Abstract
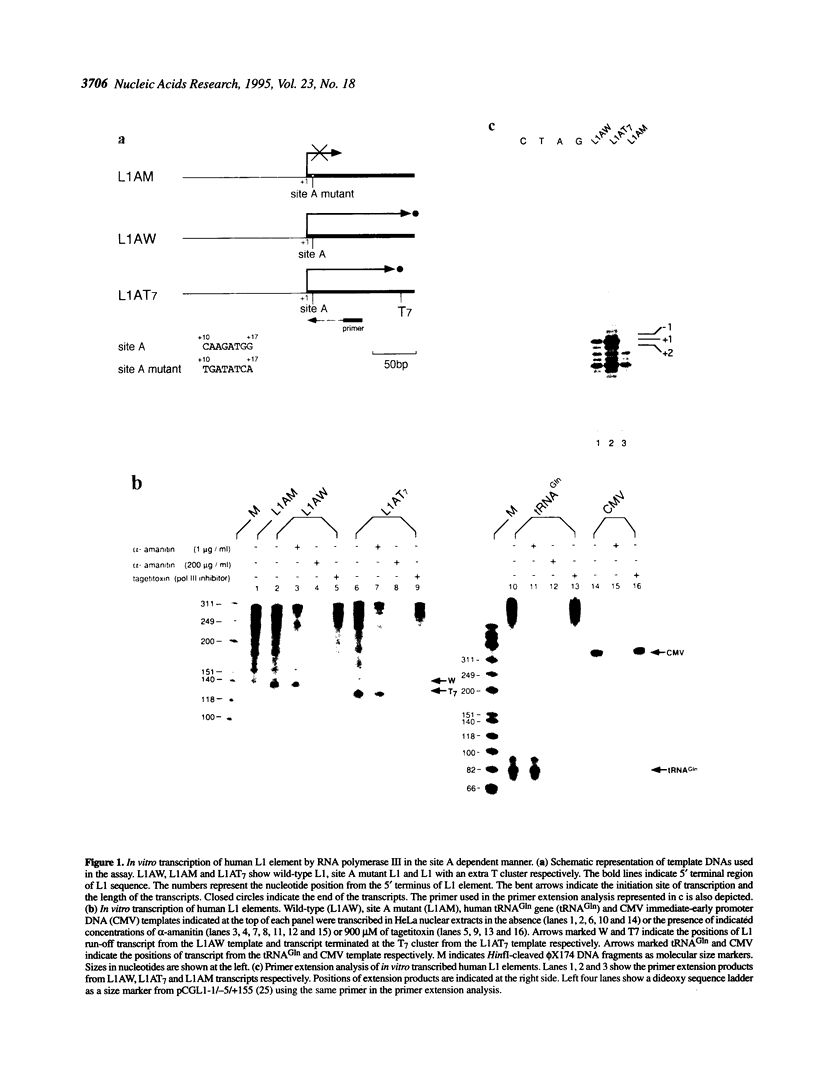
From the general views of the eukaryotic transcription systems, L1 (or L1-like) retrotransposons that encode some proteins are unusual. L1, unlike other protein-coding elements, is transcribed through an internal promoter. And the L1 internal promoter, unlike other internal promoters, is thought to be RNA polymerase II (pol II) dependent, because the L1 transcript has a large size (approximately 6 kb), protein coding capacity and a 3' terminal polyadenylation signal followed by a poly(A) tail, and also because transcription from the promoter of Drosophila L1-like element jockey was highly sensitive to alpha-amanitin. However, our in vitro transcription study reveals that transcription from the human L1 promoter is highly sensitive to tagetitoxin, a selective inhibitor of RNA polymerase III (pol III), but insensitive to 1 micrograms/ml of alpha-amanitin, indicating that the human L1 promoter is pol III-dependent. The pol III dependence is further supported by our observation that L1 and pol III-dependent tRNA gene promoters share a common nuclear factor YY1. There is evidence that YY1 is also a pol II transcription factor. We thus propose that YY1 is a possible member of the pol III transcription system.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker K. G., Swergold G. D., Ozato K., Thayer R. E. Binding of the ubiquitous nuclear transcription factor YY1 to a cis regulatory sequence in the human LINE-1 transposable element. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Oct;2(10):1697–1702. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.10.1697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Corces V. G. Transcription and reverse transcription of retrotransposons. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:403–434. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell F. E., Jr, Setzer D. R. Transcription termination by RNA polymerase III: uncoupling of polymerase release from termination signal recognition. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2260–2272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deragon J. M., Sinnett D., Labuda D. Reverse transcriptase activity from human embryonal carcinoma cells NTera2D1. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3363–3368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Sakaki Y. LINEs: a superfamily of retrotransposable ubiquitous DNA elements. Trends Genet. 1990 Feb;6(2):29–30. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. P., Palmiter R. D. Retrotransposition of a mouse L1 element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8792–8795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G., Singer M. F. LINE-1: a mammalian transposable element. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 8;910(3):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. R., Becker K. G., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Driggers P. H., Levi B. Z., Appella E., Ozato K. Cloning of a negative transcription factor that binds to the upstream conserved region of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase III (C) and its transcription factors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):412–416. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90166-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Two conserved sequence blocks within eukaryotic tRNA genes are major promoter elements. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):626–631. doi: 10.1038/294626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Delta, a transcription factor that binds to downstream elements in several polymerase II promoters, is a functionally versatile zinc finger protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9799–9803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Hidaka S., Sakaki Y. Sequence analysis of a KpnI family member near the 3' end of human beta-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7813–7827. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Kuhara S., Takenaka O., Sakaki Y. L1 family of repetitive DNA sequences in primates may be derived from a sequence encoding a reverse transcriptase-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):625–628. doi: 10.1038/321625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohjoh H., Minakami R., Sakaki Y. Selective cloning and sequence analysis of the human L1 (LINE-1) sequences which transposed in the relatively recent past. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4099–4104. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Sentenac A. The TATA-binding protein participates in TFIIIB assembly on tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6451–6454. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwu H. R., Roberts J. W., Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Insertion and/or deletion of many repeated DNA sequences in human and higher ape evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3875–3879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Joazeiro C. A., Pisano M., Geiduschek E. P., Colbert T., Hahn S., Blanco J. A. The role of the TATA-binding protein in the assembly and function of the multisubunit yeast RNA polymerase III transcription factor, TFIIIB. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1055–1064. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90399-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Wong C., Youssoufian H., Scott A. F., Phillips D. G., Antonarakis S. E. Haemophilia A resulting from de novo insertion of L1 sequences represents a novel mechanism for mutation in man. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):164–166. doi: 10.1038/332164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Etoile N. D., Fahnestock M. L., Shen Y., Aebersold R., Berk A. J. Human transcription factor IIIC box B binding subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1652–1656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibold D. M., Swergold G. D., Singer M. F., Thayer R. E., Dombroski B. A., Fanning T. G. Translation of LINE-1 DNA elements in vitro and in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6990–6994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Tanaka M., Sullivan M. L., Hernandez N. A TBP complex essential for transcription from TATA-less but not TATA-containing RNA polymerase III promoters is part of the TFIIIB fraction. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1029–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90397-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. D., Padgett R. W., Hardies S. C., Shehee W. R., Comer M. B., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd The sequence of a large L1Md element reveals a tandemly repeated 5' end and several features found in retrotransposons. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):168–182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias S. L., Scott A. F., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Boeke J. D., Gabriel A. Reverse transcriptase encoded by a human transposable element. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1808–1810. doi: 10.1126/science.1722352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki Y., Nishisho I., Horii A., Miyoshi Y., Utsunomiya J., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B., Nakamura Y. Disruption of the APC gene by a retrotransposal insertion of L1 sequence in a colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 1;52(3):643–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minakami R., Kurose K., Etoh K., Furuhata Y., Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Identification of an internal cis-element essential for the human L1 transcription and a nuclear factor(s) binding to the element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 25;20(12):3139–3145. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.12.3139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrokhi L. J., Georgieva S. G., Ilyin Y. V. jockey, a mobile Drosophila element similar to mammalian LINEs, is transcribed from the internal promoter by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):685–691. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse B., Rotherg P. G., South V. J., Spandorfer J. M., Astrin S. M. Insertional mutagenesis of the myc locus by a LINE-1 sequence in a human breast carcinoma. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):87–90. doi: 10.1038/333087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park K., Atchison M. L. Isolation of a candidate repressor/activator, NF-E1 (YY-1, delta), that binds to the immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer and the immunoglobulin heavy-chain mu E1 site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9804–9808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. K., Ayres J. A., Pasqualone D., Cabell C. H., Miller W., Hardison R. C. The 5' ends of LINE1 repeats in rabbit DNA define subfamilies and reveal a short sequence conserved between rabbits and humans. Genomics. 1992 Oct;14(2):320–331. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W. Three in one and one in three: it all depends on TBP. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90042-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs K. J., Merrell K. T., Wilson G., Calame K. Common factor 1 is a transcriptional activator which binds in the c-myc promoter, the skeletal alpha-actin promoter, and the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1765–1769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy K. L., Cooke H., Buckland R. Nucleotide sequence of a segment of human DNA containing the three tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7313–7322. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaki Y., Hattori M., Fujita A., Yoshioka K., Kuhara S., Takenaka O. The LINE-1 family of primates may encode a reverse transcriptase-like protein. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):465–469. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Seto E., Chang L. S., Shenk T. Transcriptional repression by YY1, a human GLI-Krüppel-related protein, and relief of repression by adenovirus E1A protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg T. H., Mathews D. E., Durbin R. D., Burgess R. R. Tagetitoxin: a new inhibitor of eukaryotic transcription by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):499–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swergold G. D. Identification, characterization, and cell specificity of a human LINE-1 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6718–6729. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart A. K., Fisher T. S., Pugh B. F. The TATA-binding protein and associated factors are components of pol III transcription factor TFIIIB. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1015–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90396-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usheva A., Shenk T. TATA-binding protein-independent initiation: YY1, TFIIB, and RNA polymerase II direct basal transcription on supercoiled template DNA. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1115–1121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90387-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Jackson S. P. Mechanism of TATA-binding protein recruitment to a TATA-less class III promoter. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1041–1053. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90398-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga S. K., Boulanger P. A., Berk A. J. Resolution of human transcription factor TFIIIC into two functional components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3585–3589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]