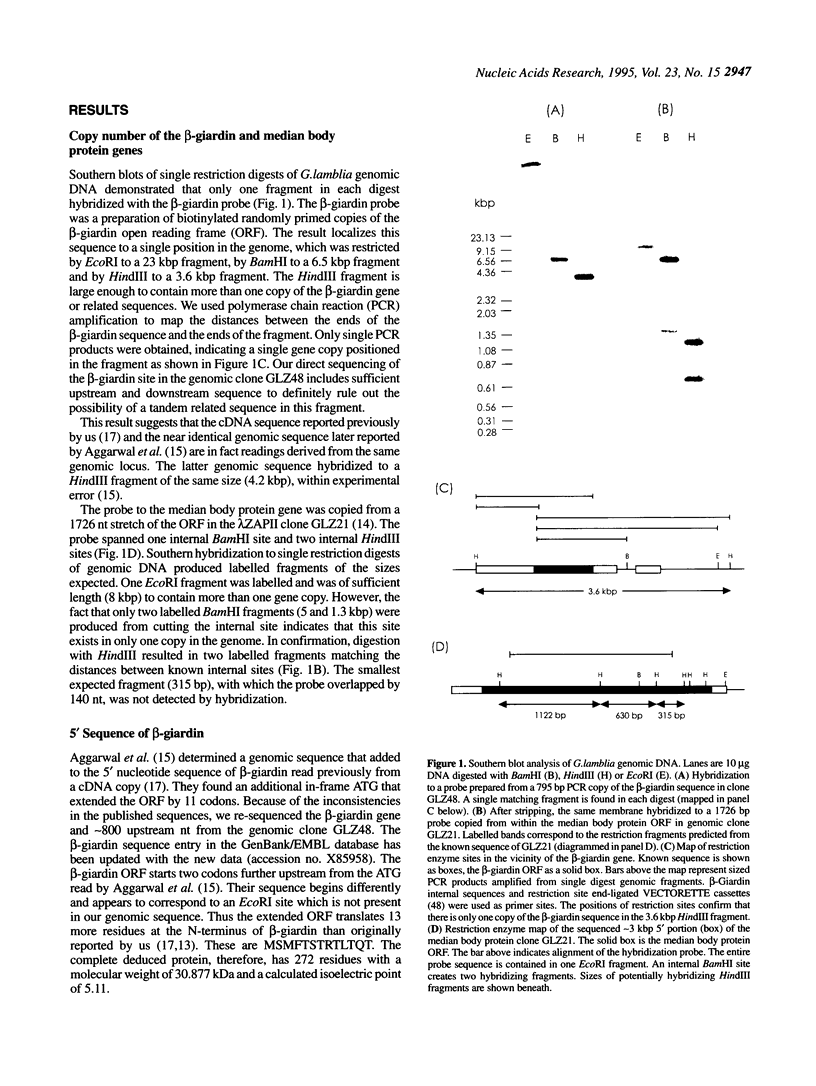
Abstract
Protein-coding genes in the ancient eukaryote Giardia lamblia lack typical promoter consensus elements. We have analysed the immediate 5' flanking sequences of seven genes of related function (structural cytoskeleton proteins) to identify shared DNA motifs that might have a role in transcription initiation. Transcription start sites for five genes have been determined previously. Genomic mapping and mRNA primer extension experiments demonstrate additionally that the genes for beta-giardin and median body protein are (i) present as single copies in the genome, (ii) transcribed with very short 5' leader sequences. Two search algorithms designed to extract conserved motifs from either aligned or non-aligned sequences independently discovered three sites constituting a common pattern in all seven promoters. Sites were optimally aligned using weight matrix building trials to achieve the maximum 'information content'. Profiling the information content of best alignments defines the extent of the homologies as: a 9 bp box (initiator) at the start site and upstream 18 and 6 bp boxes. The initiator is the most highly conserved element and contains a universal Py-A-Pu motif at which transcription starts. We show that the best matrices can be combined in a search pattern that correctly locates transcription start sites in genomic DNA sequences.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam R. D. The biology of Giardia spp. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Dec;55(4):706–732. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.4.706-732.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso R. A., Peattie D. A. Nucleotide sequence of a second alpha giardin gene and molecular analysis of the alpha giardin genes and transcripts in Giardia lamblia. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Jan;50(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90247-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker D. A., Holberton D. V., Marshall J. Sequence of a giardin subunit cDNA from Giardia lamblia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):7177–7177. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.7177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Selection of DNA binding sites by regulatory proteins. Statistical-mechanical theory and application to operators and promoters. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):723–750. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90354-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothroyd J. C., Wang A., Campbell D. A., Wang C. C. An unusually compact ribosomal DNA repeat in the protozoan Giardia lamblia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4065–4084. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher P. Weight matrix descriptions of four eukaryotic RNA polymerase II promoter elements derived from 502 unrelated promoter sequences. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):563–578. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S. The basics of basal transcription by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carcamo J., Buckbinder L., Reinberg D. The initiator directs the assembly of a transcription factor IID-dependent transcription complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8052–8056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Char S., Farthing M. J. Codon usage in Giardia lamblia. J Protozool. 1992 Sep-Oct;39(5):642–644. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1992.tb04865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copley C. G., Boot C., Bundell K., McPheat W. L. Unknown sequence amplification: application to in vitro genome walking in Chlamydia trachomatis L2. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Jan;9(1):74–79. doi: 10.1038/nbt0191-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Santis P., Palleschi A., Savino M., Scipioni A. Validity of the nearest-neighbor approximation in the evaluation of the electrophoretic manifestations of DNA curvature. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 2;29(39):9269–9273. doi: 10.1021/bi00491a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan J. B., Korman S. H., Cantor C. R., Smith C. L. Giardia lamblia: haploid genome size determined by pulsed field gel electrophoresis is less than 12 Mb. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1905–1908. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Eggert M., Waterman M. S. Rigorous pattern-recognition methods for DNA sequences. Analysis of promoter sequences from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):117–128. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90262-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Buratowski S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Yeast TATA-binding protein TFIID binds to TATA elements with both consensus and nonconsensus DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5718–5722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Perry R. P. Functional dissection of a mouse ribosomal protein promoter: significance of the polypyrimidine initiator and an element in the TATA-box region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1526–1530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington R. E. DNA curving and bending in protein-DNA recognition. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2549–2555. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N. TBP, a universal eukaryotic transcription factor? Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1291–1308. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertz G. Z., Hartzell G. W., 3rd, Stormo G. D. Identification of consensus patterns in unaligned DNA sequences known to be functionally related. Comput Appl Biosci. 1990 Apr;6(2):81–92. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/6.2.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holberton D., Baker D. A., Marshall J. Segmented alpha-helical coiled-coil structure of the protein giardin from the Giardia cytoskeleton. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 5;204(3):789–795. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90370-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javahery R., Khachi A., Lo K., Zenzie-Gregory B., Smale S. T. DNA sequence requirements for transcriptional initiator activity in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):116–127. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann J., Smale S. T. Direct recognition of initiator elements by a component of the transcription factor IID complex. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 1;8(7):821–829. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.7.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keister D. B. Axenic culture of Giardia lamblia in TYI-S-33 medium supplemented with bile. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(4):487–488. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk-Mason K. E., Turner M. J., Chakraborty P. R. Evidence for unusually short tubulin mRNA leaders and characterization of tubulin genes in Giardia lamblia. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Aug;36(1):87–99. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. F., Concino M. F., Weinmann R. Genetic profile of the transcriptional signals from the adenovirus major late promoter. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90657-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logsdon J. M., Jr, Palmer J. D. Origin of introns--early or late? Nature. 1994 Jun 16;369(6481):526–528. doi: 10.1038/369526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J., Holberton D. V. Sequence and structure of a new coiled coil protein from a microtubule bundle in Giardia. J Mol Biol. 1993 May 20;231(2):521–530. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., Hansen J. L., Dame J. B., Mullins J. A. Mung bean nuclease cleaves Plasmodium genomic DNA at sites before and after genes. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):625–628. doi: 10.1126/science.6330899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohria A., Alonso R. A., Peattie D. A. Identification and characterization of gamma-giardin and the gamma-giardin gene from Giardia lamblia. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Nov;56(1):27–37. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill M. C. Consensus methods for finding and ranking DNA binding sites. Application to Escherichia coli promoters. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea-Greenfield A., Smale S. T. Roles of TATA and initiator elements in determining the start site location and direction of RNA polymerase II transcription. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1391–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Transcription from a TATA-less promoter requires a multisubunit TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1935–1945. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quon D. V., Delgadillo M. G., Khachi A., Smale S. T., Johnson P. J. Similarity between a ubiquitous promoter element in an ancient eukaryote and mammalian initiator elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4579–4583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T. D., Stormo G. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Information content of binding sites on nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):415–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Gunderson J. H., Elwood H. J., Alonso R. A., Peattie D. A. Phylogenetic meaning of the kingdom concept: an unusual ribosomal RNA from Giardia lamblia. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2911720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Methods to define and locate patterns of motifs in sequences. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):53–60. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Hartzell G. W., 3rd Identifying protein-binding sites from unaligned DNA fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1183–1187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. S., Arratia R., Galas D. J. Pattern recognition in several sequences: consensus and alignment. Bull Math Biol. 1984;46(4):515–527. doi: 10.1007/BF02459500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. S., Jones R. Consensus methods for DNA and protein sequence alignment. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:221–237. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis L., Reinberg D. Transcription by RNA polymerase II: initiator-directed formation of transcription-competent complexes. FASEB J. 1992 Nov;6(14):3300–3309. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.14.1426767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley S. R., Kraus R. J., Mertz J. E. Functional binding of the "TATA" box binding component of transcription factor TFIID to the -30 region of TATA-less promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5814–5818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II: a multi-step process. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1993;44:67–108. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]