Abstract
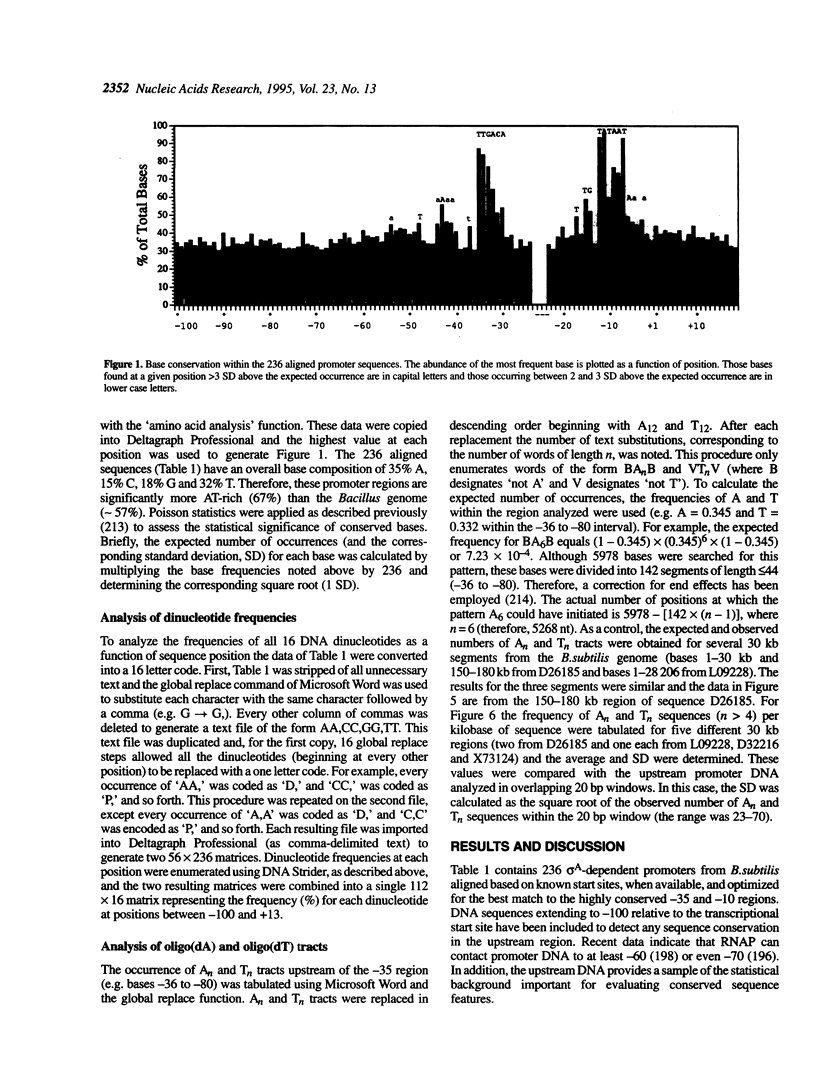
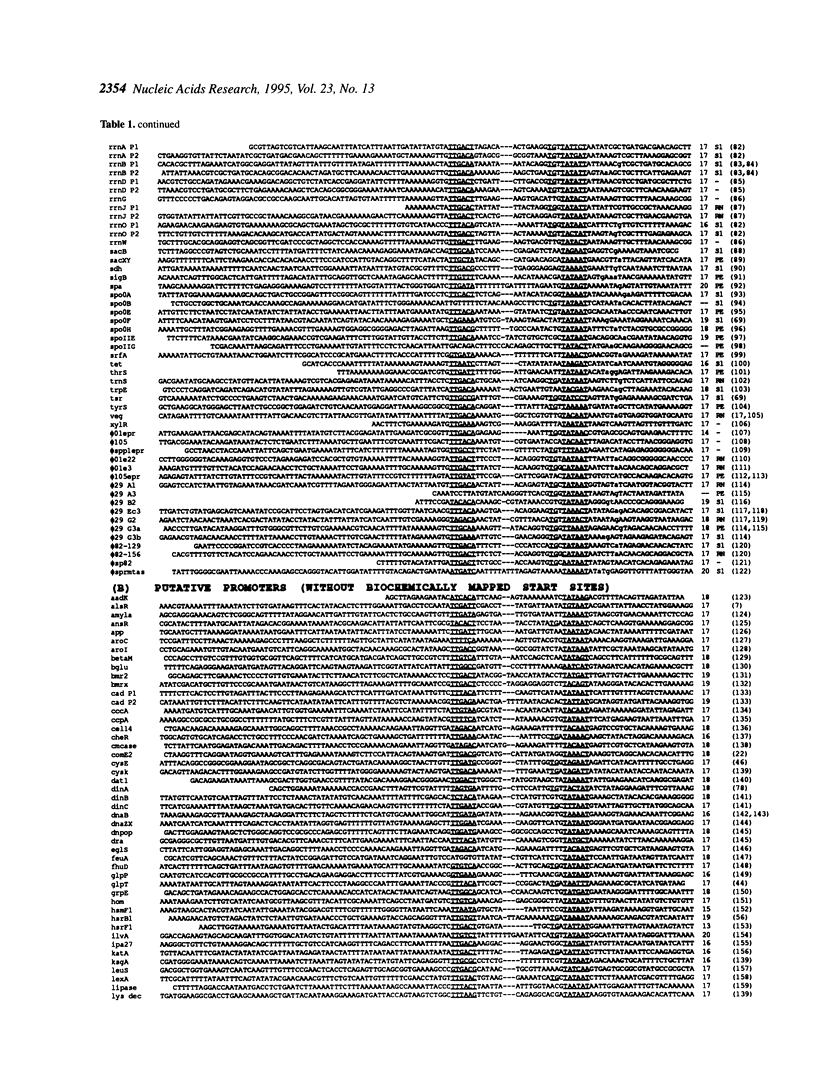
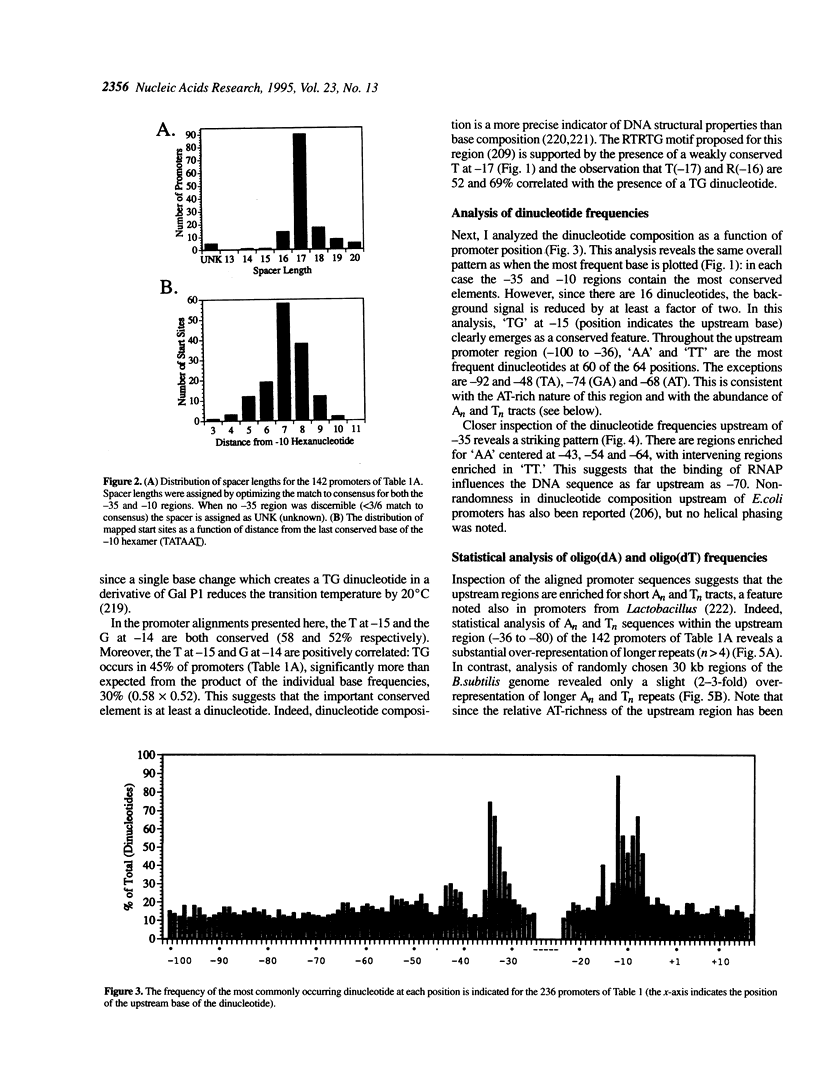
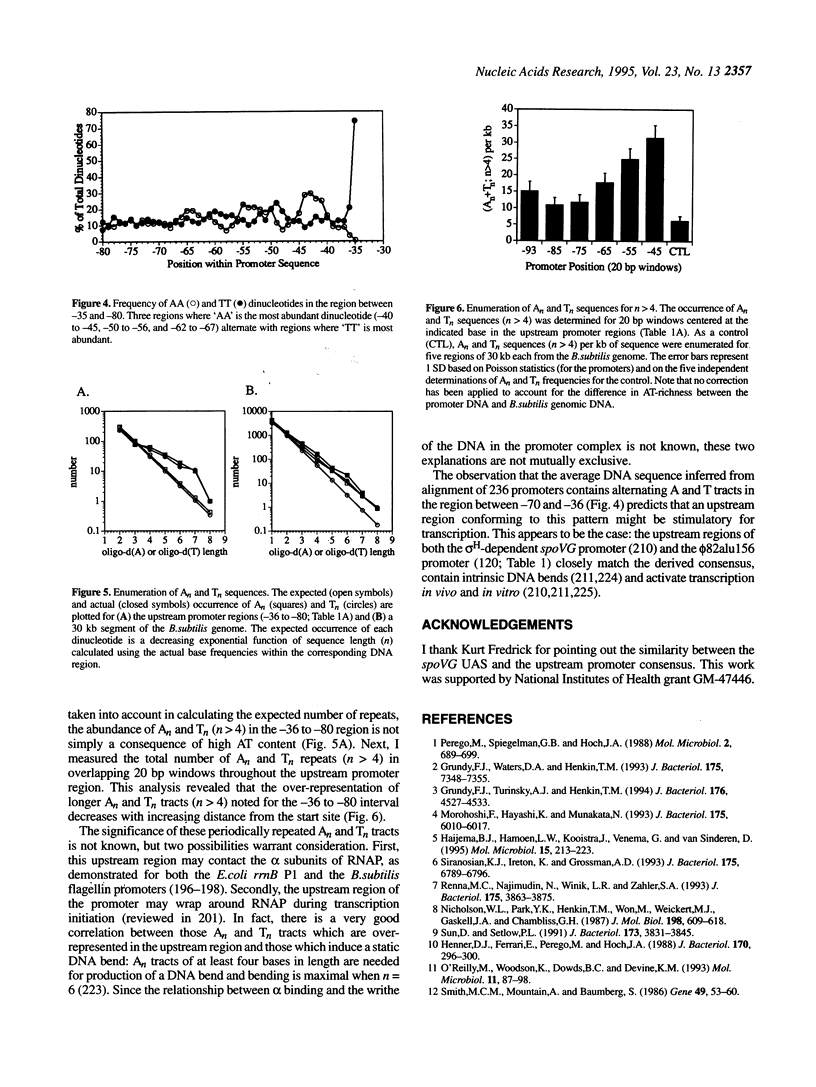
Sequence analysis of 236 promoters recognized by the Bacillus subtilis sigma A-RNA polymerase reveals an extended promoter structure. The most highly conserved bases include the -35 and -10 hexanucleotide core elements and a TG dinucleotide at position -15, -14. In addition, several weakly conserved A and T residues are present upstream of the -35 region. Analysis of dinucleotide composition reveals A2- and T2-rich sequences in the upstream promoter region (-36 to -70) which are phased with the DNA helix: An tracts are common near -43, -54 and -65; Tn tracts predominate at the intervening positions. When compared with larger regions of the genome, upstream promoter regions have an excess of An and Tn sequences for n > 4. These data indicate that an RNA polymerase binding site affects DNA sequence as far upstream as -70. This sequence conservation is discussed in light of recent evidence that the alpha subunits of the polymerase core bind DNA and that the promoter may wrap around RNA polymerase.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achberger E. C., Hilton M. D., Whiteley H. R. The effect of the delta subunit on the interaction of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase with bases in a SP82 early gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2893–2910. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albano M., Breitling R., Dubnau D. A. Nucleotide sequence and genetic organization of the Bacillus subtilis comG operon. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5386–5404. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5386-5404.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awadé A., Cleuziat P., Gonzalès T., Robert-Baudouy J. Characterization of the pcp gene encoding the pyrrolidone carboxyl peptidase of Bacillus subtilis. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 22;305(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80656-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banner C. D., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Deletion analysis of a complex promoter for a developmentally regulated gene from Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 5;168(2):351–365. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beijer L., Nilsson R. P., Holmberg C., Rutberg L. The glpP and glpF genes of the glycerol regulon in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Feb;139(2):349–359. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-2-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beijer L., Nilsson R. P., Holmberg C., Rutberg L. The glpP and glpF genes of the glycerol regulon in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Feb;139(2):349–359. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-2-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belyaeva T., Griffiths L., Minchin S., Cole J., Busby S. The Escherichia coli cysG promoter belongs to the 'extended -10' class of bacterial promoters. Biochem J. 1993 Dec 15;296(Pt 3):851–857. doi: 10.1042/bj2960851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson D. A., Boguski M., Lipman D. J., Ostell J. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Sep;22(17):3441–3444. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.17.3441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohannon D. E., Sonenshein A. L. Positive regulation of glutamate biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4718–4727. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4718-4727.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brakhage A. A., Wozny M., Putzer H. Structure and nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase genes. Biochimie. 1990 Oct;72(10):725–734. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90157-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhk H. J., Behrens B., Tailor R., Wilke K., Prada J. J., Günthert U., Noyer-Weidner M., Jentsch S., Trautner T. A. Restriction and modification in Bacillus subtilis: nucleotide sequence, functional organization and product of the DNA methyltransferase gene of bacteriophage SPR. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns H., Minchin S. Thermal energy requirement for strand separation during transcription initiation: the effect of supercoiling and extended protein DNA contacts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Sep 25;22(19):3840–3845. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.19.3840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan B., Spassky A., Busby S. The organization of open complexes between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and DNA fragments carrying promoters either with or without consensus -35 region sequences. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):141–148. doi: 10.1042/bj2700141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., James L. P., Helmann J. D. Metalloregulation in Bacillus subtilis: isolation and characterization of two genes differentially repressed by metal ions. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(17):5428–5437. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.17.5428-5437.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen N. Y., Hu F. M., Paulus H. Nucleotide sequence of the overlapping genes for the subunits of Bacillus subtilis aspartokinase II and their control regions. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8787–8798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen N. Y., Jiang S. Q., Klein D. A., Paulus H. Organization and nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis diaminopimelate operon, a cluster of genes encoding the first three enzymes of diaminopimelate synthesis and dipicolinate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9448–9465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheo D. L., Bayles K. W., Yasbin R. E. Cloning and characterization of DNA damage-inducible promoter regions from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1696–1703. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1696-1703.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheo D. L., Bayles K. W., Yasbin R. E. Elucidation of regulatory elements that control damage induction and competence induction of the Bacillus subtilis SOS system. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(18):5907–5915. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.18.5907-5915.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chibazakura T., Kawamura F., Takahashi H. Differential regulation of spo0A transcription in Bacillus subtilis: glucose represses promoter switching at the initiation of sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2625–2632. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2625-2632.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow K. C., Wong J. T. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the structural gene coding for Bacillus subtilis tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):537–543. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90518-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung Y. J., Hansen J. N. Determination of the sequence of spaE and identification of a promoter in the subtilin (spa) operon in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6699–6702. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6699-6702.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Haran T. E., Nadeau J. G. Intrinsically bent DNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7093–7096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crutz A. M., Steinmetz M. Transcription of the Bacillus subtilis sacX and sacY genes, encoding regulators of sucrose metabolism, is both inducible by sucrose and controlled by the DegS-DegU signalling system. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(19):6087–6095. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.19.6087-6095.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cully D. F., Garro A. J. Nucleotide sequence of the immunity region of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 105: identification of the repressor gene and its mRNA and protein products. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):153–164. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dartois V., Baulard A., Schanck K., Colson C. Cloning, nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli of a lipase gene from Bacillus subtilis 168. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 15;1131(3):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90023-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhaese P., Seurinck J., De Smet B., Van Montagu M. Nucleotide sequence and mutational analysis of an immunity repressor gene from Bacillus subtilis temperate phage phi 105. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5441–5455. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobinson K. F., Spiegelman G. B. Effect of the delta subunit of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase on initiation of RNA synthesis at two bacteriophage phi 29 promoters. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8206–8213. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobinson K. F., Spiegelman G. B. Nucleotide sequence and transcription of a bacteriophage 29 early promoter. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5950–5955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll J. R., Taber H. W. Sequence organization and regulation of the Bacillus subtilis menBE operon. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):5063–5071. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.5063-5071.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebbole D. J., Zalkin H. Detection of pur operon-attenuated mRNA and accumulated degradation intermediates in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10894–10902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinger T., Behnke D., Bujard H., Gralla J. D. Stalling of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in the +6 to +12 region in vivo is associated with tight binding to consensus promoter elements. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jun 17;239(4):455–465. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinger T., Behnke D., Knaus R., Bujard H., Gralla J. D. Context-dependent effects of upstream A-tracts. Stimulation or inhibition of Escherichia coli promoter function. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jun 17;239(4):466–475. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori M., Takagi M., Maruo B., Yano K. Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequencing, and expression of the Bacillus subtilis (natto) IAM1212 alpha-amylase gene, which encodes an alpha-amylase structurally similar to but enzymatically distinct from that of B. subtilis 2633. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4901–4908. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4901-4908.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouet A., Jin S. F., Raffel G., Sonenshein A. L. Multiple regulatory sites in the Bacillus subtilis citB promoter region. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5408–5415. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5408-5415.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrick K., Caramori T., Chen Y. F., Galizzi A., Helmann J. D. Promoter architecture in the flagellar regulon of Bacillus subtilis: high-level expression of flagellin by the sigma D RNA polymerase requires an upstream promoter element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2582–2586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisby D., Zuber P. Analysis of the upstream activating sequence and site of carbon and nitrogen source repression in the promoter of an early-induced sporulation gene of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7557–7564. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7557-7564.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita Y., Fujita T. Identification and nucleotide sequence of the promoter region of the Bacillus subtilis gluconate operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1237–1252. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürbass R., Marahiel M. A. Mutant analysis of interaction of the Bacillus subtilis transcription regulator AbrB with the antibiotic biosynthesis gene tycA. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 5;287(1-2):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagnon Y., Breton R., Putzer H., Pelchat M., Grunberg-Manago M., Lapointe J. Clustering and co-transcription of the Bacillus subtilis genes encoding the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases specific for glutamate and for cysteine and the first enzyme for cysteine biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7473–7482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrity D. B., Zahler S. A. The Bacillus subtilis ochre suppressor sup-3 is located in an operon of seven tRNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1993 Oct;175(20):6512–6517. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.20.6512-6517.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey K. J., Yoshikawa H., Ito J. The complete sequence of the Bacillus phage phi 29 right early region. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaur N. K., Dubnau E., Smith I. Characterization of a cloned Bacillus subtilis gene that inhibits sporulation in multiple copies. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):860–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.860-869.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendron N., Putzer H., Grunberg-Manago M. Expression of both Bacillus subtilis threonyl-tRNA synthetase genes is autogenously regulated. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jan;176(2):486–494. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.2.486-494.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser P., Kunst F., Arnaud M., Coudart M. P., Gonzales W., Hullo M. F., Ionescu M., Lubochinsky B., Marcelino L., Moszer I. Bacillus subtilis genome project: cloning and sequencing of the 97 kb region from 325 degrees to 333 degrees. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Oct;10(2):371–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollnick P., Ishino S., Kuroda M. I., Henner D. J., Yanofsky C. The mtr locus is a two-gene operon required for transcription attenuation in the trp operon of Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8726–8730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzy-Tréboul G., Karmazyn-Campelli C., Stragier P. Developmental regulation of transcription of the Bacillus subtilis ftsAZ operon. J Mol Biol. 1992 Apr 20;224(4):967–979. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90463-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzy-Tréboul G., Zagorec M., Rain-Guion M. C., Steinmetz M. Phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system of Bacillus subtilis: nucleotide sequence of ptsX, ptsH and the 5'-end of ptsI and evidence for a ptsHI operon. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jan;3(1):103–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandoni J. A., Zahler S. A., Calvo J. M. Transcriptional regulation of the ilv-leu operon of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3212–3219. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3212-3219.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves M. C., Rabinowitz J. C. In vivo and in vitro transcription of the Clostridium pasteurianum ferredoxin gene. Evidence for "extended" promoter elements in gram-positive organisms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11409–11415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. J., Vold B. S. A cluster of nine tRNA genes between ribosomal gene operons in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3147–3151. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3147-3151.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy F. J., Henkin T. M. Cloning and analysis of the Bacillus subtilis rpsD gene, encoding ribosomal protein S4. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6372–6379. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6372-6379.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy F. J., Turinsky A. J., Henkin T. M. Catabolite regulation of Bacillus subtilis acetate and acetoin utilization genes by CcpA. J Bacteriol. 1994 Aug;176(15):4527–4533. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.15.4527-4533.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy F. J., Waters D. A., Allen S. H., Henkin T. M. Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis acetate kinase gene by CcpA. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(22):7348–7355. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.22.7348-7355.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn J., Inamine G., Kozlov Y., Dubnau D. Characterization of comE, a late competence operon of Bacillus subtilis required for the binding and uptake of transforming DNA. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Oct;10(1):99–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harry E. J., Rowland S. L., Malo M. S., Wake R. G. Expression of divIB of Bacillus subtilis during vegetative growth. J Bacteriol. 1994 Feb;176(4):1172–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.4.1172-1179.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemilä H., Palva A., Paulin L., Arvidson S., Palva I. Secretory S complex of Bacillus subtilis: sequence analysis and identity to pyruvate dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5052–5063. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5052-5063.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkin T. M., Glass B. L., Grundy F. J. Analysis of the Bacillus subtilis tyrS gene: conservation of a regulatory sequence in multiple tRNA synthetase genes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1299–1306. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1299-1306.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkin T. M., Grundy F. J., Nicholson W. L., Chambliss G. H. Catabolite repression of alpha-amylase gene expression in Bacillus subtilis involves a trans-acting gene product homologous to the Escherichia coli lacl and galR repressors. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):575–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkin T. M., Moon S. H., Mattheakis L. C., Nomura M. Cloning and analysis of the spc ribosomal protein operon of Bacillus subtilis: comparison with the spc operon of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7469–7486. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkin T. M., Sonenshein A. L. Mutations of the Escherichia coli lacUV5 promoter resulting in increased expression in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):467–474. doi: 10.1007/BF00331151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner D. J., Ferrari E., Perego M., Hoch J. A. Location of the targets of the hpr-97, sacU32(Hy), and sacQ36(Hy) mutations in upstream regions of the subtilisin promoter. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):296–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.296-300.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrler M., Bang H., Marahiel M. A. Cloning and characterization of ppiB, a Bacillus subtilis gene which encodes a cyclosporin A-sensitive peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Mar;11(6):1073–1083. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg C., Beijer L., Rutberg B., Rutberg L. Glycerol catabolism in Bacillus subtilis: nucleotide sequence of the genes encoding glycerol kinase (glpK) and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (glpD). J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Dec;136(12):2367–2375. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-12-2367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg C., Rutberg B. Expression of the gene encoding glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (glpD) in Bacillus subtilis is controlled by antitermination. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Dec;5(12):2891–2900. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda K., Nakamura K., Nishiguchi M., Yamane K. Cloning and characterization of a Bacillus subtilis gene encoding a homolog of the 54-kilodalton subunit of mammalian signal recognition particle and Escherichia coli Ffh. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(15):4885–4894. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.15.4885-4894.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeyman A. L., Stewart G. C. The nucleotide sequence of the rodC operon of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1257–1268. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino T., McKenzie T., Schmidt S., Tanaka T., Sueoka N. Nucleotide sequence of Bacillus subtilis dnaB: a gene essential for DNA replication initiation and membrane attachment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hove-Jensen B. Identification of tms-26 as an allele of the gcaD gene, which encodes N-acetylglucosamine 1-phosphate uridyltransferase in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(21):6852–6856. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.21.6852-6856.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulett F. M., Lee J., Shi L., Sun G., Chesnut R., Sharkova E., Duggan M. F., Kapp N. Sequential action of two-component genetic switches regulates the PHO regulon in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(5):1348–1358. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.5.1348-1358.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwakura M., Kawata M., Tsuda K., Tanaka T. Nucleotide sequence of the thymidylate synthase B and dihydrofolate reductase genes contained in one Bacillus subtilis operon. Gene. 1988 Apr 15;64(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis E. D., Cheng S., Rudner R. Genetic structure and DNA sequences at junctions involved in the rearrangements of Bacillus subtilis strains carrying the trpE26 mutation. Genetics. 1990 Dec;126(4):785–797. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S., Sonenshein A. L. Transcriptional regulation of Bacillus subtilis citrate synthase genes. J Bacteriol. 1994 Aug;176(15):4680–4690. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.15.4680-4690.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer W., Deuschle U., Gentz R., Bujard H. Functional dissection of Escherichia coli promoters: information in the transcribed region is involved in late steps of the overall process. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2995–3000. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapfer W., Walter J., Trautner T. A. Cloning, characterization and evolution of the BsuFI restriction endonuclease gene of Bacillus subtilis and purification of the enzyme. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6457–6463. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keilty S., Rosenberg M. Constitutive function of a positively regulated promoter reveals new sequences essential for activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6389–6395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney T. J., York K., Youngman P., Moran C. P., Jr Genetic evidence that RNA polymerase associated with sigma A factor uses a sporulation-specific promoter in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9109–9113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kil Y. V., Mironov V. N., Gorishin IYu, Kreneva R. A., Perumov D. A. Riboflavin operon of Bacillus subtilis: unusual symmetric arrangement of the regulatory region. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jun;233(3):483–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00265448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch M. L., Zuberi A. R., Henner D., Peters P. D., Yazdi M. A., Ordal G. W. Chemotactic methyltransferase promotes adaptation to repellents in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25350–25356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus R., Bujard H. PL of coliphage lambda: an alternative solution for an efficient promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2919–2923. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03150.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide A., Hoch J. A. Identification of a second oligopeptide transport system in Bacillus subtilis and determination of its role in sporulation. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Aug;13(3):417–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong L., Siranosian K. J., Grossman A. D., Dubnau D. Sequence and properties of mecA, a negative regulator of genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jul;9(2):365–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer P., Gärtner D., Allmansberger R., Hillen W. Identification and sequence analysis of the Bacillus subtilis W23 xylR gene and xyl operator. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3840–3845. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3840-3845.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavigne M., Herbert M., Kolb A., Buc H. Upstream curved sequences influence the initiation of transcription at the Escherichia coli galactose operon. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 20;224(2):293–306. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90995-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Grice S. F., Sonenshein A. L. Interaction of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase with a chromosomal promoter. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 15;162(3):551–564. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90388-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDeaux J. R., Grossman A. D. Isolation and characterization of kinC, a gene that encodes a sensor kinase homologous to the sporulation sensor kinases KinA and KinB in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1995 Jan;177(1):166–175. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.1.166-175.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Pero J. Conserved nucleotide sequences in temporally controlled bacteriophage promoters. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 25;152(2):247–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Talkington C., Pero J. Nucleotide sequence of a promoter recognized by Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(1):57–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00267352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., Wong S. L. Cloning and characterization of the groESL operon from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):3981–3992. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.3981-3992.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisser S., Margalit H. Compilation of E. coli mRNA promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 11;21(7):1507–1516. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.7.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisser S., Margalit H. Determination of common structural features in Escherichia coli promoters by computer analysis. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Aug 1;223(3):823–830. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb19058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londoño-Vallejo J. A., Dubnau D. comF, a Bacillus subtilis late competence locus, encodes a protein similar to ATP-dependent RNA/DNA helicases. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jul;9(1):119–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay R. M., Lo A., Willick G., Zuker M., Baird S., Dove M., Moranelli F., Seligy V. Structure of a Bacillus subtilis endo-beta-1,4-glucanase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9159–9170. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matern H. T., Klein J. R., Henrich B., Plapp R. Determination and comparison of Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. lactis DSM7290 promoter sequences. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1994 Sep 15;122(1-2):121–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1994.tb07154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauël C., Young M., Karamata D. Genes concerned with synthesis of poly(glycerol phosphate), the essential teichoic acid in Bacillus subtilis strain 168, are organized in two divergent transcription units. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Apr;137(4):929–941. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-4-929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister C. F., Achberger E. C. Effect of polyadenine-containing curved DNA on promoter utilization in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11743–11749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister C. F., Achberger E. C. Rotational orientation of upstream curved DNA affects promoter function in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10451–10456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Mechanism and control of transcription initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:171–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., von Hippel P. H. Theoretical aspects of DNA-protein interactions: co-operative and non-co-operative binding of large ligands to a one-dimensional homogeneous lattice. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):469–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melin L., Rutberg L., von Gabain A. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of the Bacillus subtilis succinate dehydrogenase operon. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2110–2115. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2110-2115.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellado R. P., Barthelemy I., Salas M. In vitro transcription of bacteriophage phi 29 DNA. Correlation between in vitro and in vivo promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4731–4741. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micka B., Groch N., Heinemann U., Marahiel M. A. Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and characterization of the Bacillus subtilis gene encoding the DNA-binding protein HBsu. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(10):3191–3198. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.10.3191-3198.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan S., Aghion J., Guillen N., Dubnau D. Molecular cloning and characterization of comC, a late competence gene of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6043–6051. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6043-6051.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan S., Dubnau D. Transcriptional regulation of comC: evidence for a competence-specific transcription factor in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4064–4071. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4064-4071.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriya S., Fukuoka T., Ogasawara N., Yoshikawa H. Regulation of initiation of the chromosomal replication by DnaA-boxes in the origin region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2911–2917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03149.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriya S., Ogasawara N., Yoshikawa H. Structure and function of the region of the replication origin of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. III. Nucleotide sequence of some 10,000 base pairs in the origin region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2251–2265. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morohoshi F., Hayashi K., Munakata N. Bacillus subtilis gene coding for constitutive O6-methylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6531–6543. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morohoshi F., Hayashi K., Munkata N. Bacillus subtilis alkA gene encoding inducible 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylase is adjacent to the ada operon. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(18):6010–6017. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.18.6010-6017.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Msadek T., Kunst F., Henner D., Klier A., Rapoport G., Dedonder R. Signal transduction pathway controlling synthesis of a class of degradative enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: expression of the regulatory genes and analysis of mutations in degS and degU. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):824–834. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.824-834.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller J. P., Bukusoglu G., Sonenshein A. L. Transcriptional regulation of Bacillus subtilis glucose starvation-inducible genes: control of gsiA by the ComP-ComA signal transduction system. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4361–4373. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4361-4373.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller J. P., Taber H. W. Structure and expression of the cytochrome aa3 regulatory gene ctaA of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4979–4986. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4979-4986.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Hawley D. K., Entriken R., McClure W. R. Escherichia coli promoter sequences predict in vitro RNA polymerase selectivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):789–800. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Nucleotide sequences of transcription and translation initiation regions in Bacillus phage phi 29 early genes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):1053–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäntsälä P., Zalkin H. Cloning and sequence of Bacillus subtilis purA and guaA, involved in the conversion of IMP to AMP and GMP. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1883–1890. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1883-1890.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M. M., Xia L. A., Zuber P. Transcription initiation region of the srfA operon, which is controlled by the comP-comA signal transduction system in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5487–5493. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5487-5493.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M. M., Yang F., Hardin P., Zuber P. Nitrogen regulation of nasA and the nasB operon, which encode genes required for nitrate assimilation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1995 Feb;177(3):573–579. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.3.573-579.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasser W., Awadé A. C., Reverchon S., Robert-Baudouy J. Pectate lyase from Bacillus subtilis: molecular characterization of the gene, and properties of the cloned enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 13;335(3):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80410-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyfakh A. A., Bidnenko V. E., Chen L. B. Efflux-mediated multidrug resistance in Bacillus subtilis: similarities and dissimilarities with the mammalian system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4781–4785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson W. L., Park Y. K., Henkin T. M., Won M., Weickert M. J., Gaskell J. A., Chambliss G. H. Catabolite repression-resistant mutations of the Bacillus subtilis alpha-amylase promoter affect transcription levels and are in an operator-like sequence. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 20;198(4):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson D., Hove-Jensen B., Arnvig K. Primary structure of the tms and prs genes of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Sep;218(3):565–571. doi: 10.1007/BF00332425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson R. P., Beijer L., Rutberg B. The glpT and glpQ genes of the glycerol regulon in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology. 1994 Apr;140(Pt 4):723–730. doi: 10.1099/00221287-140-4-723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill M. C. Escherichia coli promoters. I. Consensus as it relates to spacing class, specificity, repeat substructure, and three-dimensional organization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5522–5530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly M., Woodson K., Dowds B. C., Devine K. M. The citrulline biosynthetic operon, argC-F, and a ribose transport operon, rbs, from Bacillus subtilis are negatively regulated by Spo0A. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Jan;11(1):87–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N., Moriya S., Mazza P. G., Yoshikawa H. Nucleotide sequence and organization of dnaB gene and neighbouring genes on the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9989–9999. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N., Moriya S., Yoshikawa H. Structure and function of the region of the replication origin of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. IV. Transcription of the oriC region and expression of DNA gyrase genes and other open reading frames. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2267–2279. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N., Moriya S., Yoshikawa H. Structure and organization of rRNA operons in the region of the replication origin of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6301–6318. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N., Moriya S., von Meyenburg K., Hansen F. G., Yoshikawa H. Conservation of genes and their organization in the chromosomal replication origin region of Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3345–3350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N., Nakai S., Yoshikawa H. Systematic sequencing of the 180 kilobase region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome containing the replication origin. DNA Res. 1994;1(1):1–14. doi: 10.1093/dnares/1.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmiya K., Tanaka T., Noguchi N., O'Hara K., Kono M. Nucleotide sequence of the chromosomal gene coding for the aminoglycoside 6-adenylyltransferase from Bacillus subtilis Marburg 168. Gene. 1989 May 30;78(2):377–378. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Matsuzaki H., Shibuya I., Matsumoto K. Cloning, sequencing, and expression in Escherichia coli of the Bacillus subtilis gene for phosphatidylserine synthase. J Bacteriol. 1994 Dec;176(24):7456–7461. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.24.7456-7461.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osburne M. S., Craig R. J. Activity of two strong promoters cloned into Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Feb;132(2):565–568. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-2-565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osburne M. S., Craig R. J., Rothstein D. M. Thermoinducible transcription system for Bacillus subtilis that utilizes control elements from temperate phage phi 105. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1101–1108. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1101-1108.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang A. S., Nathoo S., Wong S. L. Cloning and characterization of a pair of novel genes that regulate production of extracellular enzymes in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):46–54. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.46-54.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S. H., Kim H. K., Pack M. Y. Characterization and structure of the cellulase gene of Bacillus subtilis BSE616. Agric Biol Chem. 1991 Feb;55(2):441–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsot C., Cohen G. N. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis hom gene coding for homoserine dehydrogenase. Structural and evolutionary relationships with Escherichia coli aspartokinases-homoserine dehydrogenases I and II. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14654–14660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego M., Hoch J. A. Negative regulation of Bacillus subtilis sporulation by the spo0E gene product. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2514–2520. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2514-2520.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego M., Spiegelman G. B., Hoch J. A. Structure of the gene for the transition state regulator, abrB: regulator synthesis is controlled by the spo0A sporulation gene in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):689–699. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peticolas W. L., Wang Y., Thomas G. A. Some rules for predicting the base-sequence dependence of DNA conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2579–2583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petricek M., Rutberg L., Schröder I., Hederstedt L. Cloning and characterization of the hemA region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2250–2258. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2250-2258.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D. L., Setlow P. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and regulation of the Bacillus subtilis pbpE operon, which codes for penicillin-binding protein 4* and an apparent amino acid racemase. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(10):2917–2925. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.10.2917-2925.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D. L., Setlow P. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and regulation of the Bacillus subtilis pbpF gene, which codes for a putative class A high-molecular-weight penicillin-binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(15):4870–4876. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.15.4870-4876.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D. L., Setlow P. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, mutagenesis, and mapping of the Bacillus subtilis pbpD gene, which codes for penicillin-binding protein 4. J Bacteriol. 1994 Dec;176(23):7197–7205. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.23.7197-7205.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putzer H., Gendron N., Grunberg-Manago M. Co-ordinate expression of the two threonyl-tRNA synthetase genes in Bacillus subtilis: control by transcriptional antitermination involving a conserved regulatory sequence. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3117–3127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05384.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Martín J., Rojo F., de Lorenzo V. Promoters responsive to DNA bending: a common theme in prokaryotic gene expression. Microbiol Rev. 1994 Jun;58(2):268–290. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.2.268-290.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn C. L., Stephenson B. T., Switzer R. L. Functional organization and nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis pyrimidine biosynthetic operon. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9113–9127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L., Ross W., Appleman J. A., Gaal T., Leirmo S., Schlax P. J., Record M. T., Jr, Gourse R. L. Factor independent activation of rrnB P1. An "extended" promoter with an upstream element that dramatically increases promoter strength. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 4;235(5):1421–1435. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond-Denise A., Guillen N. Identification of dinR, a DNA damage-inducible regulator gene of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7084–7091. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7084-7091.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renna M. C., Najimudin N., Winik L. R., Zahler S. A. Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis alsS, alsD, and alsR genes involved in post-exponential-phase production of acetoin. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(12):3863–3875. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.12.3863-3875.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnekov O., Melin L., Carlsson P., Mannerlöv M., von Gabain A., Hederstedt L. Organization and regulation of the Bacillus subtilis odhAB operon, which encodes two of the subenzymes of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Aug;234(2):285–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00283849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riethdorf S., Völker U., Gerth U., Winkler A., Engelmann S., Hecker M. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the Bacillus subtilis lon gene. J Bacteriol. 1994 Nov;176(21):6518–6527. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.21.6518-6527.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson L. M., Chambliss G. H. Endo-beta-1,4-glucanase gene of Bacillus subtilis DLG. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2017–2025. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2017-2025.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo F., Nuez B., Mencía M., Salas M. The main early and late promoters of Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29 form unstable open complexes with sigma A-RNA polymerase that are stabilized by DNA supercoiling. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 25;21(4):935–940. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.4.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Gosink K. K., Salomon J., Igarashi K., Zou C., Ishihama A., Severinov K., Gourse R. L. A third recognition element in bacterial promoters: DNA binding by the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1407–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.8248780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudner D. Z., LeDeaux J. R., Ireton K., Grossman A. D. The spo0K locus of Bacillus subtilis is homologous to the oligopeptide permease locus and is required for sporulation and competence. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1388–1398. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1388-1398.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadaie Y., Takamatsu H., Nakamura K., Yamane K. Sequencing reveals similarity of the wild-type div+ gene of Bacillus subtilis to the Escherichia coli secA gene. Gene. 1991 Feb 1;98(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90110-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi R., Amano H., Shishido K. Nucleotide sequence homology of the tetracycline-resistance determinant naturally maintained in Bacillus subtilis Marburg 168 chromosome and the tetracycline-resistance gene of B. subtilis plasmid pNS1981. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 7;950(3):441–444. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90142-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarai A., Mazur J., Nussinov R., Jernigan R. L. Origin of DNA helical structure and its sequence dependence. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 1;27(22):8498–8502. doi: 10.1021/bi00422a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Hantke K. Iron-hydroxamate uptake systems in Bacillus subtilis: identification of a lipoprotein as part of a binding protein-dependent transport system. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Apr;8(1):111–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki T., Yoshikawa H., Takahashi H., Saito H. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of phoP, the regulatory gene for alkaline phosphatase and phosphodiesterase in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):2913–2916. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.2913-2916.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shazand K., Tucker J., Grunberg-Manago M., Rabinowitz J. C., Leighton T. Similar organization of the nusA-infB operon in Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(10):2880–2887. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.10.2880-2887.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotsu H., Henner D. J. Characterization of the Bacillus subtilis tryptophan promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6315–6319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotsu H., Henner D. J. Modulation of Bacillus subtilis levansucrase gene expression by sucrose and regulation of the steady-state mRNA level by sacU and sacQ genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):380–388. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.380-388.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siranosian K. J., Ireton K., Grossman A. D. Alanine dehydrogenase (ald) is required for normal sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):6789–6796. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.6789-6796.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack F. J., Mueller J. P., Strauch M. A., Mathiopoulos C., Sonenshein A. L. Transcriptional regulation of a Bacillus subtilis dipeptide transport operon. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1915–1925. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slock J., Stahly D. P., Han C. Y., Six E. W., Crawford I. P. An apparent Bacillus subtilis folic acid biosynthetic operon containing pab, an amphibolic trpG gene, a third gene required for synthesis of para-aminobenzoic acid, and the dihydropteroate synthase gene. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7211–7226. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7211-7226.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. C., Mountain A., Baumberg S. Sequence analysis of the Bacillus subtilis argC promoter region. Gene. 1986;49(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song B. H., Neuhard J. Chromosomal location, cloning and nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis cdd gene encoding cytidine/deoxycytidine deaminase. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Apr;216(2-3):462–468. doi: 10.1007/BF00334391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin A., Zumstein E., Azevedo V., Ehrlich S. D., Serror P. The organization of the Bacillus subtilis 168 chromosome region between the spoVA and serA genetic loci, based on sequence data. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Oct;10(2):385–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb02670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. C., Bott K. F. DNA sequence of the tandem ribosomal RNA promoter for B. subtilis operon rrnB. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6289–6300. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M. A., Aronson A. I., Brown S. W., Schreier H. J., Sonenhein A. L. Sequence of the Bacillus subtilis glutamine synthetase gene region. Gene. 1988 Nov 30;71(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M. A., Ayazifar M. Bent DNA is found in some, but not all, regions recognized by the Bacillus subtilis AbrB protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1995 Mar 20;246(6):756–760. doi: 10.1007/BF00290723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck J. C., Far R. K., Schröder W., Hucho F., Toschka H. Y., Erdmann V. A. Characterization of a 17 kDa protein gene upstream from the small cytoplasmic RNA gene of Bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):80–83. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90145-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck J. C., Vogel D. W., Ulbrich N., Erdmann V. A. A dnaZX-like open reading frame downstream from the Bacillus subtilis scRNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2720–2720. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck J. C., Vogel D. W., Ulbrich N., Erdmann V. A. The Bacillus subtilis scRNA is related to the 4.5S RNA from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2719–2719. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D. X., Setlow P. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the Bacillus subtilis ans operon, which codes for L-asparaginase and L-aspartase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3831–3845. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3831-3845.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D., Setlow P. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis ansR gene, which encodes a repressor of the ans operon coding for L-asparaginase and L-aspartase. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2501–2506. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2501-2506.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D., Setlow P. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and regulation of the Bacillus subtilis nadB gene and a nifS-like gene, both of which are essential for NAD biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(5):1423–1432. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.5.1423-1432.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tailor R., Bensi G., Morelli G., Canosi U., Trautner T. A. The genome of Bacillus subtilis phage SPP1: structure of an early promoter. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 May;131(5):1259–1262. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-5-1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trach K., Chapman J. W., Piggot P., LeCoq D., Hoch J. A. Complete sequence and transcriptional analysis of the spo0F region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4194–4208. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4194-4208.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trach K., Hoch J. A. The Bacillus subtilis spo0B stage 0 sporulation operon encodes an essential GTP-binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1362–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1362-1371.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran L., Wu X. C., Wong S. L. Cloning and expression of a novel protease gene encoding an extracellular neutral protease from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6364–6372. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6364-6372.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. Structure and function of E. coli promoter DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1987;22(3):181–219. doi: 10.3109/10409238709101483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander Horn P. B., Zahler S. A. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the leucyl-tRNA synthetase gene of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):3928–3935. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.3928-3935.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter J., Noyer-Weidner M., Trautner T. A. The amino acid sequence of the CCGG recognizing DNA methyltransferase M.BsuFI: implications for the analysis of sequence recognition by cytosine DNA methyltransferases. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1007–1013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08203.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. F., Doi R. H. Complex character of senS, a novel gene regulating expression of extracellular-protein genes of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1939–1947. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1939-1947.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. F., Doi R. H. Promoter switching during development and the termination site of the sigma 43 operon of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):114–119. doi: 10.1007/BF00331498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. Z., Doi R. H. Overlapping promoters transcribed by bacillus subtilis sigma 55 and sigma 37 RNA polymerase holoenzymes during growth and stationary phases. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8619–8625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrauch Y., Guillen N., Dubnau D. A. Sequence and transcription mapping of Bacillus subtilis competence genes comB and comA, one of which is related to a family of bacterial regulatory determinants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5362–5375. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5362-5375.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrauch Y., Msadek T., Kunst F., Dubnau D. Sequence and properties of comQ, a new competence regulatory gene of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5685–5693. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5685-5693.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J., Predich M., Dubnau E., Nair G., Smith I. Regulation of spo0H, a gene coding for the Bacillus subtilis sigma H factor. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):521–529. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.521-529.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzstein M., Schumann W. Nucleotide sequence of a Bacillus subtilis gene homologous to the grpE gene of E. coli located immediately upstream of the dnaK gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1289–1289. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzstein M., Völker U., Dedio J., Löbau S., Zuber U., Schiesswohl M., Herget C., Hecker M., Schumann W. Cloning, sequencing, and molecular analysis of the dnaK locus from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3300–3310. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3300-3310.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipple F. W., Sonenshein A. L. Mechanism of initiation of transcription by Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase at several promoters. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 20;223(2):399–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90660-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggs J. L., Bush J. W., Chamberlin M. J. Utilization of promoter and terminator sites on bacteriophage T7 DNA by RNA polymerases from a variety of bacterial orders. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willimsky G., Bang H., Fischer G., Marahiel M. A. Characterization of cspB, a Bacillus subtilis inducible cold shock gene affecting cell viability at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6326–6335. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6326-6335.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise A. A., Price C. W. Four additional genes in the sigB operon of Bacillus subtilis that control activity of the general stress factor sigma B in response to environmental signals. J Bacteriol. 1995 Jan;177(1):123–133. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.1.123-133.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray L. V., Jr, Atkinson M. R., Fisher S. H. The nitrogen-regulated Bacillus subtilis nrgAB operon encodes a membrane protein and a protein highly similar to the Escherichia coli glnB-encoded PII protein. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jan;176(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.1.108-114.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray L. V., Jr, Fisher S. H. Analysis of Bacillus subtilis hut operon expression indicates that histidine-dependent induction is mediated primarily by transcriptional antitermination and that amino acid repression is mediated by two mechanisms: regulation of transcription initiation and inhibition of histidine transport. J Bacteriol. 1994 Sep;176(17):5466–5473. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.17.5466-5473.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. L., Kapfer W., Walter J., Trautner T. A. BsuBI--an isospecific restriction and modification system of PstI: characterization of the BsuBI genes and enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6517–6523. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto J., Shimizu M., Yamane K. Nucleotide sequence of the diaminopimelate-decarboxylase gene from Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):10105–10105. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.10105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M., Ferrari E., Chen E., Henner D. J. Identification of the pleiotropic sacQ gene of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):113–119. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.113-119.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye R., Wong S. L. Transcriptional regulation of the Bacillus subtilis glucitol dehydrogenase gene. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jun;176(11):3314–3320. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.11.3314-3320.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- York K., Kenney T. J., Satola S., Moran C. P., Jr, Poth H., Youngman P. Spo0A controls the sigma A-dependent activation of Bacillus subtilis sporulation-specific transcription unit spoIIE. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2648–2658. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2648-2658.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijl J. M., de Jong A., Vehmaanperä J., Venema G., Bron S. Signal peptidase I of Bacillus subtilis: patterns of conserved amino acids in prokaryotic and eukaryotic type I signal peptidases. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2819–2828. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05349.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Sinderen D., Kiewiet R., Venema G. Differential expression of two closely related deoxyribonuclease genes, nucA and nucB, in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Jan;15(2):213–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Sinderen D., ten Berge A., Hayema B. J., Hamoen L., Venema G. Molecular cloning and sequence of comK, a gene required for genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Feb;11(4):695–703. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wachenfeldt C., Hederstedt L. Bacillus subtilis 13-kilodalton cytochrome c-550 encoded by cccA consists of a membrane-anchor and a heme domain. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13939–13948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


