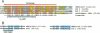Abstract
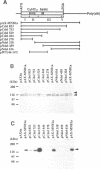
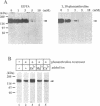
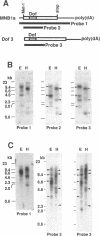
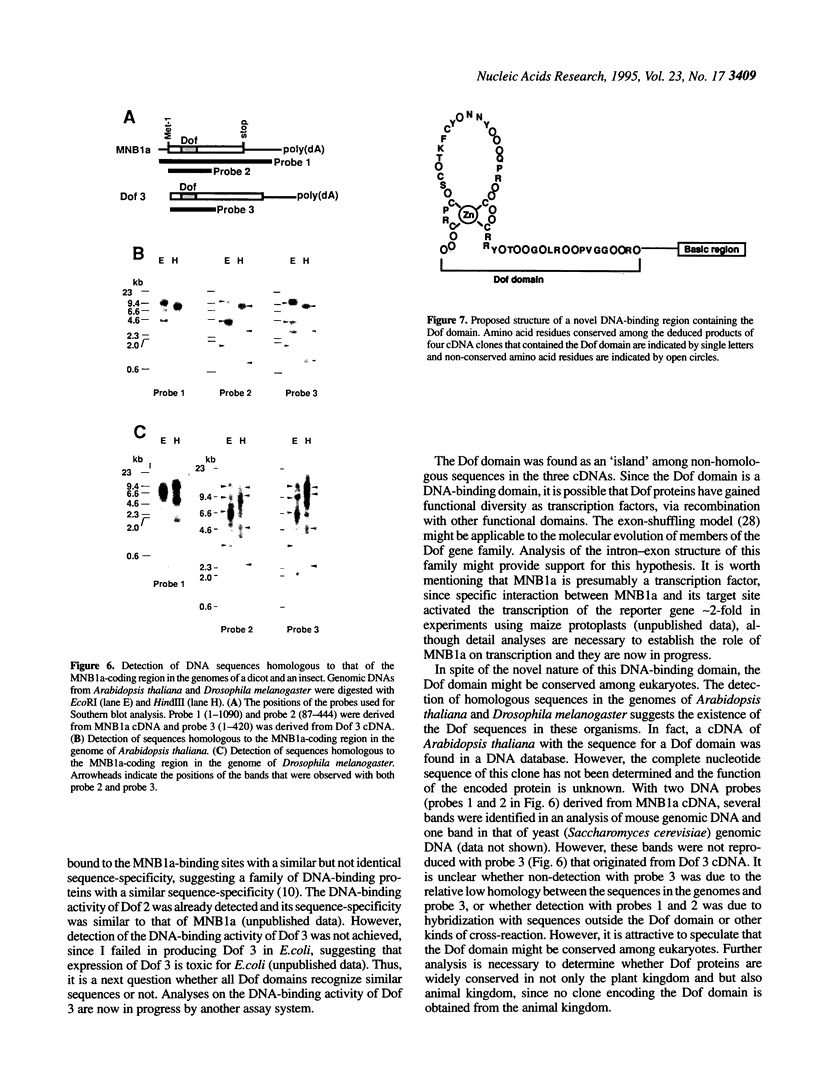
MNB1a is a DNA-binding protein from maize that interacts with the 35S promoter of cauliflower mosaic virus. This protein did not show significant homologies with any other DNA-binding protein and MNB1a seemed to be a member of a multigene family. In this study, isolation of cDNAs from the gene family to which MNB1a belongs revealed a unique conserved domain, referred to herein as the Dof domain, that contains a novel cysteine-rich motif for a single putative zinc finger. The amino acid sequence of the Dof domain and the arrangement of cysteine residues in this domain differ from those of known zinc finger motifs. However, the Dof domain was shown to be a DNA-binding domain that required Zn2+ ions for activity. Mutations at cysteine residues eliminated the DNA-binding activity of MNB1a. Thus, the Dof domain may be classified as a novel zinc finger motif. In addition, Southern blot analysis and a survey of DNA databases suggested that proteins that include Dof domains might exist in other eukaryotes, at least in the plant kingdom.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benfey P. N., Chua N. H. The Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35S Promoter: Combinatorial Regulation of Transcription in Plants. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):959–966. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4983.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfey P. N., Ren L., Chua N. H. Combinatorial and synergistic properties of CaMV 35S enhancer subdomains. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1685–1696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08292.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Matsui M., Wei N., Wagner D., Chu A. M., Feldmann K. A., Quail P. H. COP1, an Arabidopsis regulatory gene, encodes a protein with both a zinc-binding motif and a G beta homologous domain. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):791–801. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90555-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. A DNA-binding protein containing two widely separated zinc finger motifs that recognize the same DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):29–42. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyd G., Kim S. K., Horvitz H. R. Novel cysteine-rich motif and homeodomain in the product of the Caenorhabditis elegans cell lineage gene lin-11. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):876–879. doi: 10.1038/344876a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W., Marchionni M., McKnight G. On the antiquity of introns. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):151–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90730-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Hazuda D. J., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu F. Y., Wu C. W. Xenopus transcription factor A requires zinc for binding to the 5 S RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14120–14125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson O., Thor S., Norberg T., Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Insulin gene enhancer binding protein Isl-1 is a member of a novel class of proteins containing both a homeo- and a Cys-His domain. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):879–882. doi: 10.1038/344879a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmorstein R., Harrison S. C. Crystal structure of a PPR1-DNA complex: DNA recognition by proteins containing a Zn2Cys6 binuclear cluster. Genes Dev. 1994 Oct 15;8(20):2504–2512. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.20.2504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. I., Orkin S. H. Transcriptional activation and DNA binding by the erythroid factor GF-1/NF-E1/Eryf 1. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1886–1898. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli J., Gibson T. J., Vesque C., Charnay P. Base sequence discrimination by zinc-finger DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):175–178. doi: 10.1038/349175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quest A. F., Bardes E. S., Bell R. M. A phorbol ester binding domain of protein kinase C gamma. Deletion analysis of the Cys2 domain defines a minimal 43-amino acid peptide. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2961–2970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strich R., Surosky R. T., Steber C., Dubois E., Messenguy F., Esposito R. E. UME6 is a key regulator of nitrogen repression and meiotic development. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 1;8(7):796–810. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.7.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsuji H., Mori M., Benfey P. N., Ren L., Chua N. H. Characterization of a zinc finger DNA-binding protein expressed specifically in Petunia petals and seedlings. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):241–249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner C. A., Jr, Mack D. H., Davis M. M. Blimp-1, a novel zinc finger-containing protein that can drive the maturation of B lymphocytes into immunoglobulin-secreting cells. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90321-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa S., Izui K. MNF1, a leaf tissue-specific DNA-binding protein of maize, interacts with the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter as well as the C4 photosynthetic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene promoter. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Jul;19(4):545–553. doi: 10.1007/BF00026781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa S., Izui K. Maize phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase involved in C4 photosynthesis: nucleotide sequence analysis of the 5' flanking region of the gene. J Biochem. 1989 Dec;106(6):982–987. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa S., Izui K. Molecular cloning of two DNA-binding proteins of maize that are structurally different but interact with the same sequence motif. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):16028–16036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa S., Izui K. Multiple interactions between tissue-specific nuclear proteins and the promoter of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene for C4 photosynthesis in Zea mays. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Dec;224(3):325–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00262425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H. Y., Evans T. Distinct roles for the two cGATA-1 finger domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4562–4570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]