Abstract
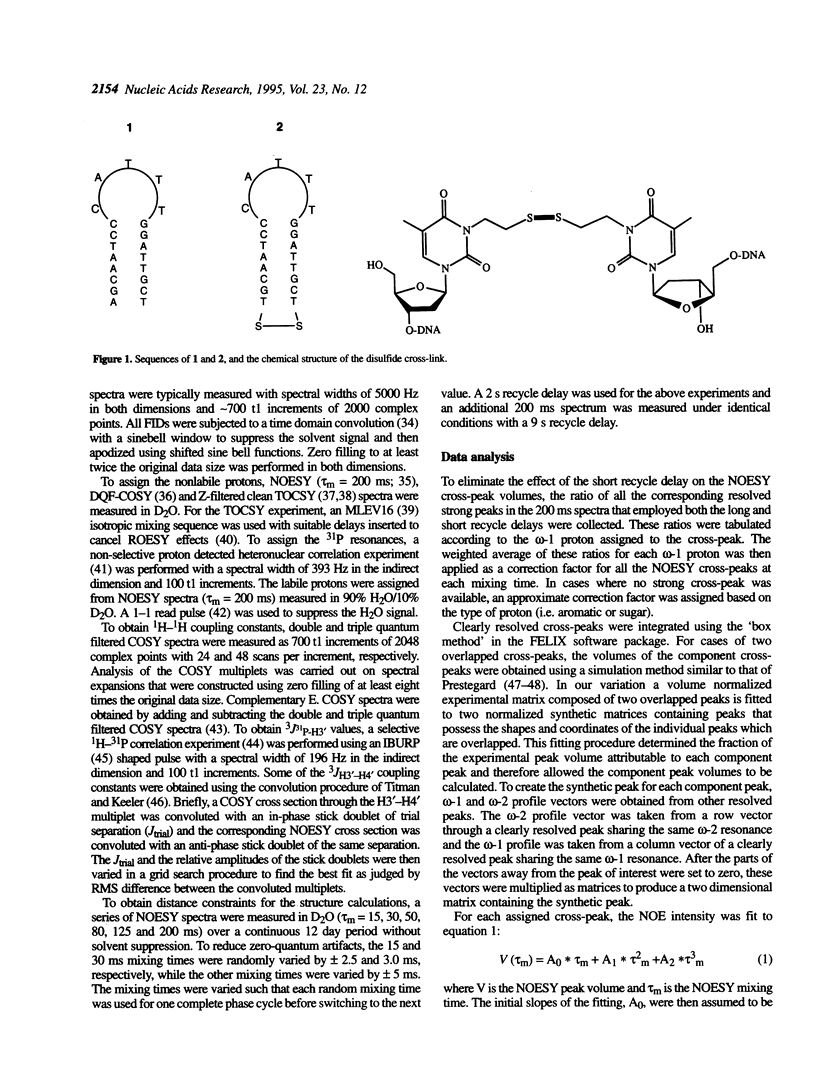
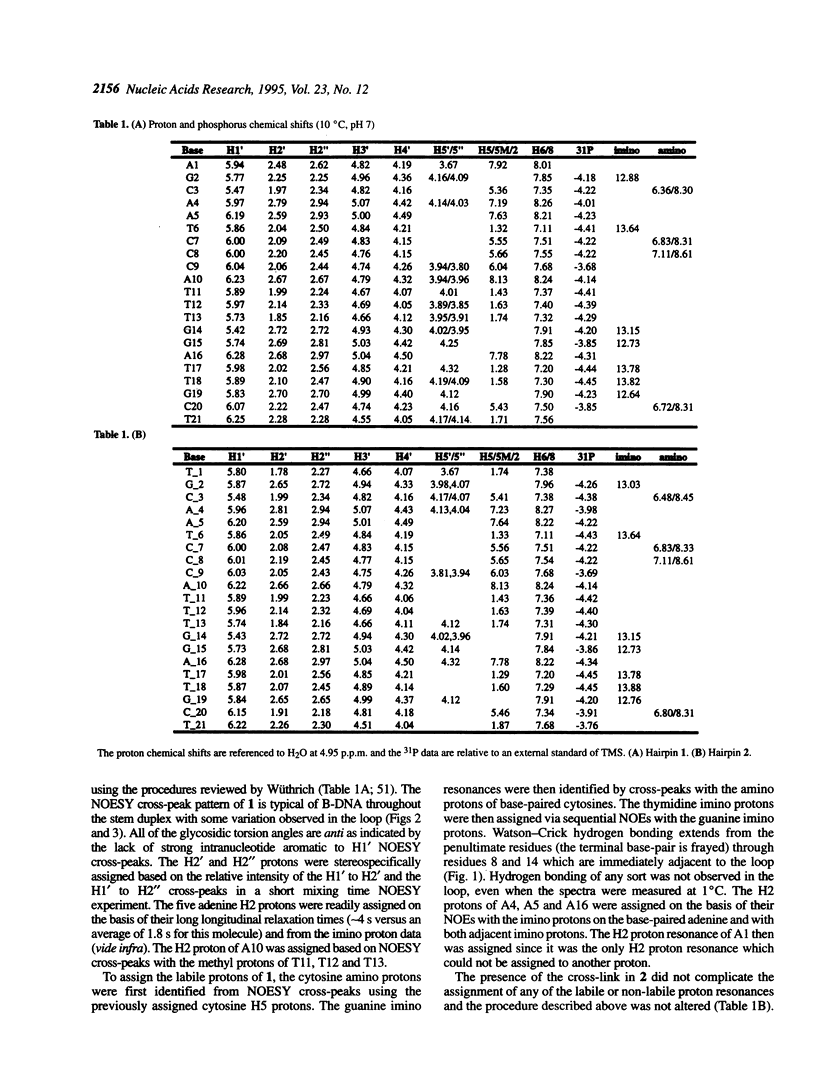
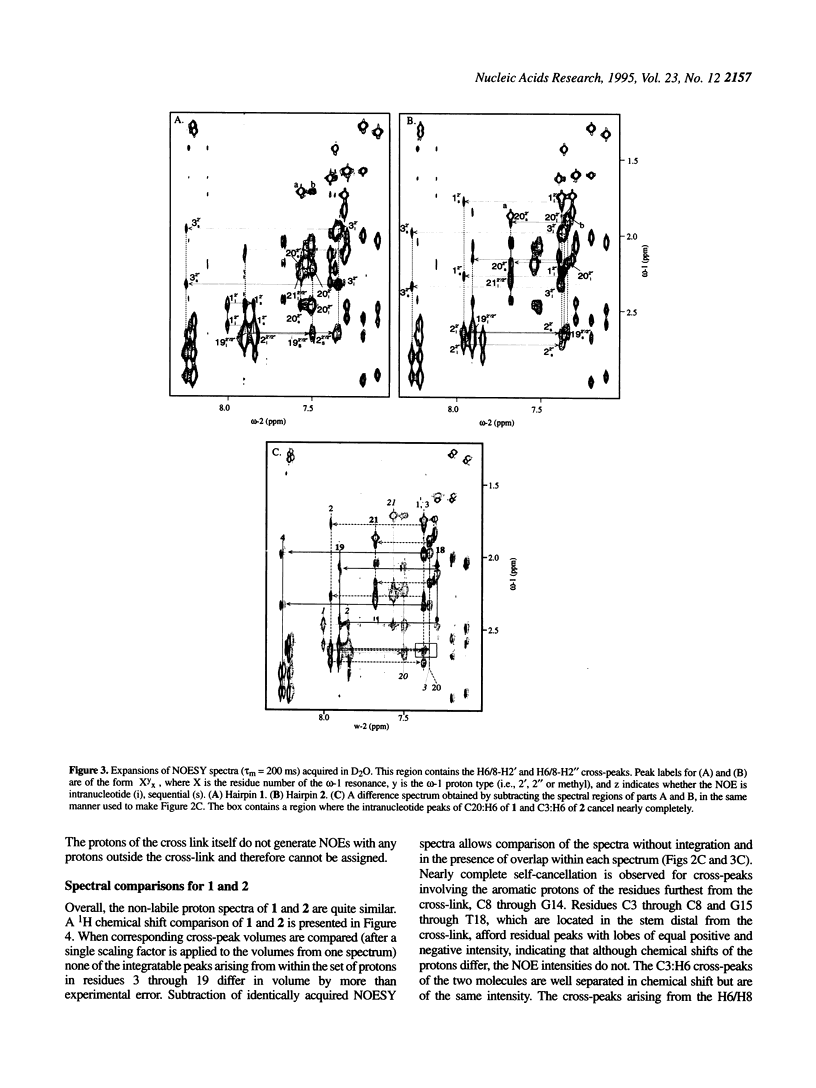
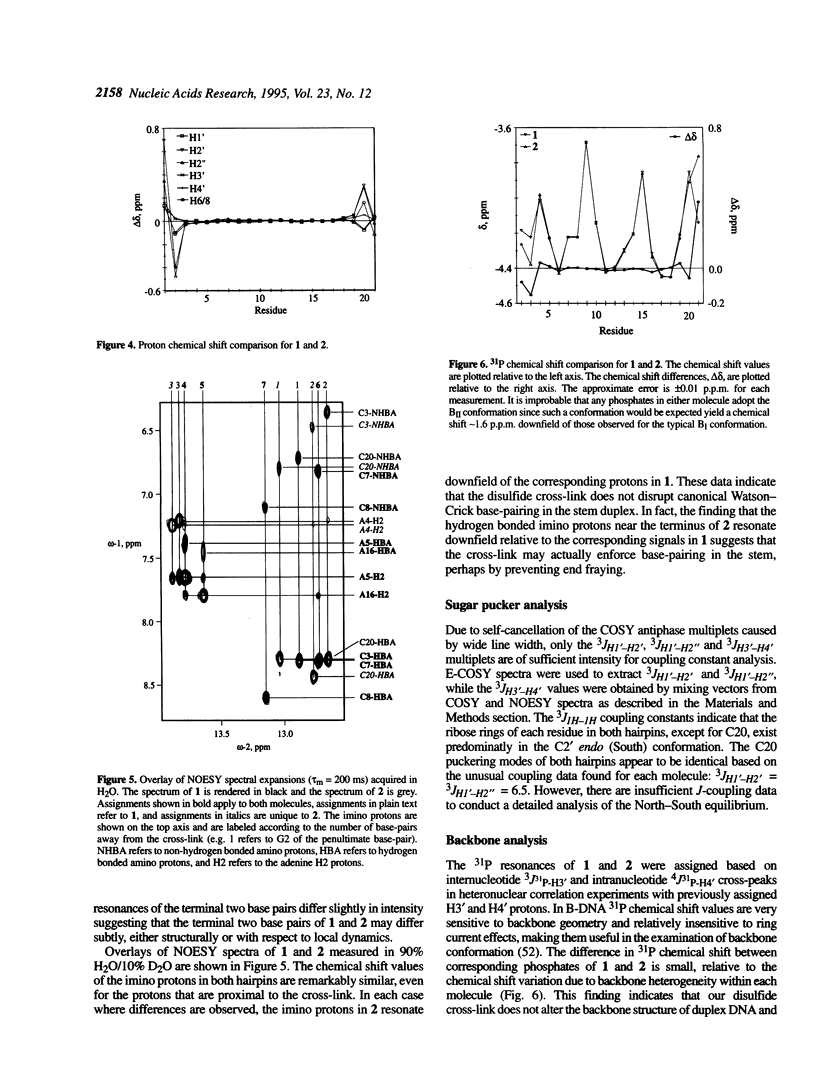
The solution structures of a 21 base long DNA hairpin derived from the ColE1 cruciform, and an analog possessing a disulfide cross-link bridging the terminal bases, have been determined by NMR spectroscopy. The 8 bp long stem of these sequences adopts a B-form helix whereas the five base long single-stranded loop appears to be flexible and cannot be represented by a unique static conformation. NOESY cross-peak volumes, proton and phosphorus chemical shifts, and both homo- and heteronuclear coupling constants for the cross-linked hairpin are virtually identical to those measured for the unmodified sequence, even for the residues that are proximal to the cross-link. These results indicate that both hairpins are structurally isomorphous. Because this cross-link can be incorporated site specifically in a sequence independent manner, and does not appear to alter native conformation, it should prove broadly applicable in studies of DNA structure and function.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blatt N. B., Osborne S. E., Cain R. J., Glick G. D. Conformational studies of hairpin sequences from the ColE1 cruciform. Biochimie. 1993;75(6):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(93)90108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowy-Borowski H., Lipman R., Tomasz M. Recognition between mitomycin C and specific DNA sequences for cross-link formation. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 27;29(12):2999–3006. doi: 10.1021/bi00464a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. F., Ewig R. A., Kohn K. W., Glaubiger D. Interstrand DNA crosslinking by 4,5'8-trimethylpsoralen plus monochromatic ultraviolet light. Studies by alkaline elution in mouse L1210 leukemia cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 14;610(1):56–63. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowart M., Benkovic S. J. A novel combined chemical-enzymatic synthesis of cross-linked DNA using a nucleoside triphosphate analogue. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 22;30(3):788–796. doi: 10.1021/bi00217a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire M. A., Schwartz A., Rahmouni A. R., Leng M. Interstrand cross-links are preferentially formed at the d(GC) sites in the reaction between cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) and DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1982–1985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion D., Wüthrich K. Application of phase sensitive two-dimensional correlated spectroscopy (COSY) for measurements of 1H-1H spin-spin coupling constants in proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 29;113(3):967–974. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard J. T., Weidner M. F., Kirchner J. J., Ribeiro S., Hopkins P. B. Sequence preferences of DNA interstrand crosslinking agents: quantitation of interstrand crosslink locations in DNA duplex fragments containing multiple crosslinkable sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1885–1891. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard J. T., White M. M. Diepoxybutane cross-links DNA at 5'-GNC sequences. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 2;32(8):2120–2124. doi: 10.1021/bi00059a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieles U., Sproat B. S., Neuner P., Cramer F. Preparation of a novel psoralen containing deoxyadenosine building block for the facile solid phase synthesis of psoralen-modified oligonucleotides for a sequence specific crosslink to a given target sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):8967–8978. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.8967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto A. L., Lippard S. J. Binding of the antitumor drug cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) (cisplatin) to DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985;780(3):167–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(85)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid B. R., Banks K., Flynn P., Nerdal W. NMR distance measurements in DNA duplexes: sugars and bases have the same correlation times. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 26;28(26):10001–10007. doi: 10.1021/bi00452a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Gamper H., Hearst J. E. Interaction of T7 RNA polymerase with DNA in an elongation complex arrested at a specific psoralen adduct site. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):527–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklenár V., Miyashiro H., Zon G., Miles H. T., Bax A. Assignment of the 31P and 1H resonances in oligonucleotides by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):94–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81539-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson P. C., Cooper B. C., Glick G. D. High resolution epitope mapping of an anti-DNA autoantibody using model DNA ligands. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 1;152(5):2601–2612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng S. P., Woodson S. A., Crothers D. M. DNA sequence specificity of mitomycin cross-linking. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3901–3907. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz M., Lipman R., Chowdary D., Pawlak J., Verdine G. L., Nakanishi K. Isolation and structure of a covalent cross-link adduct between mitomycin C and DNA. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1204–1208. doi: 10.1126/science.3103215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomic M. T., Wemmer D. E., Kim S. H. Structure of a psoralen cross-linked DNA in solution by nuclear magnetic resonance. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1722–1725. doi: 10.1126/science.3686011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


