducible genes. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Kitagawa M., Tanaka N., Yamamoto H., Harada K., Ishihara M., Taniguchi T. Anti-oncogenic and oncogenic potentials of interferon regulatory factors-1 and -2. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):971–974. doi: 10.1126/science.8438157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Takahashi E., Itoh S., Harada K., Hori T. A., Taniguchi T. Structure and regulation of the human interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) and IRF-2 genes: implications for a gene network in the interferon system. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1500–1509. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Willison K., Sakakibara J., Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Taniguchi T. Absence of the type I IFN system in EC cells: transcriptional activator (IRF-1) and repressor (IRF-2) genes are developmentally regulated. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno Y., Kozak C. A., Schindler C., Driggers P. H., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Darnell J. E., Jr, Ozato K. The genomic structure of the murine ICSBP gene reveals the presence of the gamma interferon-responsive element, to which an ISGF3 alpha subunit (or similar) molecule binds. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3951–3963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T., Matsumoto M., Sato M., Harada H., Taniguchi T., Kitagawa M. Possible involvement of the transcription factor ISGF3 gamma in virus-induced expression of the IFN-beta gene. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jan 30;358(3):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A. The macrophage and B cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is related to the ets oncogene. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko L. J., Yamamoto M., Leonard M. W., George K. M., Ting P., Engel J. D. Murine and human T-lymphocyte GATA-3 factors mediate transcription through a cis-regulatory element within the human T-cell receptor delta gene enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2778–2784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krayev A. S., Markusheva T. V., Kramerov D. A., Ryskov A. P., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A., Georgiev G. P. Ubiquitous transposon-like repeats B1 and B2 of the mouse genome: B2 sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7461–7475. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Lew D. J., Decker T., Kessler D. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Synergistic interaction between interferon-alpha and interferon-gamma through induced synthesis of one subunit of the transcription factor ISGF3. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1105–1111. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Kimura T., Kitagawa M., Pfeffer K., Kawakami T., Watanabe N., Kündig T. M., Amakawa R., Kishihara K., Wakeham A. Targeted disruption of IRF-1 or IRF-2 results in abnormal type I IFN gene induction and aberrant lymphocyte development. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):83–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer K. B., Neuberger M. S. The immunoglobulin kappa locus contains a second, stronger B-cell-specific enhancer which is located downstream of the constant region. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1959–1964. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Decker T., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon induction of gene transcription analyzed by in vivo footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Harada H., Sudo Y., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Marks M. S., Driggers P. H., Ozato K. Interferon consensus sequence-binding protein, a member of the interferon regulatory factor family, suppresses interferon-induced gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):588–599. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. A., Petersen J. M., Gunther C. V., Jonsen M. D., Graves B. J. Interaction of murine ets-1 with GGA-binding sites establishes the ETS domain as a new DNA-binding motif. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosterwegel M., van de Wetering M., Dooijes D., Klomp L., Winoto A., Georgopoulos K., Meijlink F., Clevers H. Cloning of murine TCF-1, a T cell-specific transcription factor interacting with functional motifs in the CD3-epsilon and T cell receptor alpha enhancers. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1133–1142. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. D., Banville M., Lalumière M., Vialard J., Meighen E. A. Bacterial luciferase produced with rapid-screening baculovirus vectors is a sensitive reporter for infection of insect cells and larvae. Intervirology. 1992;34(4):213–227. doi: 10.1159/000150285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risse G., Jooss K., Neuberg M., Brüller H. J., Müller R. Asymmetrical recognition of the palindromic AP1 binding site (TRE) by Fos protein complexes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3825–3832. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudin C. M., Storb U. Two conserved essential motifs of the murine immunoglobulin lambda enhancers bind B-cell-specific factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):309–320. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Fu X. Y., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr Proteins of transcription factor ISGF-3: one gene encodes the 91-and 84-kDa ISGF-3 proteins that are activated by interferon alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7836–7839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Ransohoff R. M. Interferon-induced antiviral actions and their regulation. Adv Virus Res. 1993;42:57–102. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M., Darnell J. E., Jr A single phosphotyrosine residue of Stat91 required for gene activation by interferon-gamma. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1744–1746. doi: 10.1126/science.7690989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims S. H., Cha Y., Romine M. F., Gao P. Q., Gottlieb K., Deisseroth A. B. A novel interferon-inducible domain: structural and functional analysis of the human interferon regulatory factor 1 gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):690–702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Kawakami T., Taniguchi T. Recognition DNA sequences of interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) and IRF-2, regulators of cell growth and the interferon system. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4531–4538. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis A., Amsterdam A., Belanger C., Grosschedl R. LEF-1, a gene encoding a lymphoid-specific protein with an HMG domain, regulates T-cell receptor alpha enhancer function [corrected]. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):880–894. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veals S. A., Santa Maria T., Levy D. E. Two domains of ISGF3 gamma that mediate protein-DNA and protein-protein interactions during transcription factor assembly contribute to DNA-binding specificity. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):196–206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veals S. A., Schindler C., Leonard D., Fu X. Y., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr, Levy D. E. Subunit of an alpha-interferon-responsive transcription factor is related to interferon regulatory factor and Myb families of DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3315–3324. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Q., Grigoriadis A. E., Möhle-Steinlein U., Wagner E. F. A novel target cell for c-fos-induced oncogenesis: development of chondrogenic tumours in embryonic stem cell chimeras. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2437–2450. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07783.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Distinct factors bind to apparently homologous sequences in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):846–848. doi: 10.1038/322846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisz A., Marx P., Sharf R., Appella E., Driggers P. H., Ozato K., Levi B. Z. Human interferon consensus sequence binding protein is a negative regulator of enhancer elements common to interferon-inducible genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25589–25596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. R. Transcriptional regulation of interferon-stimulated genes. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 15;200(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb21041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]