Abstract
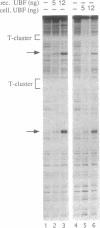
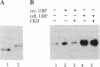
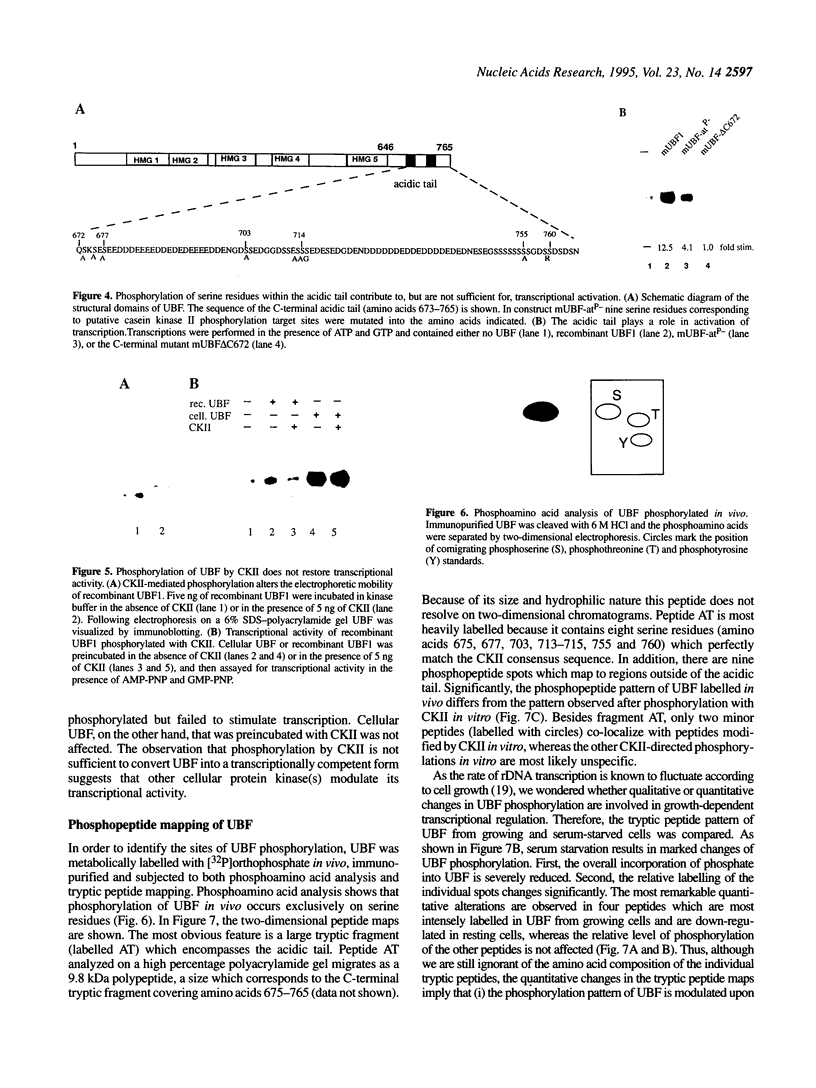
The nucleolar factor UBF is phosphorylated by casein kinase II (CKII) at serine residues within the C-terminal acidic domain which is required for transcription activation. To investigate the biological significance of UBF modification, we have compared the trans-activating properties of cellular UBF and recombinant UBF expressed in Escherichia coli. Using a variety of assays we demonstrate that unphosphorylated UBF is transcriptionally inactive and has to be phosphorylated at multiple sites to stimulate transcription. Examination of cDNA mutants in which the serine residues within the C-terminal domain were altered by site-directed mutagenesis demonstrates that CKII-mediated phosphorylations of UBF contribute to, but are not sufficient for, transcriptional activation. Besides CKII, other cellular protein kinases phosphorylate UBF at distinct sites in a growth-dependent manner. The marked differences in the tryptic peptide maps of UBF from growing and serum-starved cells suggest that alterations in the degree of UBF phosphorylation may modulate rRNA synthetic activity in response to extracellular signals.
Full text
PDF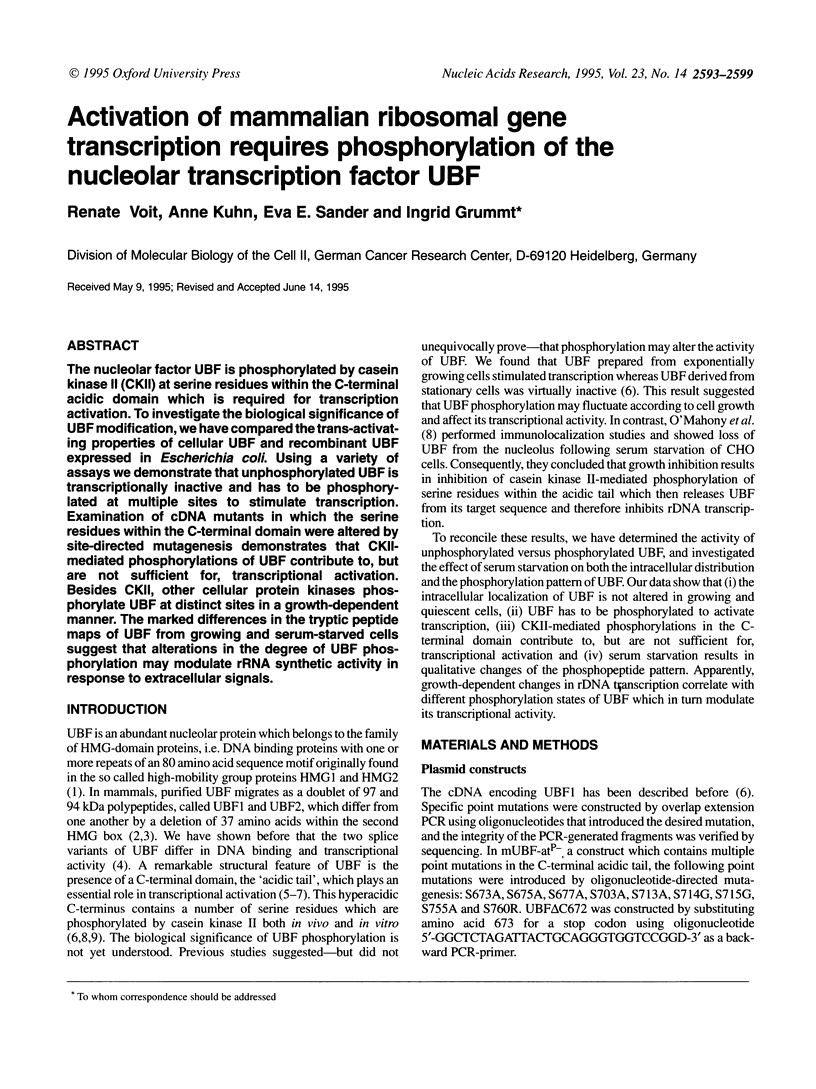





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell S. P., Learned R. M., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Functional cooperativity between transcription factors UBF1 and SL1 mediates human ribosomal RNA synthesis. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1192–1197. doi: 10.1126/science.3413483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brou C., Kuhn A., Staub A., Chaudhary S., Grummt I., Davidson I., Tora L. Sequence-specific transactivators counteract topoisomerase II-mediated inhibition of in vitro transcription by RNA polymerases I and II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 25;21(17):4011–4018. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.17.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard D., Tora L., Egly J. M., Grummt I. A TBP-containing multiprotein complex (TIF-IB) mediates transcription specificity of murine RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 11;21(18):4180–4186. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.18.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Specific transcription of mouse ribosomal DNA in a cell-free system that mimics control in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatake K., Nishimura T., Maeda Y., Hanada K., Song C. Z., Muramatsu M. Cloning and structural analysis of cDNA and the gene for mouse transcription factor UBF. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 11;19(17):4631–4637. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.17.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Chow A. M., King D. S., Tjian R. Multiple domains of the RNA polymerase I activator hUBF interact with the TATA-binding protein complex hSL1 to mediate transcription. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1950–1963. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Grummt I. Dual role of the nucleolar transcription factor UBF: trans-activator and antirepressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7340–7344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Stefanovsky V., Grummt I. The nucleolar transcription activator UBF relieves Ku antigen-mediated repression of mouse ribosomal gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 11;21(9):2057–2063. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.9.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Voit R., Stefanovsky V., Evers R., Bianchi M., Grummt I. Functional differences between the two splice variants of the nucleolar transcription factor UBF: the second HMG box determines specificity of DNA binding and transcriptional activity. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 15;13(2):416–424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon H., Green M. R. The RNA polymerase I transcription factor, upstream binding factor, interacts directly with the TATA box-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30140–30146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Frazier M. W., Reeder R. H. xUBF contains a novel dimerization domain essential for RNA polymerase I transcription. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1957–1968. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Rothblum L. I. Identification of two forms of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor UBF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Smith S. D., Xie W., Rothblum L. I. Analysis of the phosphorylation, DNA-binding and dimerization properties of the RNA polymerase I transcription factors UBF1 and UBF2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1301–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony D. J., Xie W. Q., Smith S. D., Singer H. A., Rothblum L. I. Differential phosphorylation and localization of the transcription factor UBF in vivo in response to serum deprivation. In vitro dephosphorylation of UBF reduces its transactivation properties. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):35–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel P., André C., Masson C., Géraud G., Hernandez-Verdun D. Localization of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor hUBF during the cell cycle. J Cell Sci. 1993 Feb;104(Pt 2):327–337. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.2.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp A., Grummt I. Transcription complex formation at the mouse rDNA promoter involves the stepwise association of four transcription factors and RNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24588–24595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp G., Santori F., Carles C., Riva M., Grummt I. The HMG box-containing nucleolar transcription factor UBF interacts with a specific subunit of RNA polymerase I. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):190–199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voit R., Schnapp A., Kuhn A., Rosenbauer H., Hirschmann P., Stunnenberg H. G., Grummt I. The nucleolar transcription factor mUBF is phosphorylated by casein kinase II in the C-terminal hyperacidic tail which is essential for transactivation. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2211–2218. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatsepina O. V., Voit R., Grummt I., Spring H., Semenov M. V., Trendelenburg M. F. The RNA polymerase I-specific transcription initiation factor UBF is associated with transcriptionally active and inactive ribosomal genes. Chromosoma. 1993 Nov;102(9):599–611. doi: 10.1007/BF00352307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]