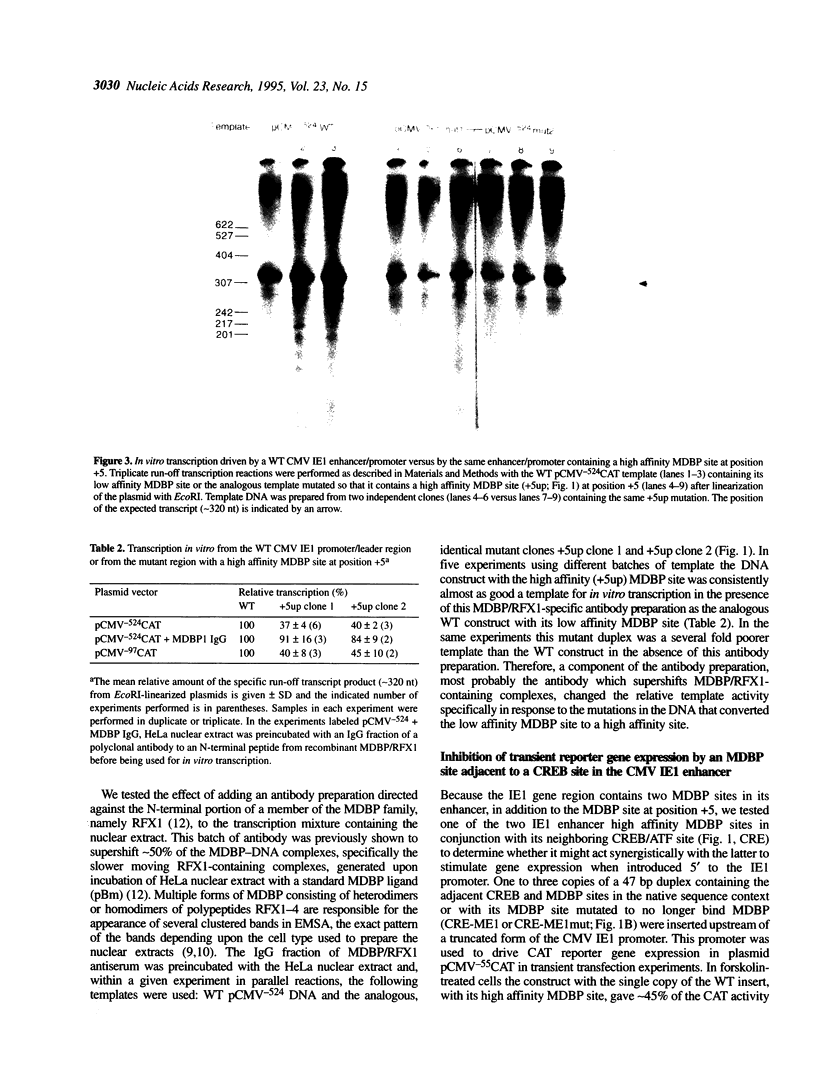
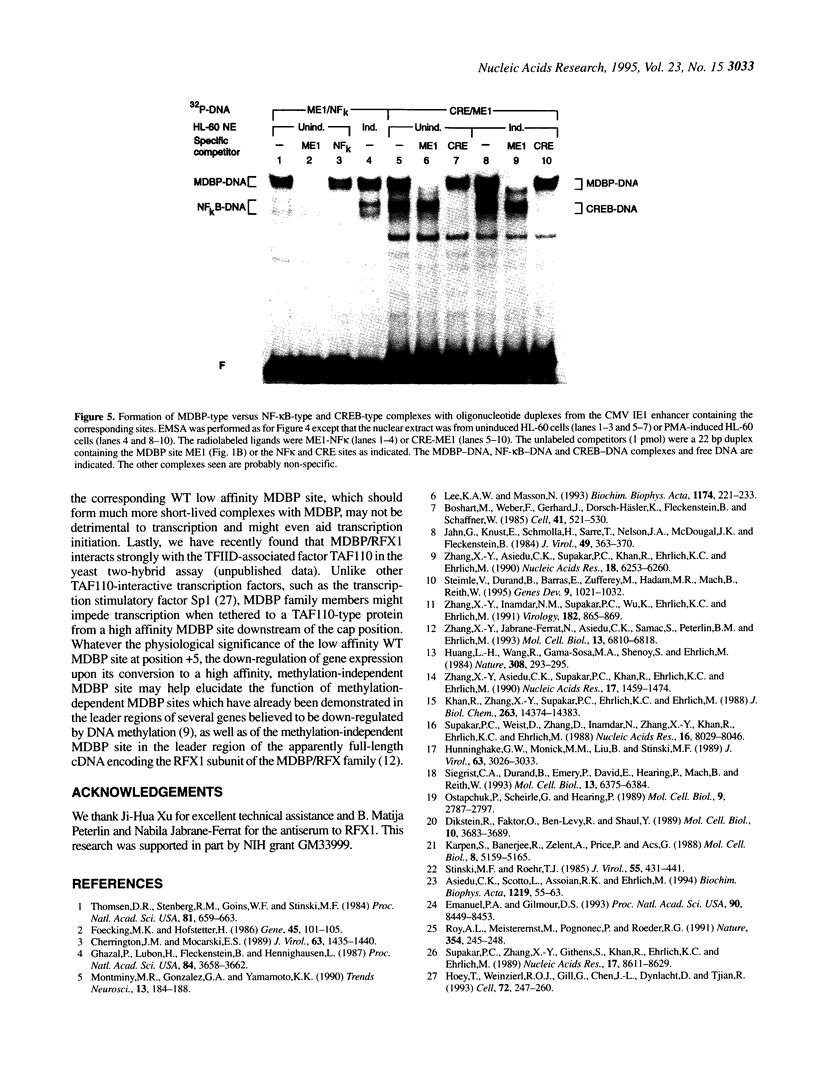
Abstract
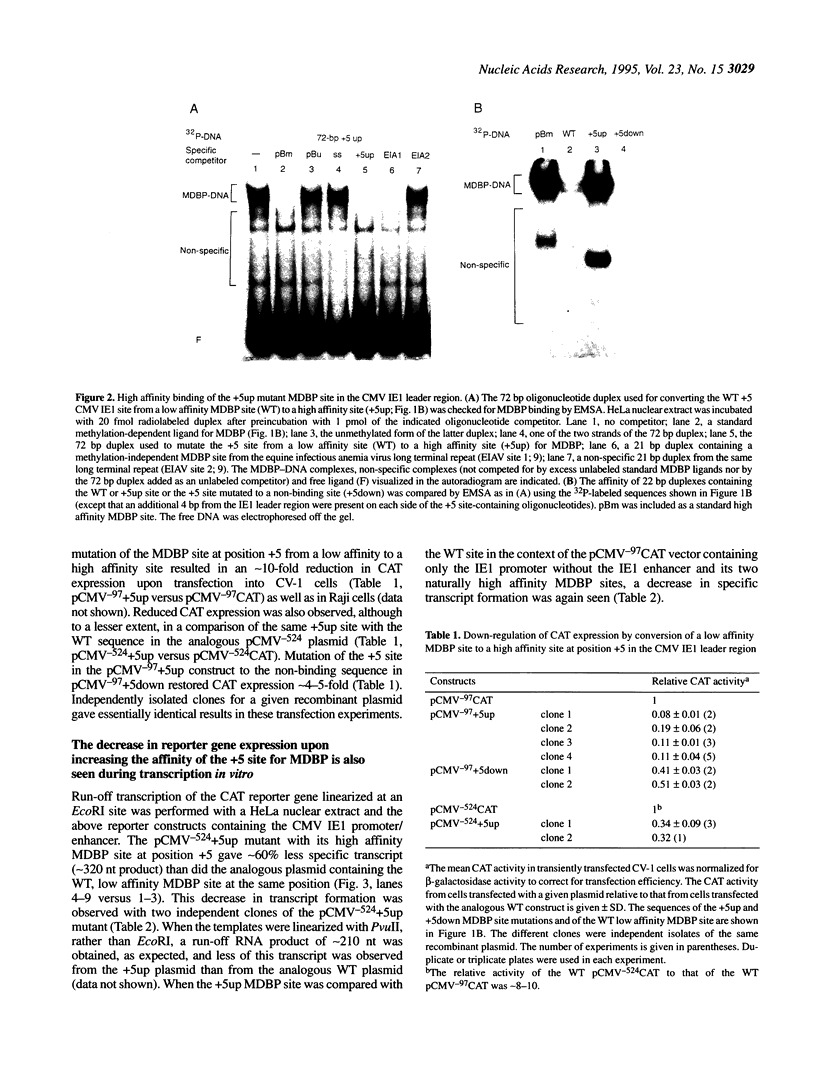
A closely related family of ubiquitous DNA binding proteins, called MDBP, binds with high affinity to two 14 base pair (bp) sites within the human cytomegalovirus immediate early gene 1 (CMV IE1) enhancer and with low affinity to one site beginning 5 bp downstream of the CMV IE1 transcription start point (+5 site). Unlike several cap position downstream MDBP sites in mammalian genes, these MDBP sites do not require cytosine methylation for optimal binding. Mutation of one of the enhancer MDBP sites to prevent MDBP recognition modestly increased the function of a neighboring CREB binding site in a transient transfection assay in the context of one promoter construct. A much larger effect on reporter gene expression (a 10-fold reduction) was seen when the low affinity MDBP recognition sequence at position +5 was converted to a high affinity site in a plasmid containing the CMV IE1 promoter upstream of the reporter gene. Evidence that the increased binding of MDBP at the mutant site is largely responsible for the observed results was provided by transfection experiments with this high affinity MDBP +5 site re-mutated to a non-binding site and by in vitro transcription assay.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asiedu C. K., Scotto L., Assoian R. K., Ehrlich M. Binding of AP-1/CREB proteins and of MDBP to contiguous sites downstream of the human TGF-beta 1 gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Sep 13;1219(1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90246-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington J. M., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus ie1 transactivates the alpha promoter-enhancer via an 18-base-pair repeat element. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1435–1440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1435-1440.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dikstein R., Faktor O., Ben-Levy R., Shaul Y. Functional organization of the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3683–3689. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel P. A., Gilmour D. S. Transcription factor TFIID recognizes DNA sequences downstream of the TATA element in the Hsp70 heat shock gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8449–8453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foecking M. K., Hofstetter H. Powerful and versatile enhancer-promoter unit for mammalian expression vectors. Gene. 1986;45(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Lubon H., Fleckenstein B., Hennighausen L. Binding of transcription factors and creation of a large nucleoprotein complex on the human cytomegalovirus enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3658–3662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Weinzierl R. O., Gill G., Chen J. L., Dynlacht B. D., Tjian R. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of Drosophila TAF110 reveal properties expected of coactivators. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):247–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90664-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. H., Wang R., Gama-Sosa M. A., Shenoy S., Ehrlich M. A protein from human placental nuclei binds preferentially to 5-methylcytosine-rich DNA. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):293–295. doi: 10.1038/308293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Monick M. M., Liu B., Stinski M. F. The promoter-regulatory region of the major immediate-early gene of human cytomegalovirus responds to T-lymphocyte stimulation and contains functional cyclic AMP-response elements. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3026–3033. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3026-3033.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn G., Knust E., Schmolla H., Sarre T., Nelson J. A., McDougall J. K., Fleckenstein B. Predominant immediate-early transcripts of human cytomegalovirus AD 169. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):363–370. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.363-370.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen S., Banerjee R., Zelent A., Price P., Acs G. Identification of protein-binding sites in the hepatitis B virus enhancer and core promoter domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5159–5165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan R., Zhang X. Y., Supakar P. C., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. Human methylated DNA-binding protein. Determinants of a pBR322 recognition site. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14374–14383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Masson N. Transcriptional regulation by CREB and its relatives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Sep 23;1174(3):221–233. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90191-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K. Regulation of cAMP-inducible genes by CREB. Trends Neurosci. 1990 May;13(5):184–188. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90045-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostapchuk P., Scheirle G., Hearing P. Binding of nuclear factor EF-C to a functional domain of the hepatitis B virus enhancer region. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2787–2797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Meisterernst M., Pognonec P., Roeder R. G. Cooperative interaction of an initiator-binding transcription initiation factor and the helix-loop-helix activator USF. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):245–248. doi: 10.1038/354245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegrist C. A., Durand B., Emery P., David E., Hearing P., Mach B., Reith W. RFX1 is identical to enhancer factor C and functions as a transactivator of the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6375–6384. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steimle V., Durand B., Barras E., Zufferey M., Hadam M. R., Mach B., Reith W. A novel DNA-binding regulatory factor is mutated in primary MHC class II deficiency (bare lymphocyte syndrome). Genes Dev. 1995 May 1;9(9):1021–1032. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.9.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Roehr T. J. Activation of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus by cis-acting elements in the promoter-regulatory sequence and by virus-specific trans-acting components. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):431–441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.431-441.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supakar P. C., Weist D., Zhang D. L., Inamdar N., Zhang X. Y., Khan R., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. Methylated DNA-binding protein is present in various mammalian cell types. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8029–8044. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supakar P. C., Zhang X. Y., Githens S., Khan R., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. How different DNA sequences are recognized by a DNA-binding protein: effects of partial proteolysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8611–8629. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goins W. F., Stinski M. F. Promoter-regulatory region of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Asiedu C. K., Supakar P. C., Khan R., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. Binding sites in mammalian genes and viral gene regulatory regions recognized by methylated DNA-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6253–6260. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Inamdar N. M., Supakar P. C., Wu K., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. Three MDBP sites in the immediate-early enhancer-promoter region of human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):865–869. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90631-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Jabrane-Ferrat N., Asiedu C. K., Samac S., Peterlin B. M., Ehrlich M. The major histocompatibility complex class II promoter-binding protein RFX (NF-X) is a methylated DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6810–6818. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Y., Supakar P. C., Khan R., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. Related sites in human and herpesvirus DNA recognized by methylated DNA-binding protein from human placenta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1459–1474. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]