Abstract
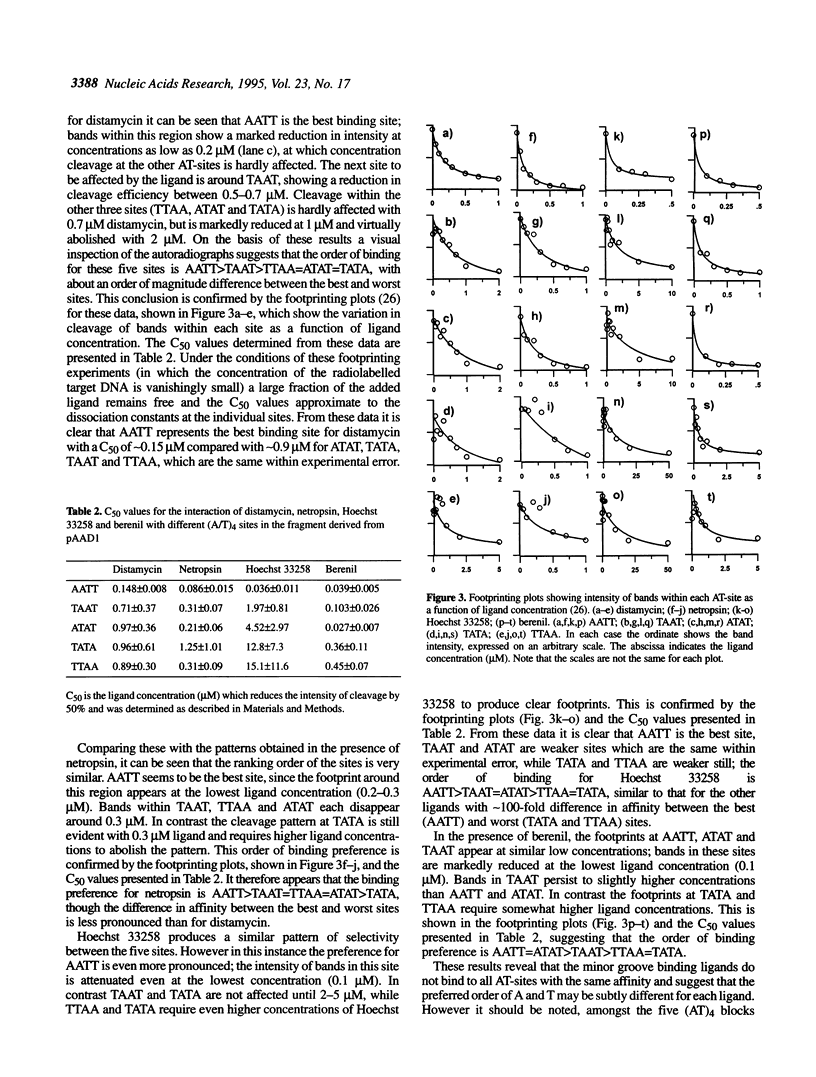
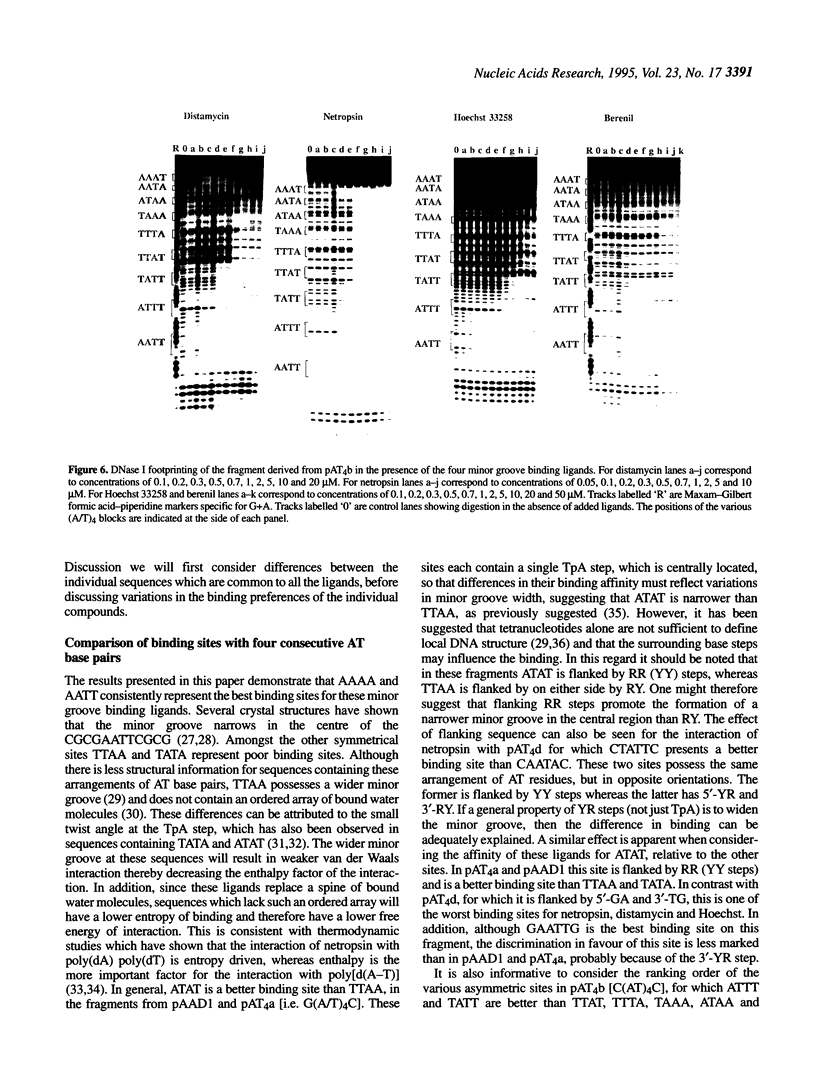
We have examined the interaction of distamycin, netropsin, Hoechst 33258 and berenil, which are AT-selective minor groove-binding ligands, with synthetic DNA fragments containing different arrangements of AT base pairs by DNase I footprinting. For fragments which contain multiple blocks of (A/T)4 quantitative DNase I footprinting reveals that AATT and AAAA are much better binding sites than TTAA and TATA. Hoechst 33258 shows that greatest discrimination between these sites with a 50-fold difference in affinity between AATT and TATA. Alone amongst these ligands, Hoechst 33258 binds to AATT better than AAAA. These differences in binding to the various AT-tracts are interpreted in terms of variations in DNA minor groove width and suggest that TpA steps within an AT-tract decrease the affinity of these ligands. The behaviour of each site also depends on the flanking sequences; adjacent pyrimidine-purine steps cause a decrease in affinity. The precise ranking order for the various binding sites is not the same for each ligand.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breslauer K. J., Remeta D. P., Chou W. Y., Ferrante R., Curry J., Zaunczkowski D., Snyder J. G., Marky L. A. Enthalpy-entropy compensations in drug-DNA binding studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8922–8926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. G., Sanderson M. R., Garman E., Neidle S. Crystal structure of a berenil-d(CGCAAATTTGCG) complex. An example of drug-DNA recognition based on sequence-dependent structural features. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jul 20;226(2):481–490. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90962-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. G., Sanderson M. R., Skelly J. V., Jenkins T. C., Brown T., Garman E., Stuart D. I., Neidle S. Crystal structure of a berenil-dodecanucleotide complex: the role of water in sequence-specific ligand binding. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1329–1334. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08242.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrondo M. A., Coll M., Aymami J., Wang A. H., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Rich A. Binding of a Hoechst dye to d(CGCGATATCGCG) and its influence on the conformation of the DNA fragment. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7849–7859. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J. W., Chou S. H., Salazar M., Reid B. R. Solution structure of [d(GCGTATACGC)]2. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 5;228(1):118–137. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90496-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill M. E., Hayes J. J., Tullius T. D. Detection of drug binding to DNA by hydroxyl radical footprinting. Relationship of distamycin binding sites to DNA structure and positioned nucleosomes on 5S RNA genes of Xenopus. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 26;29(25):6043–6050. doi: 10.1021/bi00477a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll M., Aymami J., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Rich A., Wang A. H. Molecular structure of the netropsin-d(CGCGATATCGCG) complex: DNA conformation in an alternating AT segment. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):310–320. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embrey K. J., Searle M. S., Craik D. J. Interaction of Hoechst 33258 with the minor groove of the A + T-rich DNA duplex d(GGTAATTACC)2 studied in solution by NMR spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Feb 1;211(3):437–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R. Probing the conformations of eight cloned DNA dodecamers; CGCGAATTCGCG, CGCGTTAACGCG, CGCGTATACGCG, CGCGATATCGCG, CGCAAATTTGCG, CGCTTTAAAGCG, CGCGGATCCGCG and CGCGGTACCGCG. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6487–6493. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. DNA structural variations produced by actinomycin and distamycin as revealed by DNAase I footprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9271–9285. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman K. D., Dervan P. B. Molecular recognition of B-DNA by Hoechst 33258. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4825–4835. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. H., Weisz K., James T. L., Shafer R. H. H-NMR studies on d(GCTTAAGC)2 and its complex with berenil. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 15;204(1):31–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Yoon C., Goodsell D., Pjura P., Dickerson R. E. Binding of an antitumor drug to DNA, Netropsin and C-G-C-G-A-A-T-T-BrC-G-C-G. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 25;183(4):553–563. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Yoon C., Goodsell D., Pjura P., Dickerson R. E. The molecular origin of DNA-drug specificity in netropsin and distamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1376–1380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughton C. A., Jenkins T. C., Fox K. R., Neidle S. Interaction of berenil with the tyrT DNA sequence studied by footprinting and molecular modelling. Implications for the design of sequence-specific DNA recognition agents. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4479–4488. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard G. A., Hunter W. N. Crystal and molecular structure of d(CGTAGATCTACG) at 2.25 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1993 Nov 5;234(1):198–208. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liepinsh E., Leupin W., Otting G. Hydration of DNA in aqueous solution: NMR evidence for a kinetic destabilization of the minor groove hydration of d-(TTAA)2 versus d-(AATT)2 segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jun 25;22(12):2249–2254. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.12.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marky L. A., Breslauer K. J. Origins of netropsin binding affinity and specificity: correlations of thermodynamic and structural data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4359–4363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearl L. H., Skelly J. V., Hudson B. D., Neidle S. The crystal structure of the DNA-binding drug berenil: molecular modelling studies of berenil-DNA complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3469–3478. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pjura P. E., Grzeskowiak K., Dickerson R. E. Binding of Hoechst 33258 to the minor groove of B-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Sep 20;197(2):257–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portugal J., Waring M. J. Assignment of DNA binding sites for 4',6-diamidine-2-phenylindole and bisbenzimide (Hoechst 33258). A comparative footprinting study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 28;949(2):158–168. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90079-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portugal J., Waring M. J. Comparison of binding sites in DNA for berenil, netropsin and distamycin. A footprinting study. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Sep 1;167(2):281–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portugal J., Waring M. J. Hydroxyl radical footprinting of the sequence-selective binding of netropsin and distamycin to DNA. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 10;225(1-2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintana J. R., Grzeskowiak K., Yanagi K., Dickerson R. E. Structure of a B-DNA decamer with a central T-A step: C-G-A-T-T-A-A-T-C-G. J Mol Biol. 1992 May 20;225(2):379–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90928-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spink N., Brown D. G., Skelly J. V., Neidle S. Sequence-dependent effects in drug-DNA interaction: the crystal structure of Hoechst 33258 bound to the d(CGCAAATTTGCG)2 duplex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 May 11;22(9):1607–1612. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.9.1607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng M. K., Usman N., Frederick C. A., Wang A. H. The molecular structure of the complex of Hoechst 33258 and the DNA dodecamer d(CGCGAATTCGCG). Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2671–2690. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Map of distamycin, netropsin, and actinomycin binding sites on heterogeneous DNA: DNA cleavage-inhibition patterns with methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5470–5474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega M. C., García Sáez I., Aymamí J., Eritja R., Van der Marel G. A., Van Boom J. H., Rich A., Coll M. Three-dimensional crystal structure of the A-tract DNA dodecamer d(CGCAAATTTGCG) complexed with the minor-groove-binding drug Hoechst 33258. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jun 15;222(3):721–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward B., Rehfuss R., Goodisman J., Dabrowiak J. C. Determination of netropsin-DNA binding constants from footprinting data. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 23;27(4):1198–1205. doi: 10.1021/bi00404a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon C., Privé G. G., Goodsell D. S., Dickerson R. E. Structure of an alternating-B DNA helix and its relationship to A-tract DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6332–6336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C., Marck C., Schneider C., Guschlbauer W. Influence of nucleotide sequence on dA.dT-specific binding of Netropsin to double stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 25;6(8):2831–2837. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.8.2831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






