Abstract
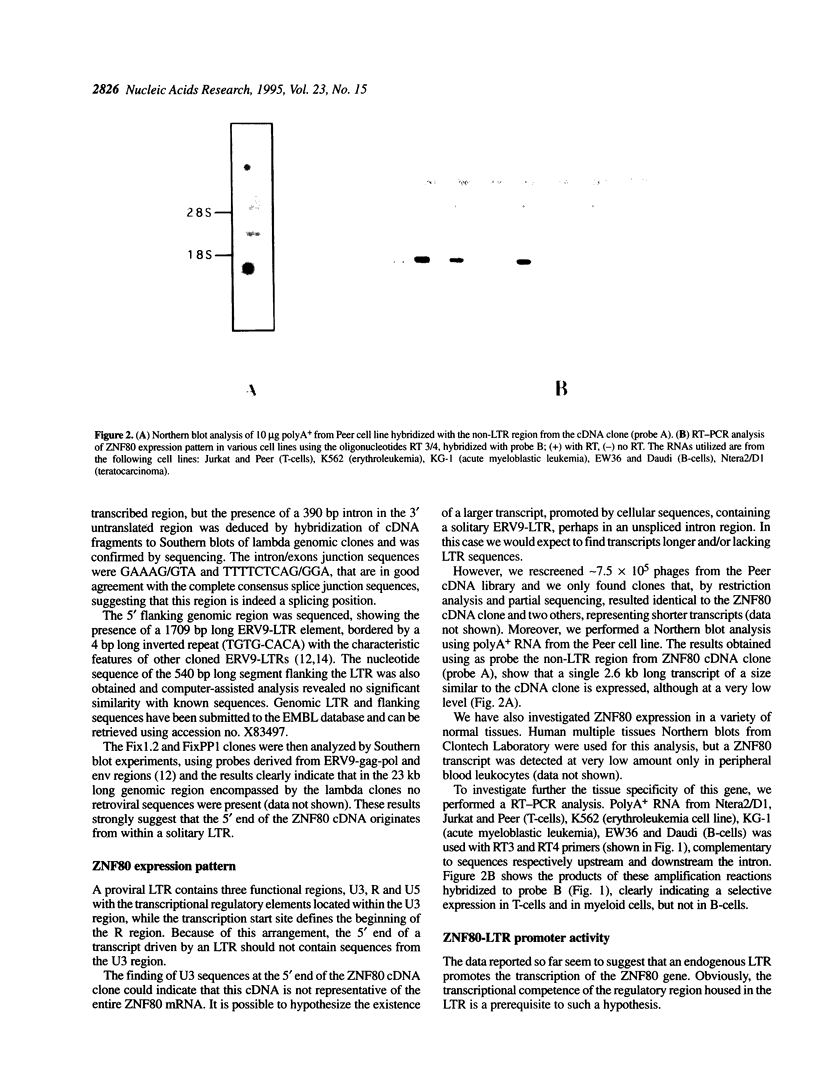
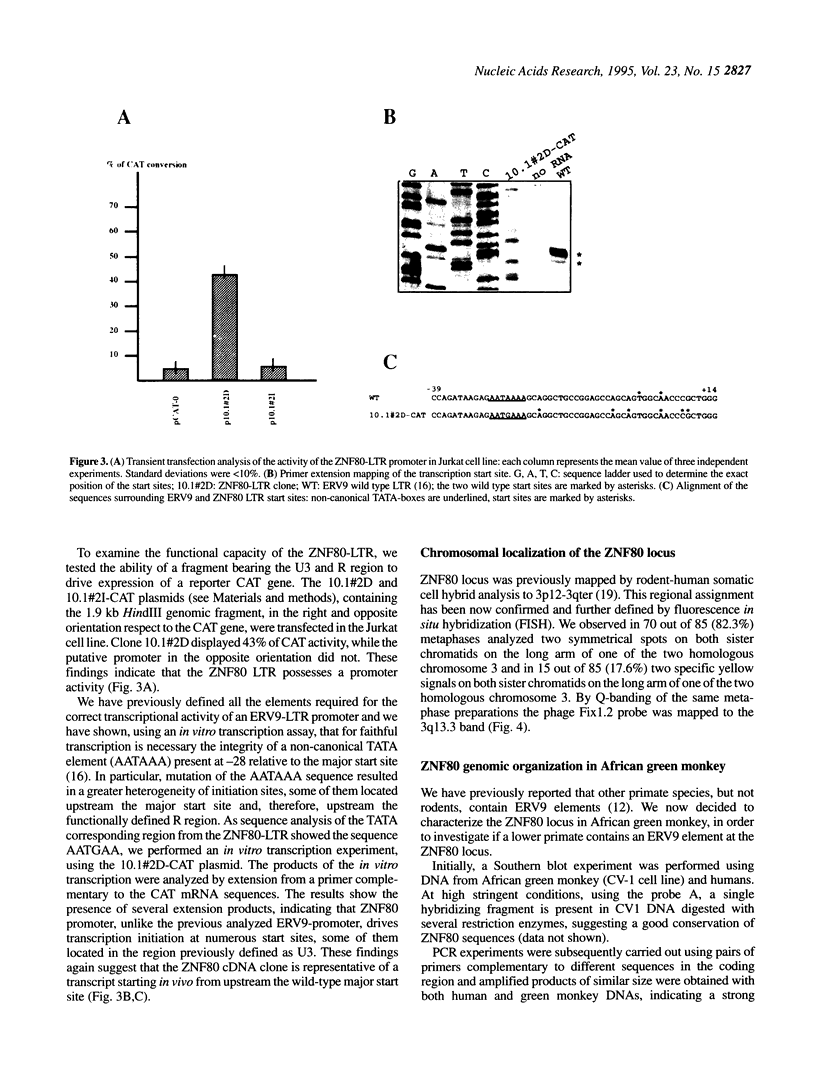
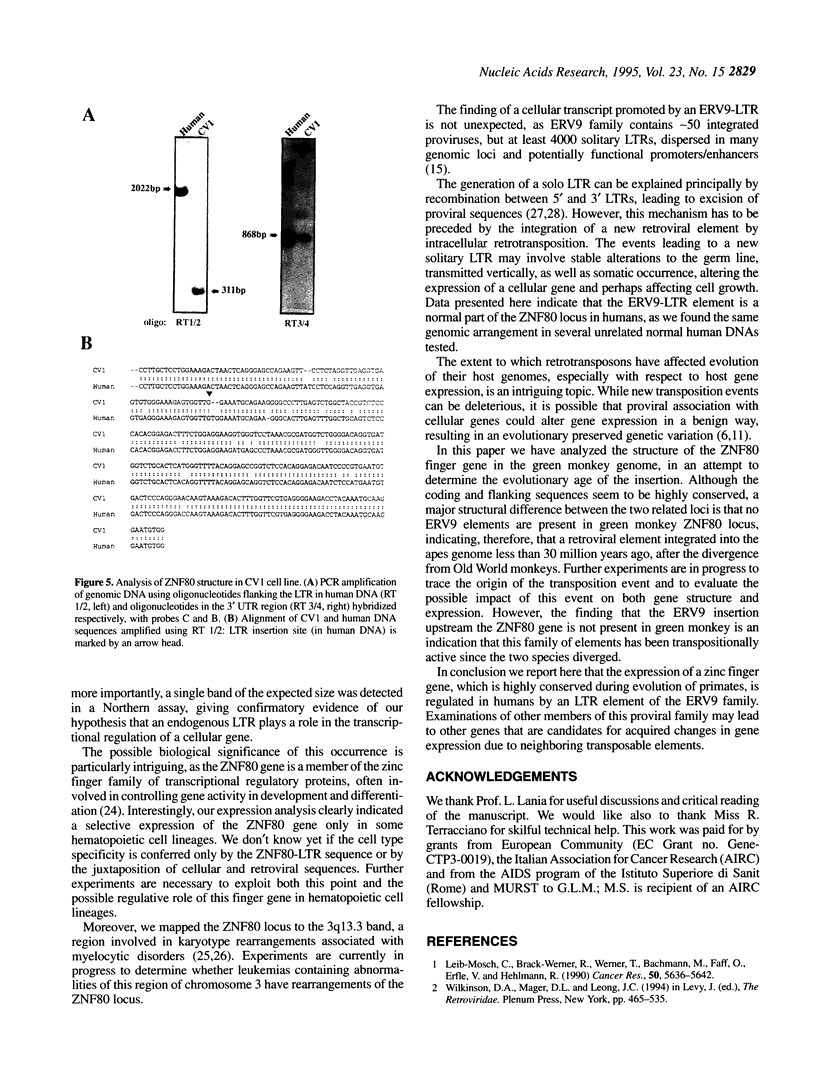
ERV9 is a low repeated family of human endogenous retroviral elements, which has close to 50 members, in addition to at least 4000 solitary LTRs. Previous work has shown that randomly selected LTRs can promote transcription of reporter genes, raising the possibility that these sequences may affect the expression of adjacent cellular genes. We describe here the structure of the ZNF80 cDNA clone putatively coding for a zinc-finger protein, whose 5' terminus starts from within an ERV9-LTR. Characterization of the single copy genomic locus indicates that a complete ERV9-LTR element is present upstream of the ZNF80 coding region and that this element acts as a functional promoter in both in vivo and in vitro experiments. A 2.6 kb long transcript is selectively expressed only in some hematopoietic cell lineages. Interestingly we mapped the ZNF80 locus to the 3q13.3 band, a region involved in karyotype rearrangements associated with myelocytic disorders. We have also analyzed the ZNF80 genomic organization in African green monkey and we show that this lower primate does not harbour an ERV9 element at this locus. Our findings strongly suggest that the expression of a zinc finger gene, which is highly conserved during evolution of primates, is regulated in humans by an LTR element of the ERV9 family.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bessler M., Hillmen P., Longo L., Luzzatto L., Mason P. J. Genomic organization of the X-linked gene (PIG-A) that is mutated in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria and of a related autosomal pseudogene mapped to 12q21. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 May;3(5):751–757. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.5.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billström R., Heim S., Kristoffersson U., Mandahl N., Mitelman F. Structural chromosomal abnormalities of 3q in myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukaemia with Sweet's syndrome. Eur J Haematol. 1990 Sep;45(3):150–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1990.tb00442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuchter-Murthy A. E., Freeman J. D., Mager D. L. Splicing of a human endogenous retrovirus to a novel phospholipase A2 related gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 11;21(1):135–143. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuchter A. E., Freeman J. D., Mager D. L. Strategy for detecting cellular transcripts promoted by human endogenous long terminal repeats: identification of a novel gene (CDC4L) with homology to yeast CDC4. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1237–1246. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90041-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild N. L., Wilkinson D. A., Mager D. L. A human endogenous long terminal repeat provides a polyadenylation signal to a novel, alternatively spliced transcript in normal placenta. Gene. 1992 Nov 16;121(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90133-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner K., Druck T., LaForgia S., Lasota J., Croce C. M., Lanfrancone L., Donti E., Pengue G., La Mantia G., Pelicci P. G. Chromosomal localization of four human zinc finger cDNAs. Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;91(3):217–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00218259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Shimotohno K., VanLeeuwen D., Cohen M. Human proviral mRNAs down regulated in choriocarcinoma encode a zinc finger protein related to Krüppel. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4401–4405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kongsuwan K., Allen J., Adams J. M. Expression of Hox-2.4 homeobox gene directed by proviral insertion in a myeloid leukemia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1881–1892. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Mantia G., Maglione D., Pengue G., Di Cristofano A., Simeone A., Lanfrancone L., Lania L. Identification and characterization of novel human endogenous retroviral sequences prefentially expressed in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1513–1520. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Mantia G., Majello B., Di Cristofano A., Strazzullo M., Minchiotti G., Lania L. Identification of regulatory elements within the minimal promoter region of the human endogenous ERV9 proviruses: accurate transcription initiation is controlled by an Inr-like element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4129–4136. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Mantia G., Pengue G., Maglione D., Pannuti A., Pascucci A., Lania L. Identification of new human repetitive sequences: characterization of the corresponding cDNAs and their expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):5913–5922. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.5913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lania L., Di Cristofano A., Strazzullo M., Pengue G., Majello B., La Mantia G. Structural and functional organization of the human endogenous retroviral ERV9 sequences. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):464–468. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90211-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie K. B., Lee F., Schrader J. W. Intracisternal A-type particle-mediated activations of cytokine genes in a murine myelomonocytic leukemia: generation of functional cytokine mRNAs by retroviral splicing events. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5562–5570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K., Nabel G. J. HTLV-1 transactivator induces interleukin-2 receptor expression through an NF-kappa B-like factor. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):776–778. doi: 10.1038/333776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A. Y., Abraham B. A. Subtractive cloning of a hybrid human endogenous retrovirus and calbindin gene in the prostate cell line PC3. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):4107–4110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L., Goodchild N. L. Homologous recombination between the LTRs of a human retrovirus-like element causes a 5-kb deletion in two siblings. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;45(6):848–854. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L. Polyadenylation function and sequence variability of the long terminal repeats of the human endogenous retrovirus-like family RTVL-H. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):591–599. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90570-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalová K., Bartsch O., Starý J., Jelínek J., Wiegant J., Bubanská E. Partial trisomy of 3q detected by chromosome painting in a case of juvenile chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1993 Nov;71(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(93)90203-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson K. E., Deka N., Schmid C. W., Misra R., Schindler C. W., Rush M. G., Kadyk L., Leinwand L. A transposon-like element in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):359–361. doi: 10.1038/316359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson K. E., Matera A. G., Deka N., Schmid C. W. Transcription of a human transposon-like sequence is usually directed by other promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5199–5215. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavenhagen J. B., Robins D. M. An ancient provirus has imposed androgen regulation on the adjacent mouse sex-limited protein gene. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strazzullo M., Majello B., Lania L., La Mantia G. Mutational analysis of the human endogenous ERV9 proviruses promoter region. Virology. 1994 May 1;200(2):686–695. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Hosokawa Y., Toda H., Nishikimi M., Ozawa T. Common protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking regions of human genes for cytochrome c1 and ubiquinone-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8159–8163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting C. N., Rosenberg M. P., Snow C. M., Samuelson L. C., Meisler M. H. Endogenous retroviral sequences are required for tissue-specific expression of a human salivary amylase gene. Genes Dev. 1992 Aug;6(8):1457–1465. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.8.1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ymer S., Tucker W. Q., Sanderson C. J., Hapel A. J., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Constitutive synthesis of interleukin-3 by leukaemia cell line WEHI-3B is due to retroviral insertion near the gene. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):255–258. doi: 10.1038/317255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Baradi T., Pieler T. Zinc finger proteins: what we know and what we would like to know. Mech Dev. 1991 Nov;35(3):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]