Abstract
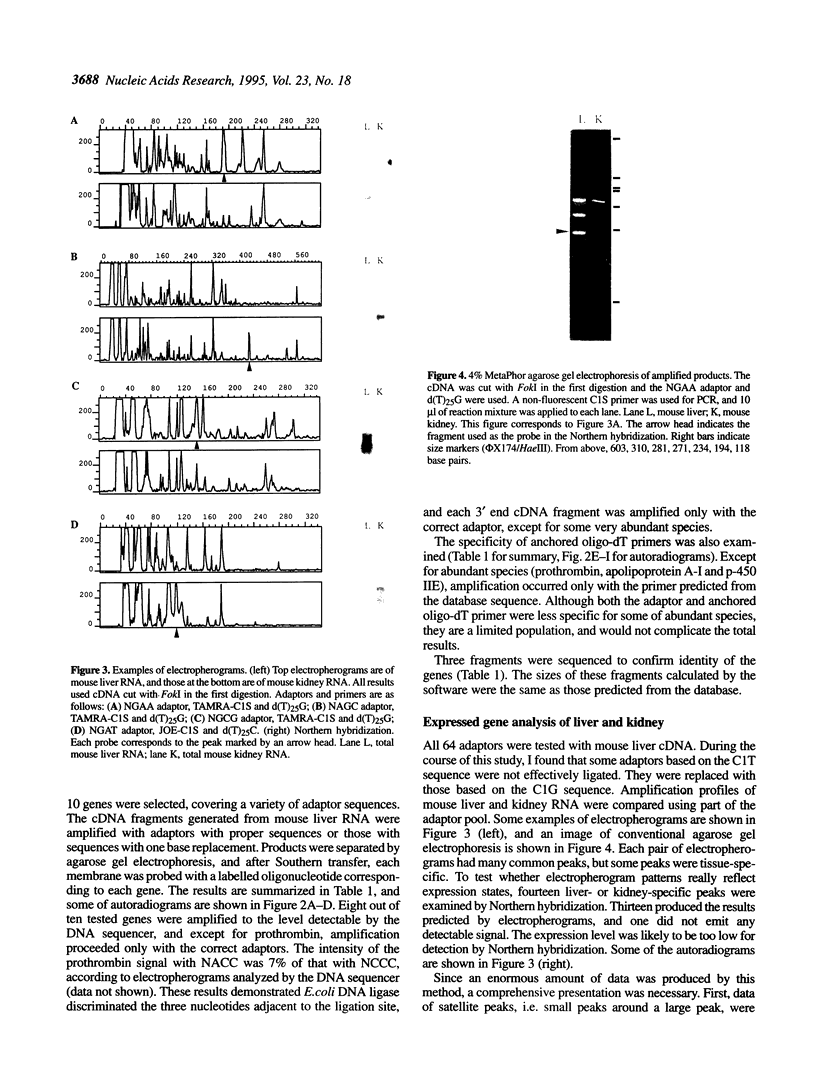
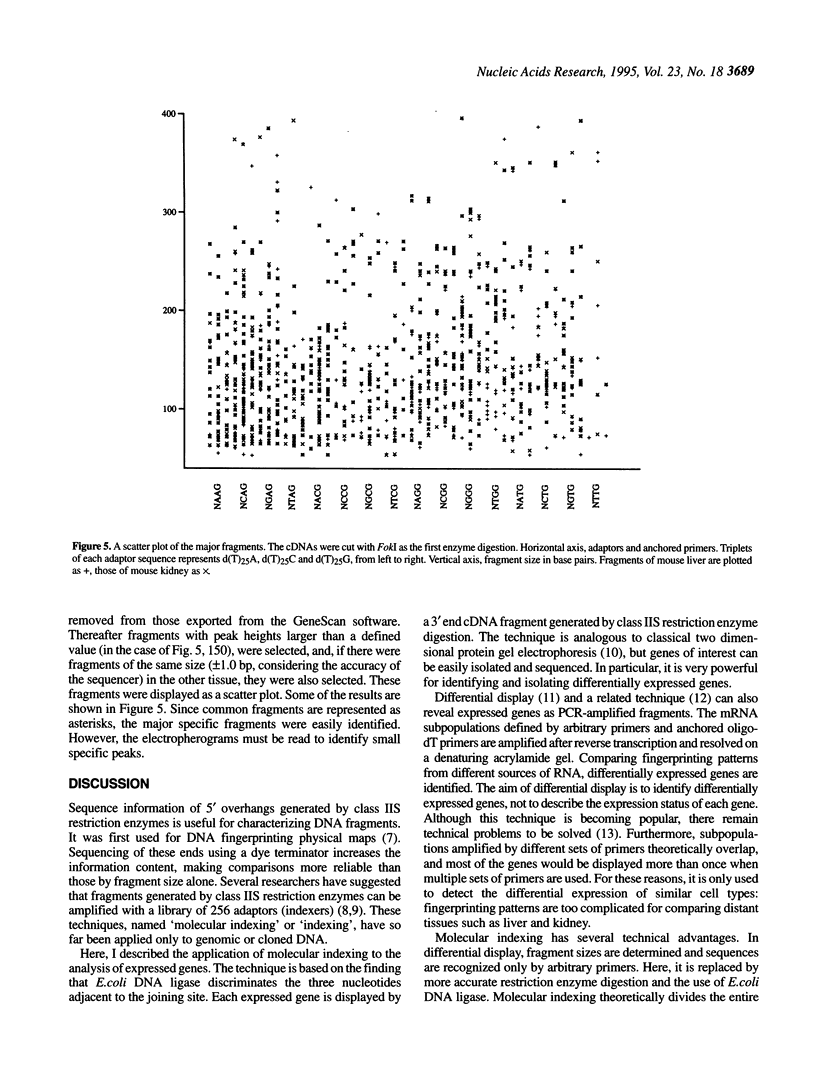
A novel means of recording the expression status of the total gene population is described. Digestion of cDNA by class IIS restriction enzymes produces a fragment with a poly (A) stretch and a 5' overhang with an unknown sequence. This fragment contains information such as the class IIS enzyme that cuts cDNA nearest to the poly (A) stretch, the sequence of the 5' overhang, and the size of the fragment. Expressed genes can be discriminated and displayed by the fragment as follows: (i) cut the cDNA with one class IIS restriction enzyme; (ii) ligate the digested cDNA to that from a pool of 64 biotinylated adaptors cohesive to all possible overhangs; (iii) digest by other two class IIS enzymes; (iv) recover the ligated molecules with streptavidin-coated paramagnetic beads; (v) perform PCR with the adaptor-primer and an anchored oligo-dT primer; (vi) separate the amplified fragments by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Repeat the experiment with 64 adaptors, three enzymes and three anchored oligo-dT primers displays most of the expressed genes. Because redundancy is minimized, this technique is also ideal for generating tags for expressed genes, with which to construct a transcript map of the genome.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. D., Kelley J. M., Gocayne J. D., Dubnick M., Polymeropoulos M. H., Xiao H., Merril C. R., Wu A., Olde B., Moreno R. F. Complementary DNA sequencing: expressed sequence tags and human genome project. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1651–1656. doi: 10.1126/science.2047873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S., Livak K. J. DNA fingerprinting by sampled sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8902–8906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. M., Hoppe B. L., Conti-Tronconi B. M. AmpliGrease: "hot start" PCR using petroleum jelly. Biotechniques. 1994 Jan;16(1):42–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato Kikuya. A Collection of cDNA Clones with Specific Expression Patterns in Mouse Brain. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(8):704–711. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko M. S. An 'equalized cDNA library' by the reassociation of short double-stranded cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5705–5711. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Averboukh L., Pardee A. B. Distribution and cloning of eukaryotic mRNAs by means of differential display: refinements and optimization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3269–3275. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Pardee A. B. Differential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):967–971. doi: 10.1126/science.1354393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R. Ligation-mediated PCR of restriction fragments from large DNA molecules. PCR Methods Appl. 1992 Aug;2(1):21–27. doi: 10.1101/gr.2.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Genome mapping: cDNA approaches. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Jun;2(3):412–416. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szybalski W., Kim S. C., Hasan N., Podhajska A. J. Class-IIS restriction enzymes--a review. Gene. 1991 Apr;100:13–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90345-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unrau P., Deugau K. V. Non-cloning amplification of specific DNA fragments from whole genomic DNA digests using DNA 'indexers'. Gene. 1994 Aug 5;145(2):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., Chada K., Dalal S. S., Cheng R., Ralph D., McClelland M. Arbitrarily primed PCR fingerprinting of RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):4965–4970. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.4965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]