Abstract
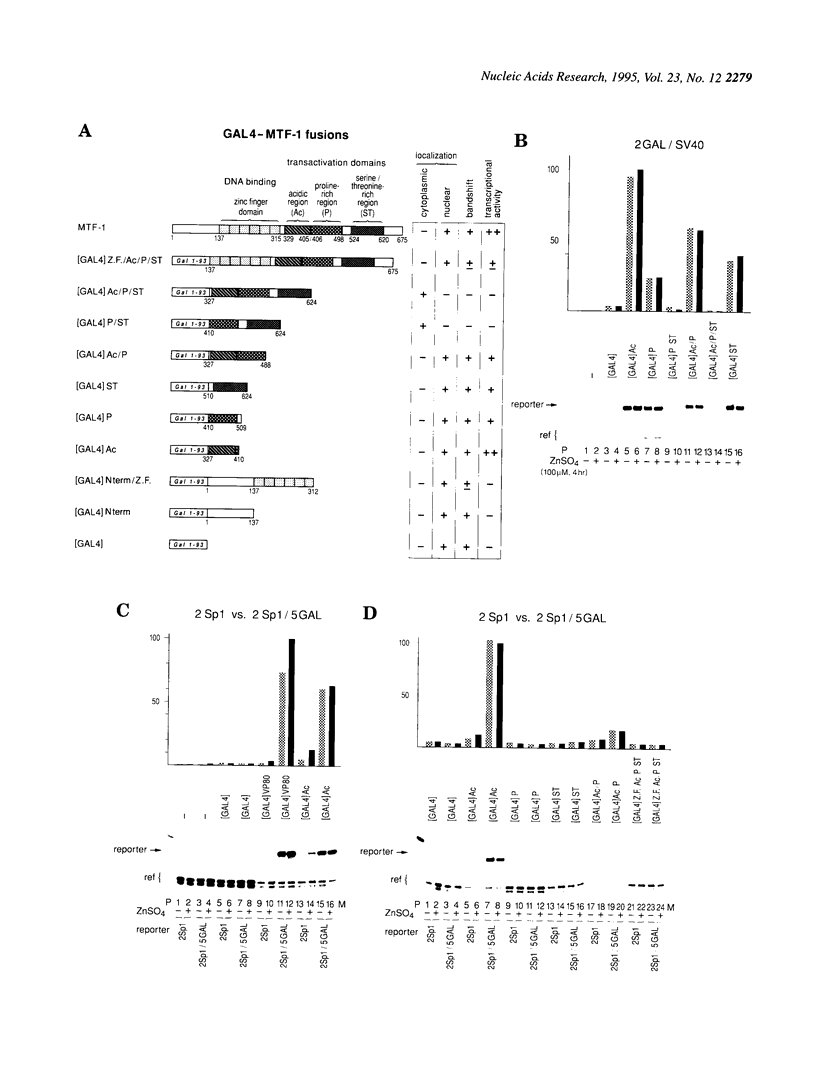
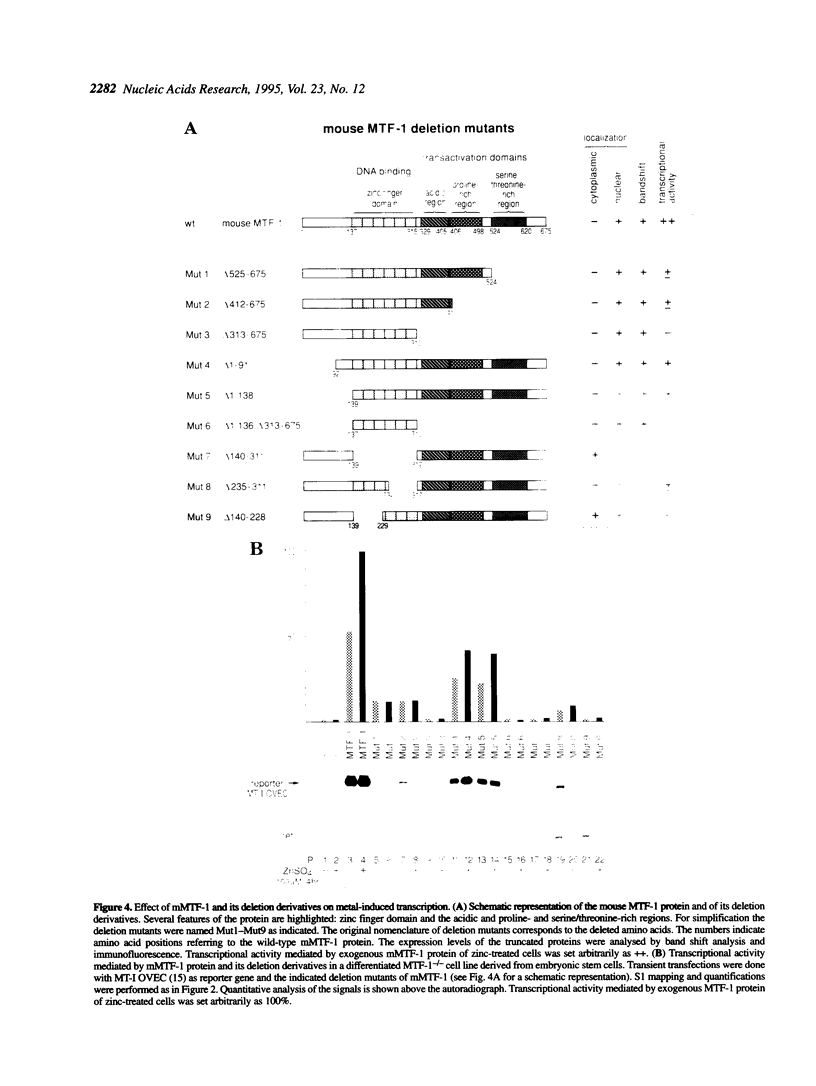
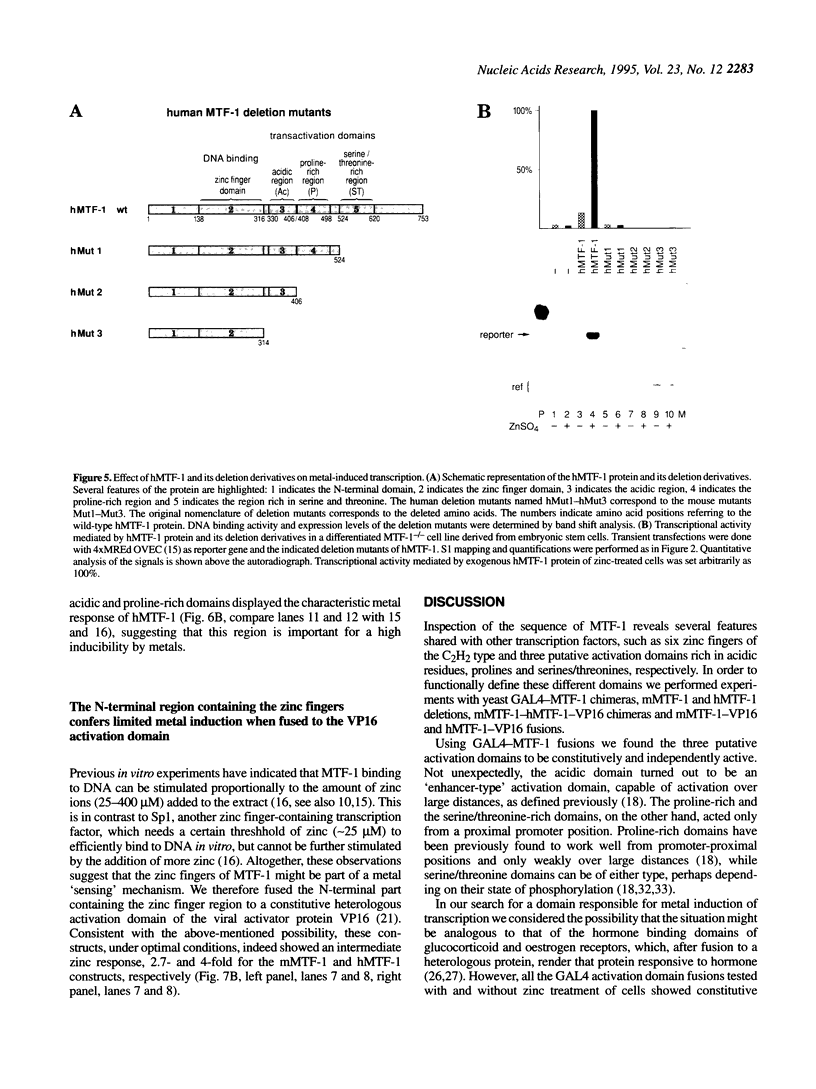
Metallothioneins (MTs) constitute a class of low molecular weight, cysteine-rich, metal binding proteins which are regulated at the level of gene transcription in response to heavy metals and other adverse treatments. We have previously cloned a zinc finger factor (MTF-1) that binds specifically to heavy metal-responsive DNA sequence elements in metallothionein promoters and shown that this factor is essential for basal and heavy metal-induced transcription. Here we report that the C-terminal part of MTF-1 downstream of the DNA binding zinc fingers harbours three different transactivation domains, namely an acidic domain, a proline-rich domain and a domain rich in serine and threonine. When fused to the heterologous DNA binding domain of the yeast factor GAL4 these activation domains function constitutively, i.e. transcription of a GAL4-driven reporter gene is not induced by heavy metals. In search of the region(s) responsible for metal induction, external and internal deletion mutations of mouse and human MTF-1 and chimeric variants thereof were tested with a reporter gene driven by a metal-responsive promoter. The N-terminal part of MTF-1 containing the zinc fingers, which are dependent on zinc for efficient DNA binding, can indeed confer a limited (3- to 4-fold) zinc-responsive transcription when fused to the heterologous activation domain of the viral VP16 protein. Another region containing the acidic and proline-rich activation domains also contributes to metal inducibility, but only in the context of intact MTF-1. This indicates that the activity of MTF-1 results from a complex interplay of different functional domains.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen R. D., Taplitz S. J., Oberbauer A. M., Calame K. L., Herschman H. R. Metal-dependent binding of a nuclear factor to the rat metallothionein-I promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6049–6055. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews G. K. Regulation of metallothionein gene expression. Prog Food Nutr Sci. 1990;14(2-3):193–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugnera E., Georgiev O., Radtke F., Heuchel R., Baker E., Sutherland G. R., Schaffner W. Cloning, chromosomal mapping and characterization of the human metal-regulatory transcription factor MTF-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 11;22(15):3167–3173. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.15.3167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Kakidani H., Leatherwood J., Mostashari F., Ptashne M. An amino-terminal fragment of GAL4 binds DNA as a dimer. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 5;209(3):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter A. D., Felber B. K., Walling M. J., Jubier M. F., Schmidt C. J., Hamer D. H. Duplicated heavy metal control sequences of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7392–7396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cress W. D., Triezenberg S. J. Critical structural elements of the VP16 transcriptional activation domain. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):87–90. doi: 10.1126/science.1846049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst P., Hu S., Hackett R., Hamer D. Copper activates metallothionein gene transcription by altering the conformation of a specific DNA binding protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):705–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuchel R., Radtke F., Georgiev O., Stark G., Aguet M., Schaffner W. The transcription factor MTF-1 is essential for basal and heavy metal-induced metallothionein gene expression. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2870–2875. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06581.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi J. H. Overview of metallothionein. Methods Enzymol. 1991;205:613–626. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)05145-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi J. H., Schäffer A. Biochemistry of metallothionein. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8509–8515. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters B. A., Kelly E. J., Quaife C. J., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Targeted disruption of metallothionein I and II genes increases sensitivity to cadmium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):584–588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalska A. E., Choo K. H. Targeting and germ-line transmission of a null mutation at the metallothionein I and II loci in mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8088–8092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Salser S. J., Wold B. Constitutive and metal-inducible protein:DNA interactions at the mouse metallothionein I promoter examined by in vivo and in vitro footprinting. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):412–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Immerglück M. M., Schaffner W., Matthias P. Transcription factor Oct-2A contains functionally redundant activating domains and works selectively from a promoter but not from a remote enhancer position in non-lymphoid (HeLa) cells. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1625–1634. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Yamamoto K. R. Two signals mediate hormone-dependent nuclear localization of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3333–3340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radtke F., Heuchel R., Georgiev O., Hergersberg M., Gariglio M., Dembic Z., Schaffner W. Cloned transcription factor MTF-1 activates the mouse metallothionein I promoter. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1355–1362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusconi S., Yamamoto K. R. Functional dissection of the hormone and DNA binding activities of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1309–1315. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02369.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ptashne M. A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7539–7539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F. Zinc dependent binding of a liver nuclear factor to metal response element MRE-a of the mouse metallothionein-I gene and variant sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seipel K., Georgiev O., Gerber H. P., Schaffner W. C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA-polymerase II and N-terminal segment of the human TATA binding protein (TBP) can mediate remote and proximal transcriptional activation, respectively. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 11;21(24):5609–5615. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.24.5609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seipel K., Georgiev O., Schaffner W. Different activation domains stimulate transcription from remote ('enhancer') and proximal ('promoter') positions. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4961–4968. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05603.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serfling E., Lübbe A., Dorsch-Häsler K., Schaffner W. Metal-dependent SV40 viruses containing inducible enhancers from the upstream region of metallothionein genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3851–3859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Palmiter R. D. Identification of multiple metal regulatory elements in mouse metallothionein-I promoter by assaying synthetic sequences. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):828–831. doi: 10.1038/317828a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguin C., Prévost J. Detection of a nuclear protein that interacts with a metal regulatory element of the mouse metallothionein 1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10547–10560. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triezenberg S. J., Kingsbury R. C., McKnight S. L. Functional dissection of VP16, the trans-activator of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene expression. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):718–729. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Gerster T., Müller M. M., Schaffner G., Schaffner W. OVEC, a versatile system to study transcription in mammalian cells and cell-free extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6787–6798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Schaffner W. A zinc-responsive factor interacts with a metal-regulated enhancer element (MRE) of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3763–3770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Schaffner W. Heavy metal ions in transcription factors from HeLa cells: Sp1, but not octamer transcription factor requires zinc for DNA binding and for activator function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5771–5781. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu L., Rungger D., Georgiev O., Seipel K., Schaffner W. Different potential of cellular and viral activators of transcription revealed in oocytes and early embryos of Xenopus laevis. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1994 Feb;375(2):105–112. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1994.375.2.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]